Abstract
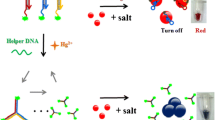
In this work, we proposed a ratiometric silver nanoclusters (AgNCs) fluorescent assay by designing a bifunctional-blocker-aided hybridization chain reaction (HCR). Hairpin probe 1 (HP1) containing two special DNA fragments (5′-CACCGCT-3′ and 5′-ATTTGCCTTTTGGGGACGGATA-3′) at two terminals creates a red-emitting AgNC nucleation sequence (rNS, 5′-CACCGCTATTTGCCTTTTGGGGACGGATA-3′). We found that the presence of a toehold fragment (5′-TGCCC-3′) in HP1 could silence the rNS. Upon the addition of a target nucleic acid, HCR of HP1 and hairpin probe 2 (HP2) could be initiated, resulting in the formation of long chain of DNA duplexes with multibranched rNS. As the toehold fragment in HP1 participated in generating duplexes, a strong emission of rNS-templated AgNCs was observed at 670 nm. More significantly, a bifunctional blocker was introduced not only to reduce the background red-emitting fluorescence but also to play as an internal green-emitting AgNCs nucleation sequence. On the one hand, the blocker could increase the signal-to-noise-ratio of the constructed biosensor, and on the other hand, the blocker also helped to prepare ratiometric HCR-AgNCs assay with self-calibrating ability to strengthen its reproducibility. Compared with the traditional HCR-AgNCs sensors, the developed ratiometric assay based on the bifunctional-blocker-aided HCR has higher reliability, which is important for the fabrication of biosensors in various fields for practical biosensing applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the relevant data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Li MY, Mai CY, Zou L. Recent advances in nucleic acid amplification-based optical biosensors for disease diagnosis. Chin J Anal Lab. 2022;41(7):842–50.
Yang J, Yang F, Zhang C, He X, Jin R. Metal nanoclusters as biomaterials for bioapplications: atomic precision as the next goal. ACS Mater Lett. 2022;4(7):1279–96.
Nasrollahpour H, Sánchez BJ, Sillanpää M, Moradi R. Metal nanoclusters in point-of-care sensing and biosensing applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023;6(14):12609–72.
Chen Z, Song J. Special Topic: Near-infrared I/II theranostics. J Anal Test. 2023;7(3):187–8.
Hou Y, Lv CC, Guo YL, Ma XH, Liu W, Jin Y, Li BX, Yang M, Yao SY. Recent advances and applications in paper-based devices for point-of-care testing. J Anal Test. 2022;6(3):247–73.
Petty JT, Zheng J, Hud NV, Dickson RM. DNA-templated Ag nanocluster formation. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(16):5207–12.
Liu H, Zhu C, Mou C. Duplex-specific nuclease and Exo-III enzyme-assisted signal amplification cooperating DNA-templated silver nanoclusters for label-free and sensitive miRNA detection. J Anal Sci Technol. 2022;13(1):26.
Zhang BJ, Ma WW, Guo J, Zhao QF, Zhang CC, Zhu SL, Xu HB, Yin YY. Dual signal amplification coupling with DNA-templated silver nanoclusters for sensitive and label-free detection of thrombin. J Anal Sci Technol. 2023;14(1):6.
Ma G, Huo L, Tong Y, Wang Y, Li C, Jia H. Label-free and sensitive MiRNA detection based on turn-on fluorescence of DNA-templated silver nanoclusters coupled with duplex-specific nuclease-assisted signal amplification. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(10):355.
Ma J, Niu H, Gu S. The spatial organization of trace silver atoms on a DNA template. RSC Adv. 2021;11(2):1153–63.
Zhang L, Wang E. Metal nanoclusters: New fluorescent probes for sensors and bioimaging. Nano Today. 2014;9(1):132–57.
Qiu Q, Gao RR, Xie A, Jiao Y, Dong W. A ratiometric fluorescent sensor with different DNA-templated Ag NCs as signals for ATP detection. J Photoch Photobio A-Chem. 2020;400:112725.
He JY, Luo SH, Deng HL, Yang CL, Zhang YQ, Li MD, Yuan R, Xu WJ. Fluorescent features and applicable biosensing of a core–shell Ag nanocluster shielded by a DNA tetrahedral nanocage. Anal Chem. 2023;95(39):14805–15.
Guha R, Rafik M, Gonzàlez-Rosell A, Copp SM. Heat, pH, and salt: synthesis strategies to favor formation of near-infrared emissive DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters. Chem Commun. 2023;59(70):10488–91.
Chen HY, Zhou SY, Ou RF, Lai TT, Gao SJ, Huang ZX, Zhou WR, Mai WY, Yang JP. Research progress of aptamer-functionalized DNA nano-biosensors. Chin J Anal Lab. 2023;42(9):1260–6.
Yang CL, Zhang YQ, He JY, Li MD, Yuan R, Xu WJ. Target deoxyribonucleic acid-recycled lighting-up amplifiable ratiometric fluorescence biosensing of bicolor silver nanoclusters hosted in a switchable deoxyribonucleic acid construct. Anal Chem. 2022;94(18):6703–10.
New SY, Lee ST, Su XD. DNA-templated silver nanoclusters: structural correlation and fluorescence modulation. Nanoscale. 2016;8(41):17729–46.
Hu HJ, Tan H, Zhou HM, He XH, Zhang SJ. An excitation ratiometric fluorescent probe with wide-range pH response constructed by poly (Nisopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) silver nanoclusters. Chin J Anal Lab. 2022;41(1):7–11.
Liu L, Zhu S, Sun J, Xia M, Xu G. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of bleomycin based on proximity-dependent fluorescence conversion of DNA-templated silver nanoclusters. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32(2):906–9.
Bogh SA, Cerretani C, Kacenauskaite L, Carro-Temboury MR, Vosch T. Excited-state relaxation and Förster resonance energy transfer in an organic fluorophore/silver nanocluster dyad. ACS Omega. 2017;2(8):4657–64.
Wang S, Lu S, Zhao J, Yang X. A ratiometric fluorescent DNA radar based on contrary response of DNA/silver nanoclusters and G-quadruplex/crystal violet. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11(28):25066–73.
Borghei YS, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR. Fluorometric determination of microRNA via FRET between silver nanoclusters and CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(12):4713–21.
Qin L, Zhang K, Feng B, Zhang P, Qing T, Fei J. Proximity sequence-dependent spectral conversion of silver nanoclusters and construction of ratiometric nanoprobe. Chem Eng J. 2022;441: 136001.
Liu M, Shen R, Li H, Jia Y, Mak PI, Martins RP. Ratiometric fluorescence analysis for miR-141 detection with hairpin DNA-templated silver nanoclusters. J Mater Chem C. 2022;10(2):655–64.
Qian J, Yang Y, Gong F, Shan X, Ji X, He Z. Ratiometric fluorescence biosensing of silver nanocluster beacons for ATP detection based on ligation- triggered rolling cycle amplification. Microchem J. 2023;190:108663.
Jiang Y, Ma X, Shao X, Wang M, Jiang Y, Miao P. Chameleon silver nanoclusters for ratiometric sensing of miRNA. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019;297:126788.
Wong ZW, Ng JF, New SY. Ratiometric detection of microRNA using hybridization chain reaction and fluorogenic silver nanoclusters. Chem-Asian J. 2021;16(24):4081–6.
Wong ZW, Muthoosamy K, Mohamed NAH, New SY. A ratiometric fluorescent biosensor based on magnetic-assisted hybridization chain reaction and DNA-templated silver nanoclusters for sensitive microRNA detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;12:100244.
Yuan Y, Ma YY, Luo L, Wang Q, Huang J, Liu JB, Yang XH, Wang KM. Ratiometric determination of human papillomavirus-16 DNA by using fluorescent DNA-templated silver nanoclusters and hairpin-blocked DNAzyme-assisted cascade amplification. Microchim Acta. 2019;186(9):613.
Wu N, Wang K, Wang YT, Chen ML, Chen XW, Yang T, Wang JH. Three-dimensional DNA nanomachine biosensor by integrating DNA walker and rolling machine cascade amplification for ultrasensitive detection of cancer-related gene. Anal Chem. 2020;92(16):11111–8.
Ge L, Sun X, Hong Q, Li F. Ratiometric catalyzed-assembly of nanocluster beacons: a nonenzymatic approach for amplified DNA detection. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2017;9(37):32089–96.
Huang M, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Lu H, Zhang H, Liu F, Qin X, Qin X, Li X, Yang F. Bottom-up signal boosting with fractal nanostructuring and primer exchange reaction for ultrasensitive detection of cancerous exosomes. ACS Sens. 2023;8:1308–17.
Xiang Y, Zhang H, Lu H, Wei B, Su C, Qin X, Fang M, Li X, Yang F. Bioorthogonal microbubbles with antifouling nanofilm for instant and suspended enrichment of circulating tumor cells. ACS Nano. 2023;17:9633–46.
Ge L, Sun X, Hong Q, Li F. Ratiometric nanocluster beacon: a label-free and sensitive fluorescent DNA detection platform. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2017;9(15):13102–10.
Kondo J, Tada Y, Dairaku T, Hattori Y, Saneyoshi H, Ono A, Tanaka Y. A metallo-DNA nanowire with uninterrupted one-dimensional silver array. Nat Chem. 2017;9(10):956–60.
Ma K, Shao Y, Cui Q, Wu F, Xu S, Liu G. Base-stacking-determined fluorescence emission of DNA abasic site-templated silver nanoclusters. Langmuir. 2012;28(43):15313–22.
Peng J, Shao Y, Liu L, Zhang L, Liu H. Specific recognition of DNA bulge sites by in situ grown fluorescent Ag nanoclusters with high selectivity. Dalton T. 2014;43(4):1534–41.
Wu Y, Zhou GB, Ma ZY, Zhang D, Li L. Sensitive fluorescent determination of nucleic acids by a cytosine-rich loop and silver nanoclusters in the hybridization chain reaction (HCR). Anal Lett. 2023;57(2):213–24.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22304062), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LTGY24B050002), the Program for Science and Technology of Jiaxing (2023AY40028) and the Baiqing Foundation of Jiaxing University (CD70621010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhou, G., Yang, H. et al. A Bifunctional-Blocker-Aided Hybridization Chain Reaction Lighting-Up Self-calibrating Nanocluster Fluorescence for Reliable Nucleic Acid Detection. J. Anal. Test. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-024-00297-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-024-00297-z