Abstract
Introduction
THick Gaseous Electron Multiplier (THGEM) has many advantages while the moderate position resolution is regarded as the main inferiority comparing with the traditional GEM, so this limits the applications of THGEM, such as X-ray imaging and charge particle tracking.
Materials and methods
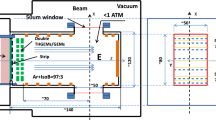
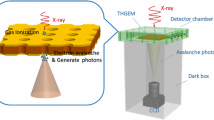
By improving the production techniques, THGEMs with smaller pitch and hole diameter can be made, i.e., 0.4 and 0.15 mm by mechanical drilling, and 0.3 and 0.1 mm by laser etching, respectively. Based on the new THGEMs, a two-dimensional imaging detector with 50\(\times \)50mm sensitive area was developed for 0.1 \(\sim \) 50 MeV low-energy electrons detection and reaching better than 100\(\upmu \)m position resolution (sigma). At the same time, a set of front-end electronics was developed based on homemade ASIC chips, i.e., Charge Amplifier and Shaping Amplifier for GEM (CASAGEM), and applied successfully to the detector.
Conclusion
The X-ray and beam tests results indicate that both detector and Front End Electronics (FEE) worked well, and the position resolution achieved 74.9\(\upmu \)m by using the charge center-of-gravity method. This indicates that the high-position resolution THGEM is promising for imaging and tracking application.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Breskin et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 598, 107–111 (2009)
M. Cortesi et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 572, 175–176 (2007)
C. Shalem et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 558, 475–489 (2006)
A. Breskin et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 623, 132–134 (2010)
Z. Ai-Wu et al., Chin. Phys. C 36(2), 142–145 (2012)
Y. Xie et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 729, 809–815 (2013)
X. Zhang, S. Niu, Y. Xie et.al., JINST 10 P10043 (2015)
H.B. Liu et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 659, 237–241 (2011)
Y. Lei et al., Chin. Phys. C 39(5), 64–68 (2015)
H.E. Li et al., Chin. Phys. C 38(10), 106101 (2014)
A. Zhang et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 722, 43–48 (2013)
H. Daojin et al., Chin. Phys. C 39(9), 096002 (2015)
L.V. Xin-Yu et al., Chin. Phys. C 36(3), 228–234 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work is a part of the development of Linear Electron Accelerator Test Beam Facility newly built in IHEP. This work is supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (11205173, 11305190) and in part by the State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics (H9294206TD). We acknowledge the support and cooperation of Huizhou King Brother circuit technology Co., LTD (KBC) and the CASGEM group of Tsinghua University. We thank the members of the Beijing Test Beam Facility (BTBF) and Physics Department of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS) for their help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Xie, YG., Yan, WQ. et al. Development and study of an imaging detector based on high-position resolution THGEM. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 1, 6 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-017-0009-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-017-0009-z