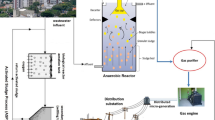
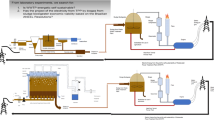
Abstract
The wastewater treatment has a fundamental role for all the industrial processes, being a crucial part in the water cycle. The meat industry around the world has severe problems associated with the huge freshwater requirements that increase with the population growth. However, nowadays, the most used slaughterhouse wastewater treatment (SWWT) system has negative environment impacts. Hence, the inclusion of the life cycle assessment method, as decision technique in the design and configuration of the treatment train for these industries, results in an attractive innovation. Particularly for the SWWT, the aerobic process is the most used approach; however, its high-energy requirements increase significantly the associated total cost. On the other hand, the upflow anaerobic sludge blanket process has been reported as an attractive treatment, but this needs a secondary treatment for achieving the environmental regulations for some pollutants. Therefore, this paper presents a techno-economic–environmental–social evaluation as a sustainable alternative in wastewater treatment train configuration based on the obtained results of the Trail and Refrigerator of the city of Morelia in Mexico. The results show that with the new configuration, the energetic requirement is reduced by 76%; thus, the operational cost is minimized in the same way, while the environmental impact is reduced by 30% with the integration of anaerobic and aerobic processes.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SWWT:
-
Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment
- LCA:
-
Life cycle assessment
- UASB:
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket
- WWS:
-
Slaughterhouse wastewater
- MPN:
-
Most probable number
- BOD:
-
Biochemical oxygen demand
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
- TP:
-
Total phosphorous
- FOG:
-
Fats, oils, and greases
- TSS:
-
Total suspended solids
- TDS:
-
Total dissolved solids
- EIA:
-
Environmental impact analysis
- EIAP:
-
Aerobic process environmental impact analysis
- EIANP:
-
Anaerobic process environmental impact analysis
- EIA-WW:
-
Untreatment wastewater discharge environmental impact analysis
References
Ahmadian M, Yousefi N, Van-Ginkel SW, Zare MR, Rahimi S, Fatehizadeh A (2012) Kinectic study of slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation using Fe electrodes. Water Sci Technol 66(4):754–760. doi:10.2166/wst.2012.232
Ahmed R, Mohd S, Johan S, Aznah A, Salmiati Sivarama L (2017) Performance of integrated anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactor treating poultry slaughterhouse wastewater. Chem Eng J 3013:967–974. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.144
Arredondo-Ramírez K, Rubio-Castro E, Nápoles-Rivera F, Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, El-Halwagi MM (2015) Optimal design of agricultural water systems with multiperiod collection, storage, and distribution. Agric Water Manag 152(1):161–172. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2015.01.007
Bare JC (2011) The tool for the reduction and assessment of chemical and other environmental impacts (TRACI). Clean Technol Environ Policy 13(5):687–696. doi:10.1162/108819802766269539 (Springer, New York)
Bustillo-Lecompte C, Mehrvar M (2015) Slaughterhouse wastewater characteristics, treatment, and management in meat processing industry: a review on trends and advances. J Environ Manag 161(1):287–302. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.07.008
Bustillo-Lecompte C, Mehrvar M (2016) Treatment of an actual slaughterhouse wastewater by integration of biological and advanced oxidation processes: modeling, optimization and cost-effectiveness analysis. J Environ Manag 182:651–666. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.044
Cao W, Mehrvar M (2011) Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by combined anaerobic baffled reactor and UV/H2O2 processes. Chem Eng Res Des 89:1136–1143. doi:10.1016/j.cherd.2010.12.001
Davarnejad R, Samaneh N (2017) Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment using an advanced oxidation process: optimization study. Environ Pollut 223:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.008
Del Nery V, Damianovic M, Moura R, Pozzi E, Pires E, Foresti E (2016) Poultry slaughterhouse wastewater treatment plant for high effluent. Water Sci Technol 73(2):309–316. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.144
Do A, Bach D, Do U, Prieto A, Huong H (2016) Performance of airlift MBR for on-site treatment slaughterhouse wastewater in urban areas of Vietnam. Water Sci Technol 74(9):2245–2251. doi:10.2166/wst.2016.418
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2016) Water withdrawal by sector, around 2010. Available on DIALOG. http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/tables/WorldData-Withdrawal_eng.pdf
García-Montoya M, Nápoles-Rivera F, Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, El-Halwagi MM (2014) Optimal design of reusing water systems in a housing complex. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17(2):343–357. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0784-x
García-Montoya M, Sengupta D, Nápoles-Rivera F, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM (2016) Environmental and economic analysis for the optimal reuse of water in a residential complex. J Clean Prod 130(1):82–91. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.109
Gu Y, Dong Y, Wang H, Keller A, Xu J, Chiramba T, Li F (2016) Quantification of the water, energy and carbon footprint of wastewater treatment plants in China considering a water-energy nexus perspective. Ecol Ind 60(1):40–409. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.07.012
Harris P, McCabe B (2015) Review of pre-treatments used in anaerobic digestion and their potential application in high-fat cattle slaughterhouse wastewater. Appl Energy 155:560–575. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.06.026
ISO 14040 (2006) Environmental management life cycle assessment-principles and framework. Geneva, Switzerland. Available on DIALOG. http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=37456
Jensen P, Sullivan T, Carney C, Batstone D (2014) Analysis of the potential to recover energy and nutrient resources from cattle slaughterhouses in Australia by employing anaerobic digestion. Appl Energy 136:23–31. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.09.009
Johns M (1995) Developments in wastewater treatment in the meat processing industry: a review. Biores Technol 54:203–216. doi:10.1016/0960-8524(95)00140-9
Li J, Healy M, Zhan X, Rodgers M (2008) Nutrient removal from slaughterhouse wastewater in an intermittently aerated sequencing batch reactor. Biores Technol 99:7644–7650. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.02.001
Liu Y, Kang X, Li X, Yuan Y (2015) Performance of aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch bioreactor for slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. Biores Technol 190(1):487–491. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.03.008
Mitra S, Gupta S (2014) Pilot-scale treatment of a trichloethylene rich synthetic wastewater in anaerobic hybrid reactor, with morphological study of the sludge granules. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16(5):947–956. doi:10.1007/s10098-013-0695-2
Morera S, Ll Corominas, Poch M, Aldaya MM, Comas J (2016) Water footprint assessment in wastewater treatment plants. J Clean Prod 112(1):4741–4748. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.102
Rodríguez J, Rodríguez I, Pedraza E, Balagurusamy N, Sosa G, Garza Y (2002) Kinetics of anaerobic treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in batch and upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Bioresour Technol 85(1):235–241. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00141-4
Rodríguez-Martínez J, Rodríguez-Garza I, Pedraza-Flores E, Balagurusamy N, Sosa-Santillan G, Garza Y (2002) Kinetics of anaerobic treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in batch and upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Bioresour Technol 85:235–241. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00141-4
Vidal J, Huiliñir C, Salazar R (2016) Removal of organic matter contained in slaughterhouse wastewater using a combination of anaerobic digestion and solar photoelectron-Fenton processes. Electrochim Acta 210:163–170. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2016.05.064
Wu P, Mittal G (2011) Characterization of provincially inspected slaughterhouses wastewater in Ontario Canada. Biosyst Eng 53(1):6.9–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palomares-Rodríguez, C., Martínez-Guido, S.I., Apolinar-Cortés, J. et al. Environmental, Technical, and Economic Evaluation of a New Treatment for Wastewater from Slaughterhouses. Int J Environ Res 11, 535–545 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0047-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0047-x