Abstract
Conduction electrons in metallic nano-objects (\(1\,\mathrm{nm} = 10^{-9}\, \mathrm{m}\)) behave as mobile negative charges confined by a fixed positively charged background, the atomic ions. In many respects, this electron gas displays typical plasma properties such as screening and Langmuir waves, with more or less pronounced quantum features depending on the size of the object. To study these dynamical effects, the mathematical artillery of condensed matter theorists mainly relies on wave function \(\psi (\varvec{r},t)\)-based methods, such as the celebrated Hartree–Fock equations. The theoretical plasma physicist, in contrast, lives and breaths in the six-dimensional phase space, where the electron gas is fully described by a probability distribution function \(f(\varvec{r},\varvec{p},t)\) that evolves according to an appropriate kinetic equation. Here, we illustrate the power and flexibility of the phase-space approach to describe the electron dynamics in small nano-objects. Starting from classical and semiclassical scenarios, we progressively add further features that are relevant to solid-state plasmas: quantum, spin, and relativistic effects, as well as collisions and dissipation. As examples of applications, we study the spin-induced modifications to the linear response of a homogeneous electron gas and the nonlinear dynamics of the electrons confined in a thin metal films of nanometric dimensions.

From Cobley et al. (2009)

From Bigot et al. (2009)



From Sun et al. (2016)





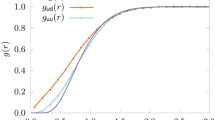
From Manfredi et al. (2010)

From Manfredi et al. (2010)

From Manfredi et al. (2010)










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Aeschlimann, M. Bauer, S. Pawlik, R. Knorren, G. Bouzerar, K. Bennemann, Transport and dynamics of optically excited electrons in metals. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 71(5), 485–491 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390000704
A. Alekhin, I. Razdolski, N. Ilin, J.P. Meyburg, D. Diesing, V. Roddatis, I. Rungger, M. Stamenova, S. Sanvito, U. Bovensiepen, A. Melnikov, Femtosecond spin current pulses generated by the nonthermal spin-dependent seebeck effect and interacting with ferromagnets in spin valves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 017202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.017202
A. Arnold, H. Steinrück, The ’electromagnetic’ Wigner equation for an electron with spin. ZAMP Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 40(6), 793–815 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00945803
F.A. Asenjo, J. Zamanian, M. Marklund, G. Brodin, P. Johansson, Semi-relativistic effects in spin-1/2 quantum plasmas. New J. Phys. 14(7), 073042 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/14/7/073042
A. Banerjee, M.K. Harbola, Hydrodynamic approach to time-dependent density functional theory. Response properties of metal clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 113, 5614–5623 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1290610
L. Barletti, Wigner envelope functions for electron transport in semiconductor devices. Transp. Theory Stat. Phys. 32(3–4), 253–277 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1081/TT-120024764
M. Battiato, K. Carva, P.M. Oppeneer, Superdiffusive spin transport as a mechanism of ultrafast demagnetization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(2), 027203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.027203
E. Beaurepaire, J.C. Merle, A. Daunois, J.Y. Bigot, Ultrafast spin dynamics in ferromagnetic nickel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(22), 4250–4253 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.4250
A. Bertoni, P. Bordone, R. Brunetti, C. Jacoboni, The Wigner function for electron transport in mesoscopic systems. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11(31), 5999–6012 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/11/31/308
I. Bialynicki-Birula, Relativistic Wigner functions. EPJ Web Conf. 78, 01001 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/20147801001
J.Y. Bigot, V. Halté, J.C. Merle, A. Daunois, Electron dynamics in metallic nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. 251(1), 181–203 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0104(99)00298-0
J.Y. Bigot, M. Vomir, E. Beaurepaire, Coherent ultrafast magnetism induced by femtosecond laser pulses. Nat. Phys. 5(7), 515–520 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1285
M. Brewczyk, K. Rzazewski, C.W. Clark, Multielectron dissociative ionization of molecules by intense laser radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78(2), 191–194 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.191
S.D. Brorson, J.G. Fujimoto, E.P. Ippen, Femtosecond electronic heat-transport dynamics in thin gold films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 1962–1965 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.1962
J. Butet, J. Duboisset, G. Bachelier, I. Russier-Antoine, E. Benichou, C. Jonin, P.F. Brevet, Optical second harmonic generation of single metallic nanoparticles embedded in a homogeneous medium. Nano Lett. 10(5), 1717–1721 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl1000949
F. Calvayrac, P.G. Reinhard, E. Suraud, C. Ullrich, Nonlinear electron dynamics in metal clusters. Phys. Rep. 337(6), 493–578 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0370-1573(00)00043-0
C.M. Cobley, S.E. Skrabalak, D.J. Campbell, Y. Xia, Shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles for plasmonic and sensing applications. Plasmonics 4(2), 171–179 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-009-9088-0
L. Cohen, The Weyl Operator and its Generalization (Springer Basel, Basel, 2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-0294-9
N. Crouseilles, P.A. Hervieux, G. Manfredi, Quantum hydrodynamic model for the nonlinear electron dynamics in thin metal films. Phys. Rev. B 78(15), 155412 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.155412
J. Daligault, On the quantum landau collision operator and electron collisions in dense plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 23(3), 032706 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4944392
J. Daligault, C. Guet, Large amplitude femtosecond electron dynamics in metal clusters. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 36(22), 5847–5855 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4470/36/22/304
M.C. Daniel, D. Astruc, Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 104, 239–346 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030698+
S. Deléglise, I. Dotsenko, C. Sayrin, J. Bernu, M. Brune, J.M. Raimond, S. Haroche, Reconstruction of non-classical cavity field states with snapshots of their decoherence. Nature 455(7212), 510–514 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07288
P.M. Dinh, L. Lacombe, P.G. Reinhard, É. Suraud, M. Vincendon, On the inclusion of dissipation on top of mean-field approaches. Eur. Phys. J. B 91(10), 246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-90147-0
T. Dittrich, E.A. Gómez, L.A. Pachón, Semiclassical propagation of Wigner functions. J. Chem. Phys. 132(21), 214102 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3425881
A. Dixit, Y. Hinschberger, J. Zamanian, G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Lagrangian approach to the semirelativistic electron dynamics in the mean-field approximation. Phys. Rev. A 88(3), 032117 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.88.032117
A. Domps, P.G. Reinhard, E. Suraud, Theoretical estimation of the importance of two-electron collisions for relaxation in metal clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(25), 5524–5527 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.5524
A. Dragan, T. Odrzygóźdź, A half-page derivation of the Thomas precession. Am. J. Phys. 81(8), 631 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1119/1.4807564
P. Drude, Zur Elektronentheorie der Metalle. Annalen der Physik 306(3), 566–613 (1900). https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.19003060312
A.G. Eguiluz, D.A. Campbell, A.A. Maradudin, R.F. Wallis, Static response of a jellium surface: the image potential and indirect interaction between two charges. Phys. Rev. B 30, 5449–5459 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.30.5449
O. Ekici, R.K. Harrison, N.J. Durr, D.S. Eversole, M. Lee, A. Ben-Yakar, Thermal analysis of gold nanorods heated with femtosecond laser pulses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41(18), 185501 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/41/18/185501
R. Ekman, F.A. Asenjo, J. Zamanian, Relativistic kinetic equation for spin-1/2 particles in the long-scale-length approximation. Phys. Rev. E 96, 023207 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.96.023207
V. Fock, Näherungsmethode zur Lösung des quantenmechanischen Mehrkörperproblems. Zeitschrift für Physik 61(1–2), 126–148 (1930). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01340294
L.L. Foldy, S.A. Wouthuysen, On the Dirac theory of spin 1/2 particles and its non-relativistic limit. Phys. Rev. 78(1), 29–36 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.78.29
S.V. Fomichev, D.F. Zaretsky, Vlasov theory of Mie resonance broadening in metal clusters. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 32(21), 5083–5102 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/32/21/303
C. Fourment, F. Deneuville, D. Descamps, F. Dorchies, S. Petit, O. Peyrusse, B. Holst, V. Recoules, Experimental determination of temperature-dependent electron–electron collision frequency in isochorically heated warm dense gold. Phys. Rev. B (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.89.161110
B.D. Fried, S.D. Conte, The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the Gaussian (Academic Press, New York, 1961)
W. Gerlach, O. Stern, Der experimentelle Nachweis der Richtungsquantelung im Magnetfeld. Zeitschrift für Physik 9(1), 349–352 (1922). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01326983
C. Guillon, P. Langot, N.D. Fatti, F. Vallée, Nonequilibrium electron energy-loss kinetics in metal clusters. New J. Phys. 5(1), 13–13 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/5/1/313
O. Gunnarsson, B.I. Lundqvist, Exchange and correlation in atoms, molecules, and solids by the spin-density-functional formalism. Phys. Rev. B 13(10), 4274–4298 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.13.4274
F. Haas, Quantum Plasmas: An Hydrodynamic Approach (Springer, Berlin, 2011)
F. Haas, G. Manfredi, P.K. Shukla, P.A. Hervieux, Breather mode in the many-electron dynamics of semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 80(7), 073301 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.073301
J.F. Hainfeld, D.N. Slatkin, H.M. Smilowitz, The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys. Med. Biol. Phys. Med. Biol. 49(4904), 309–315 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/49/18/N03
D.R. Hartree, The wave mechanics of an atom with a non-coulomb central field. Part I. Theory and methods. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 24(01), 89 (1928). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0305004100011919
E.J. Heller, Wigner phase space method: analysis for semiclassical applications. J. Chem. Phys. 65(4), 1289–1298 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.433238
Y. Hinschberger, P.A. Hervieux, Foldy–Wouthuysen transformation applied to the interaction of an electron with ultrafast electromagnetic fields. Phys. Lett. A 376(6), 813–819 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2012.01.023
P. Hohenberg, W. Kohn, Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 136(3B), B864–B871 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.136.B864
J. Hurst, P.A. Hervieux, G. Manfredi, Phase-space methods for the spin dynamics in condensed matter systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 375, 20160199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2016.0199
J. Hurst, P.A. Hervieux, G. Manfredi, Spin current generation by ultrafast laser pulses in ferromagnetic nickel films. Phys. Rev. B 97, 014424 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.014424
J. Hurst, O. Morandi, G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Semiclassical Vlasov and fluid models for an electron gas with spin effects. Eur. Phys. J. D 68(6), 176 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2014-50205-5. arxiv:1405.1184
R. Jasiak, G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Quantum-classical transition in the electron dynamics of thin metal films. New J. Phys. 11(6), 063042 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/11/6/063042
R. Jasiak, G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Electron thermalization and quantum decoherence in metal nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 81(24), 241401 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.81.241401
R.O. Jones, Density functional theory: its origins, rise to prominence, and future. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87(3), 897–923 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.87.897
W. Jones, N.H.N.H. March, Theoretical Solid State Physics (Dover Publications, Mineola, 1985)
G. Kaniadakis, P. Quarati, Kinetic equation for classical particles obeying an exclusion principle. Phys. Rev. E 48, 4263–4270 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.48.4263
A. Kenfack, K. yczkowski, Negativity of the wigner function as an indicator of non-classicality. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclassical Opt. 6(10), 396–404 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/1464-4266/6/10/003
W. Kohn, L.J. Sham, Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 140(4A), A1133–A1138 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.140.A1133
F. Komori, S. Okuma, S. ichi Kobayashi, Inelastic scattering time and metal-insulator transition in thick disordered bismuth films. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 56(2), 691–696 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1143/jpsj.56.691
P. Kravanja, M. Van Barel, O. Ragos, M.N. Vrahatis, F.A. Zafiropoulos, ZEAL: a mathematical software package for computing zeros of analytic functions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 124(124), 212–232 (2000)
U. Kreibig, M. Vollmer, Optical Properties of Metal Clusters (Springer, Berlin, 1995)
K. Krieger, J.K. Dewhurst, P. Elliott, S. Sharma, E.K.U. Gross, Laser-induced demagnetization at ultrashort time scales: predictions of TDDFT. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 11(10), 4870–4874 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00621
B. Lamprecht, J.R. Krenn, A. Leitner, F.R. Aussenegg, Resonant and off-resonant light-driven plasmons in metal nanoparticles studied by femtosecond-resolution third-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(21), 4421–4424 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.4421
L.D. Landau, On the vibrations of the electronic plasma. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 10, 25 (1946)
G. Lindblad, On the generators of quantum dynamical semigroups. Commun. Math. Phys. 48(2), 119–130 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01608499
X. Liu, R. Stock, W. Rudolph, Ballistic electron transport in AU films. Phys. Rev. B 72, 195431 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.195431
L. Loomba, T. Scarabelli, Metallic nanoparticles and their medicinal potential. Part II: aluminosilicates, nanobiomagnets, quantum dots and cochleates. Ther. Deliv. 4(9), 1179–1196 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4155/tde.13.74
Y. Luo, A.I. Fernandez-Dominguez, A. Wiener, S.A. Maier, J.B. Pendry, Surface plasmons and nonlocality: a simple model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(9), 093901 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.093901
L.H. Lyu, Elementary Space Plasma Physics, 2nd edn. (Airiti Press, Taiwan, ROC, 2014)
M. Maier, G. Wrigge, M.A. Hoffmann, P. Didier, Bv Issendorff, Observation of electron gas cooling in free sodium clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(11), 117405 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.117405
G. Manfredi, How to model quantum plasmas. Fields Inst. Commun. Ser. 46, 263–287 (2005). arxiv:quant-ph/0505004
G. Manfredi, Non-relativistic limits of Maxwell’s equations. Eur. J. Phys. 34(4), 859–871 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0143-0807/34/4/859
G. Manfredi, Preface to special topic: plasmonics and solid state plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 25(3), 031701 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5026653
G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Vlasov simulations of ultrafast electron dynamics and transport in thin metal films. Phys. Rev. B 70, 201402 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.70.201402
G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Finite-size and nonlinear effects on the ultrafast electron transport in thin metal films. Phys. Rev. B 72(15), 155421 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.155421
G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Nonlinear absorption of ultrashort laser pulses in thin metal films. Opt. Lett. 30(22), 3090–3092 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.30.003090
G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, F. Haas, Nonlinear dynamics of electron–positron clusters. New J. Phys. 14(7), 075012 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/14/7/075012
G. Manfredi, P.A. Hervieux, Y. Yin, N. Crouseilles, Collective Electron Dynamics in Metallic and Semiconductor Nanostructures (Springer, Berlin, 2010), pp. 1–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04650-6_1
R.A. Maniyara, D. Rodrigo, R. Yu, J. Canet-Ferrer, D.S. Ghosh, R. Yongsunthon, D.E. Baker, A. Rezikyan, F.J.G. de Abajo, V. Pruneri, Tunable plasmons in ultrathin metal films. Nat. Photonics 13(5), 328–333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0366-x
M. Marklund, J. Zamanian, G. Brodin, Spin kinetic theory-quantum kinetic theory in extended phase space. Transp. Theory Stat. Phys. 39(5–7), 502–523 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/00411450.2011.566502
E. Maurat, P.A. Hervieux, Thermal properties of open-shell metal clusters. New J. Phys. 11(10), 103031 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/11/10/103031
R.A. Molina, D. Weinmann, R.A. Jalabert, Oscillatory size dependence of the surface plasmon linewidth in metallic nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 65(15), 155427 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.65.155427
O. Morandi, Effective classical Liouville-like evolution equation for the quantum phase-space dynamics. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 43(36), 365302 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/43/36/365302
O. Morandi, P.A. Hervieux, G. Manfredi, Ultrafast magnetization dynamics in diluted magnetic semiconductors. New J. Phys. 11(7), 073010 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/11/7/073010
O. Morandi, F. Schürrer, Wigner model for quantum transport in graphene. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 44(26), 265301 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/44/26/265301
A. Moreau, C. Ciracì, J.J. Mock, R.T. Hill, Q. Wang, B.J. Wiley, A. Chilkoti, D.R. Smith, Controlled-reflectance surfaces with film-coupled colloidal nanoantennas. Nature 492(7427), 86–89 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11615
T. Müller, W. Parz, G. Strasser, K. Unterrainer, Influence of carrier–carrier interaction on time-dependent intersubband absorption in a semiconductor quantum well. Phys. Rev. B 70(15), 155324 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.70.155324
M. Pereira, H. Wenzel, Interplay of Coulomb and nonparabolicity effects in the intersubband absorption of electrons and holes in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 70(20), 205331 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.70.205331
D. Pines, P.P. Nozières, Theory of Quantum Liquids (Addison-Wesley Pub. Co., Boston, 1995)
A. Puente, M. Casas, L. Serra, A semiclassical approach to the ground state and density oscillations of quantum dots. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 8(4), 387–397 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-9477(99)00042-9
S. Raza, N. Stenger, S. Kadkhodazadeh, S.V. Fischer, N. Kostesha, A.P. Jauho, A. Burrows, M. Wubs, N.A. Mortensen, Blueshift of the surface plasmon resonance in silver nanoparticles studied with EELS. Nanophotonics 2(2), 131–138 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2012-0032
B. Rethfeld, A. Kaiser, M. Vicanek, G. Simon, Ultrafast dynamics of nonequilibrium electrons in metals under femtosecond laser irradiation. Phys. Rev. B 65(21), 214303 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.65.214303
E. Runge, E.K.U. Gross, Density functional theory for time dependent systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52(12), 997–1000 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.52.997
O. Salata, Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine. J. Nanobiotechnology 2(1), 3 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-2-3
J.A. Scholl, A.L. Koh, J.A. Dionne, Quantum plasmon resonances of individual metallic nanoparticles. Nature 483(7390), 421–427 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10904
U. Schwengelbeck, L. Plaja, L. Roso, E.C. Jarque, Plasmon-induced photon emission from thin metal films. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 33(8), 1653–1661 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/33/8/314
O.T. Serimaa, J. Javanainen, S. Varró, Gauge-independent Wigner functions: general formulation. Phys. Rev. A 33(5), 2913–2927 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.33.2913
L. Serra, A. Puente, Magnetic Thomas-Fermi-Weizsäcker model for quantum dots: a comparison with Kohn-Sham ground states. Eur. Phys. J. D 14(1), 77–81 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530170237
T.V. Shahbazyan, Landau damping of surface plasmons in metal nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 94(23), 235431 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.94.235431
P.K. Shukla, B. Eliasson, Formation and dynamics of dark solitons and vortices in quantum electron plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(24), 245001 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.245001
P.K. Shukla, B. Eliasson, Nonlinear aspects of quantum plasma physics. Physics Uspekhi 53(1), 51–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3367/UFNe.0180.201001b.0055
H. Singhal, R.A. Ganeev, P.A. Naik, A.K. Srivastava, A. Singh, R. Chari, R.A. Khan, J.A. Chakera, P.D. Gupta, Study of high-order harmonic generation from nanoparticles. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 43(2), 025603 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/43/2/025603
J.C. Slater, The theory of complex spectra. Phys. Rev. 34(10), 1293–1322 (1929). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.34.1293
D.T. Smithey, M. Beck, M.G. Raymer, A. Faridani, Measurement of the Wigner distribution and the density matrix of a light mode using optical homodyne tomography: application to squeezed states and the vacuum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(9), 1244–1247 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.1244
R.F. Snider, K.S. Lewchuk, Irreversible thermodynamics of a fluid system with spin. J. Chem. Phys. 46(8), 3163–3172 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1841187
M. Stamenova, J. Simoni, S. Sanvito, Role of spin-orbit interaction in the ultrafast demagnetization of small iron clusters. Phys. Rev. B 94(1), 014423 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.94.014423
M.I. Stockman, Nanoplasmonics: the physics behind the applications. Phys. Today 64(2), 39–44 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3554315
P. Strange, Relativistic quantum mechanics: with applications in condensed matter and atomic physics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998)
R.L. Stratonovich, On the statistical interpretation of quantum theory. Sov. Phys. JETP 5(6), 1206–1216 (1957) [original Russian edition: J. Exptl. Theoret. Phys. (U.S.S.R.) 32, 1483–1495 (June, 1957)].
C. Suárez, W.E. Bron, T. Juhasz, Dynamics and transport of electronic carriers in thin gold films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75(24), 4536–4539 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.4536
N.D. Suh, M.R. Feix, P. Bertrand, Numerical simulation of the quantum Liouville-Poisson system. J. Comput. Phys. 94(2), 403–418 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(91)90227-C
L. Sun, P. Chen, L. Lin, Enhanced molecular spectroscopy via localized surface plasmon resonance, in Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy to Current Research in the Chemical and Biological Sciences, Chap. 8, ed. by M.T. Stauffer (IntechOpen, Rijeka, 2016). https://doi.org/10.5772/64380
M.S. Tame, K.R. McEnery, K. Özdemir, J. Lee, S.A. Maier, M.S. Kim, Quantum plasmonics. Nat. Phys. 9(6), 329–340 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2615
F. Tanjia, J. Hurst, P.A. Hervieux, G. Manfredi, Plasmonic breathing modes in \({\rm C}_{60}\) molecules: a quantum hydrodynamic approach. Phys. Rev. A 98, 043430 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.98.043430
E. Tatsuro, K. Kagan, N. Naoki, H. Ha Minh, K. Do-Kyun, Y. Yuji, N. Koichi, T. Eiichi, Multiple LabelFree detection of antigen antibody reaction using localized surface plasmon resonance based core shell structured nanoparticle layer nanochip. Anal. Chem. 78, 6465–6475 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/AC0608321
T.V. Teperik, P. Nordlander, J. Aizpurua, A.G. Borisov, Robust subnanometric plasmon ruler by rescaling of the nonlocal optical response. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(26), 263901 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.263901
L.H. Thomas, The motion of the spinning electron. Nature 117(2945), 514–514 (1926). https://doi.org/10.1038/117514a0
M.W. Thomas, R.F. Snider, Boltzmann equation and angular momentum conservation. J. Stat. Phys. 2(1), 61–81 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01009711
E.A. Uehling, G.E. Uhlenbeck, Transport phenomena in einstein-bose and fermi-dirac gases. Phys. Rev. I 43, 552–561 (1933). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.43.552
C.A. Ullrich, P.G. Reinhard, E. Suraud, Simplified implementation of self-interaction correction in sodium clusters. Phys. Rev. A 62(5), 053202 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.62.053202
G. Vignale, W. Kohn, Current-dependent exchange-correlation potential for dynamical linear response theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2037–2040 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.2037
S.V. Vladimirov, Y.O. Tyshetskiy, On description of a collisionless quantum plasma. Physics Uspekhi 54(12), 1243–1256 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3367/UFNe.0181.201112g.1313
A.A. Vlasov, On the oscillation properties of an electron gas. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 8, 291–318 (1938)
C. Voisin, D. Christofilos, N. Del Fatti, F. Vallée, B. Prével, E. Cottancin, J. Lermé, M. Pellarin, M. Broyer, Size-dependent electron-electron interactions in metal nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(10), 2200–2203 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.2200
H. Weyl, Quantenmechanik und Gruppentheorie. Zeitschrift für Physik 46(1–2), 1–46 (1927). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02055756
E. Wigner, On the quantum correction for thermodynamic equilibrium. Phys. Rev. 40(5), 749–759 (1932). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.40.749
Y. Yin, P.A. Hervieux, R.A. Jalabert, G. Manfredi, E. Maurat, D. Weinmann, Spin-dependent dipole excitation in alkali–metal nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 80(11), 115416 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.115416
J. Zamanian, M. Marklund, G. Brodin, Scalar quantum kinetic theory for spin-1/2 particles: mean field theory. New J. Phys. 12(4), 043019 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/12/4/043019
J. Zamanian, M. Stefan, M. Marklund, G. Brodin, From extended phase space dynamics to fluid theory. Phys. Plasmas 17(10), 102109 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3496053
D.F. Zaretsky, P.A. Korneev, S.V. Popruzhenko, W. Becker, Landau damping in thin films irradiated by a strong laser field. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 37(24), 4817–4830 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/37/24/008
W.H. Zurek, Decoherence, einselection, and the quantum origins of the classical. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 715–775 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.75.715
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manfredi, G., Hervieux, PA. & Hurst, J. Phase-space modeling of solid-state plasmas. Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 3, 13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41614-019-0034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41614-019-0034-0