Abstract
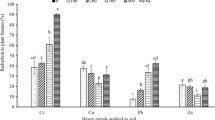
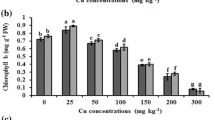
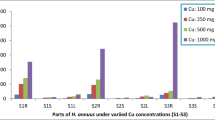
Increasing world population triggers intensive agricultural practices responsible for higher heavy metal contamination of soil and water. The present study was conducted to evaluate the morpho-physiological and biochemical response along with phytoextraction potential of Alternanthera bettzickiana for cobalt (Co) and copper (Cu) contaminated soil. Healthy and uniform plants of A. bettzickiana were collected and placed in pots each filled with 5 kg of sandy loam soil. Plants were treated with different concentrations of Cu and Co (2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10 mM). After 8 weeks of treatments, plant agronomic traits such as plant growth, biomass, chlorophyll content, and activities of antioxidant enzymes were measured and results revealed no visual signs of toxicity whereas all characteristics were enhanced as compared to control plants except 10 mM where it significantly decreased the plant’s morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics. Further, Cu and Co concentration and accumulation in all parts of plants significantly increased with increasing concentration of applied heavy metal. The plants significantly accumulate 2.1 and 2.0 times more Cu in shoots and 1.5 and 1.2 times more Co in roots as compared to controls. The results concluded that A. bettzickiana is a potential hyperaccumulator and halophyte of Co and Cu therefore it can be a potential candidate for the remediation of Cu and Co contaminated sites.
Graphic Abstract

Article Highlights
-
Alternanthera bettzickiana showed greater tolerance towards copper and cobalt.
-
Higher metal doses altered biochemical functions and decreased agronomic traits.
-
Antioxidant defense system boosted up to scavenge reactive oxygen species production.
-
Alternanthera bettzickiana proved as good hyper-accumulator of cobalt and copper.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Mentasti E, Sarzanini C, Petrella F (2002) Heavy metal in agricultural soils from Piedmont, Italy. Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere 49(6):545–557
Abollino O, Malandrino M, Berto S, La Gioia C, Maruccia V, Conca E, Giacomino A (2019) Stripping voltammetry for field determination of traces of copper in soil extracts and natural waters. Microchem J 149:104015
Adriano DC (2001) Arsenic. Trace elements in terrestrial environment. Springer, New York, pp 219–261
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Abbas F, Abbasi GH (2015) Citric acid enhances the phyto-extraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(15):11679–11689
Ahmad R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Dawood M, Farid M, Hussain A, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates chromium stress on cauliflower by restricting its uptake and enhancing antioxidative system. Physiol Planta 168:289
Ali A, Iqbal N, Ali F, Afzal B (2012) Alternanthera bettzickiana (Regel) G. Nicholson, a potential halophytic ornamental plant: growth and physiological adaptations. Flora Morphol Distrib Funct Ecol Plants 207(4):318–321
Ali S, Chaudhary A, Rizwan M, Anwar HT, Adrees M, Farid M, Irshad MK, Hayat T, Anjum SA (2015) Alleviation of chromium toxicity by glycinebetaine is related to elevated antioxidant enzymes and suppressed chromium uptake and oxidative stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(14):10669–10678
Anjum S, Arora A, Alam MS, Gupta B (2016) Development of antimicrobial and scar preventive chitosan hydrogel wound dressings. Int J Pharm 508(1–2):92–101
Arshad M, Ali S, Noman A, Ali Q, Rizwan M, Farid M, Irshad MK (2016) Phosphorus amendment decreased cadmium (Cd) uptake and ameliorates chlorophyll contents, gas exchange attributes, antioxidants, and mineral nutrients in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under Cd stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62(4):533–546
Baisak R, Rana D, Acharya PB, Kar M (1994) Alterations in the activities of active oxygen scavenging enzymes of wheat leaves subjected to water stress. Plant Cell Physiol 35(3):489–495
Bang J, Kamala-Kannan S, Lee KJ, Cho M, Kim CH, Kim YJ, Oh BT (2015) Phytoremediation of heavy metals in contaminated water and soil using Miscanthus sp. Goedae-Uksae 1. Int J Phytoremediat 17(6):515–520
Beyersmann D (2002) Effects of carcinogenic metals on gene expression. Toxicol Lett 127(1–3):63–68
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bukhari SA, Zheng W, Xie L, Zhang G, Shang S, Wu F (2016) Cr-induced changes in leaf protein profile, ultrastructure and photosynthetic traits in the two contrasting tobacco genotypes. Plant Growth Regul 79(2):147–156
Cho-Ruk K, Kurukote J, Supprung P, Vetayasuporn S (2006) Perennial plants in the phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soils. Biotechnology 5(1):1–4
Demidchik V, Straltsova D, Medvedev SS, Pozhvanov GA, Sokolik A, Yurin V (2014) Stress-induced electrolyte leakage: the role of K+ permeable channels and involvement in programmed cell death and metabolic adjustment. J Exp Bot 65:1259–1270
Dezfoulian AH, Aliarabi H (2017) A comparison between different concentrations and sources of cobalt in goat kid nutrition. Animal 11(4):600–607
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32(1):93–101
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135(1):1–9
Ehsan S, Ali S, Noureen S, Faird M, Shakoor MB, Aslam A, Bharwana SA, Tauqeer HM (2013) Comparative assessment of different heavy metals in urban soil and vegetables irrigated with sewage/industrial waste water. Ecoterra 35:37–53
Ehsan S, Ali S, Noureen S, Mahmood K, Farid M, Ishaque W, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M (2014) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:164–172
Farid M, Ali S, Ishaque W, Shakoor MB, Niazi NK, Bibi I, Dawood M, Gill RA, Abbas F (2015) Exogenous application of ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid enhanced phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:3981–3992
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M (2016) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassica napus L. Arsenic research and global sustainability. In: Proceedings of the sixth international congress on arsenic in the environment (As 2016), June 19–23, 2016, Stockholm, Sweden
Farid M, Ali S, Akram NA, Rizwan M, Abbas F, Bukhari SAH, Saeed R (2017a) Phyto-management of Cr-contaminated soils by sunflower hybrids: physiological and biochemical response and metal extractability under Cr stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(20):16845–16859
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Abbas F, Bukhari SAH, Saeed R, Wu L (2017b) Citric acid assisted phytoextraction of chromium by sunflower; morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations in plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:90–102
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Saeed R, Tauqeer HM, Sallah-Ud-Din R, Azam A, Raza N (2017c) Microwave irradiation and citric acid assisted seed germination and phytoextraction of nickel (Ni) by Brassica napus L.: morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations under Ni stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(25):2150–2164
Farid M, Ali S, Zubair M, Saeed R, Rizwan M, Sallah-Ud-Din R, Azam A, Ashraf R, Ashraf W (2018) Glutamic acid assisted phyto-management of silver contaminated soils through sunflower; physiological and biochemical response. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(25):25390–25400
Farid M, Ali S, Saeed R, Rizwan M, Bukhari SAH, Abbasi GH, Hussain A, Ali B, Zamir MSI, Ahmad I (2019) Combined application of citric acid and 5-aminolevulinic acid improved biomass, photosynthesis and gas exchange attributes of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) grown on chromium contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediation 21(8):760–767
Fazeli G, Karbassi A, Khoramnejadian S, Nasrabadi T (2019) Evaluation of urban soil pollution: a combined approach of toxic metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Int J Environ Res 13(5):801–811
Freeman JL, Garcia D, Kim D, Hopf A, Salt DE (2005) Constitutively elevated salicylic acid signals glutathione-mediated nickel tolerance in Thlaspi nickel hyperaccumulators. Plant Physiol 137(3):1082–1091
Ghnaya T, Nouairi I, Slama I, Messedi D, Grignon C, Abdelly C, Ghorbel MH (2005) Cadmium effects on growth and mineral nutrition of two halophytes: Sesuvium portulacastrum and Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. J Plant Physiol 162(10):1133–1140
Ghnaya T, Slama I, Messedi D, Grignon C, Ghorbel MH, Adbelly C (2007) Effects of Cd2+ on K+, Ca2+ and N uptake in two halophytes Sesuvium portulacastrum and Mesembryanthemum crystallinum: consequences on growth. Chemosphere 67:72–79
Habiba U, Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(2):1534–1544
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198
Hegedüs A, Erdei S, Horváth G (2001) Comparative studies of H2O2 detoxifying enzymes in green and greening barley seedlings under cadmium stress. Plant Sci 160(6):1085–1093
Jabeen N, Abbas Z, Iqbal M, Rizwan M, Jabbar A, Farid M, Ali S, Ibrahim M, Abbas F (2016) Glycinebetaine mediates chromium tolerance in mung bean through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant system. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62(5):648–662
Jana S, Choudhari MA (1982) Senescence in submerged aquatic angiosperms: effect of heavy metals. New Phytol 90:477–484
Jordan FL, Robin-Abbott M, Maier RM, Glenn EP (2002) A comparison of chelator-facilitated metal uptake by a halophyte and a glycophyte. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(12):2698–2704
Kadukova J, Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N (2008) Pb and Cd accumulation and phyto-excretion by salt cedar (Tamarix smyrnensis Bunge). Int J Phytoremediat 10(1):31–46
Kamran MA, Mufti R, Mubariz N, Syed JH, Bano A, Javed MT, Chaudhary HJ (2014) The potential of the flora from different regions of Pakistan in phytoremediation: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(2):801–812
Kanwal U, Ibrahim M, Ali S, Adrees M, Mahmood A, Rizwan M, Abbas F, Dawood M, Muhammad TAD (2019) Potential of Alternanthera bettzickiana (Regel) G. Nicholson for remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil using citric acid. Pak J Agric Sci 56(3):89
Lefèvre I, Marchal G, Meerts P, Corréal E, Lutts S (2009) Chloride salinity reduces cadmium accumulation by the Mediterranean halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. Environ Exp Bot 65(1):142–152
Lewis S, Donkin ME, Depledge MH (2001) Hsp 70 expression in Enteromorpha intestinalis (chlorophyta) exposed to environmental stressors. Aquat Toxicol 51:277–291
Leyssens L, Vinck B, Van Der Straeten C, Wuyts F, Maes L (2017) Cobalt toxicity in humans—a review of the potential sources and systemic health effects. Toxicology 387:43–56
Li CC, Dang F, Li M, Zhu M, Zhong H, Hintelmann H, Zhou DM (2017) Effects of exposure pathways on the accumulation and phytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in soybean and rice. Nanotoxicology 11:699–709
Lutts S, Lefevre I, Delpérée C, Kivits S, Dechamps C, Robledo A, Correal E (2004) Heavy metal accumulation by the halophyte species Mediterranean saltbush. J Environ Qual 33(4):1271–1279
Manousaki E, Kadukova J, Papadantonakis N, Kalogerakis N (2008) Phytoextraction and phytoexcretion of Cd by the leaves of Tamarix smyrnensis growing on contaminated non-saline and saline soils. Environ Res 106(3):326–332
Metwally A, Safronova VI, Belimov AA, Dietz KJ (2005) Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. J Exp Bot 56:167–178
Metzner AB (1965) Heat transfer in non-Newtonian fluids. Adv Heat Transf 2:357–397
Modaihsh A, Al-Swailem M, Mahjoub M (2004) Heavy metal contents of commercial inorganic fertilizer used in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Agric Mar Sci 9:21–25
Najeeb U, Xua L, Ali S, Jilani G, Gong HJ, Shen WQ, Zhou WJ (2009) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of manganese and plant growth by alleviating the ultrastructural damages in Juncus effusus L. J Hazard Mater 170:1156–1163
Nedjimi B, Daoud Y (2009) Cadmium accumulation in Atriplex halimus subsp. schweinfurthii and its influence on growth, proline, root hydraulic conductivity and nutrient uptake. Flora Morphol Distrib Funct Ecol Plant 204(4):316–324
Pandey V, Dixit V, Shyam R (2005) Antioxidative responses in relation to growth of mustard (Brassica juncea cv. Pusa Jaikisan) plants exposed to hexavalent chromium. Chemosphere 61:40–47
Raghunathan VK, Devey M, Hawkins S, Hails L, Davis SA, Mann S, Chang IT, Ingham E, Malhas A, Vaux DJ, Lane JD (2013) Influence of particle size and reactive oxygen species on cobalt chrome nanoparticle-mediated genotoxicity. Biomaterials 34(14):3559–3570
Raziuddin F, Hassan G, Akmal M, Shah S, Mohammad FM, Shafi J, Zhou W (2011) Effect of cadmium and salinity on growth and photosynthesis parameters of brassica species. Pak J Bot 43:333–340
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17859–17879
Sallah-Ud-Din R, Farid M, Saeed R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Tauqeer HM, Bukhari SAH (2017) Citric acid enhanced the antioxidant defense system and chromium uptake by Lemna minor L. grown in hydroponics under Cr stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):17669–17678
Salt DE, Smith RD, Raskin I (1998) Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 49(1):643–668
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Schreck E, Xiong T, Niazi NK (2017) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: a comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J Hazard Mater 325:36–58
Shevyakova NI, Netronina IA, Aronova E, Kuznetso V (2003) Compartmentation of cadmium and iron in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum plants during the adaptation to cadmium stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 50(5):678–685
Shtangeeva I (2010) Uptake of uranium and thorium by native and cultivated plants. J Environ Radioact 101(6):458–463
Tauqeer HM, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Saeed R, Iftikhar U, Ahmad R, Farid M, Abbasi GH (2016) Phytoremediation of heavy metals by Alternanthera bettzickiana: growth and physiological response. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:138–146
Vamerali T, Bandiera M, Mosca G (2010) Field crops for phytoremediation of metal-contaminated land. A review. Environ Chem Lett 8(1):1–17
Vasarevičius S, Danila V, Paliulis D (2019) Application of stabilized nano zero valent iron particles for immobilization of available Cd2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions in soil. Int J Environ Res 13(3):465–474
Wang C, Wu B, Jiang K, Zhou J (2018) Effects of different types of heavy metal pollution on functional traits of invasive redroot pigweed and native red amaranth. Int J Environ Res 12(4):419–427
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int Sch Res Netw Ecol 2011:20
Younis A, Riaz A, Ikram S, Nawaz T, Hameed M, Fatima S, Ahmad F (2013) Salinity-induced structural and functional changes in 3 cultivars of Alternanthera bettzickiana (Regel) G. Nicholson. Turk J Agric For 37(6):674–687
Zhang H, Xia Y, Wang G, Shen Z (2008) Excess copper induces accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and increases lipid peroxidation and total activity of copper–zinc superoxide dismutase in roots of Elsholtzia haichowensis. Planta 227(2):465–475
Zhang J, Kirkham MB (1994) Drought-stress-induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase in wheat species. Plant Cell Physiol 35:785–791
Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhou Y, Gong T, Wang J, Ge Y (2013) Enhanced phytoremediation of mixed heavy metal (mercury)–organic pollutants (trichloroethylene) with transgenic alfalfa co-expressing glutathione S-transferase and human P450 2E1. J Hazard Mater 260:1100–1107
Zhao Z, Xi M, Jiang G, Liu X, Bai Z, Huang Y (2010) Effects of IDSA, EDDS and EDTA on heavy metals accumulation in hydroponically grown maize (Zea mays, L.). J Hazard Mater 181(1):455–459
Acknowledgements
The authors want to say thanks to University of Gujrat, Gujrat, Pakistan and Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan for financial and technical support under NRPU Project No. 8996/Punjab/NRPU/HEC/R&D/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalid, A., Farid, M., Zubair, M. et al. Efficacy of Alternanthera bettzickiana to Remediate Copper and Cobalt Contaminated Soil Physiological and Biochemical Alterations. Int J Environ Res 14, 243–255 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00251-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00251-8