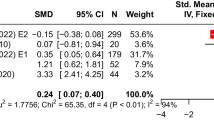
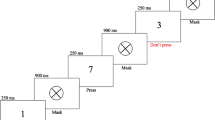
Abstract
Mind wandering refers to the process of generating thoughts unassociated with the task at hand or surrounding environment. Previous studies indicate that persistent mind wandering often contributes to negative mood states. Thus, a neuromodulatory technique enabling a reduction in the propensity to mind wander would be desirable. Binaural and monaural beat stimulation is a novel, non-invasive brain stimulation method which has been shown to modify brain activity in regions supposedly involved in mind wandering. In the current study, 40 participants performed a variant of a sustained attention to response task with embedded experience sampling probes, to identify episodes of mind wandering and to assess meta-awareness. During the execution of the task, participants were exposed to binaural and monaural beats at 5 Hz and 40 Hz, in addition to two control conditions (silence (no sound, headphones-only) and pure sine wave at 440 Hz). In the overall group and across all stimulation conditions, we observed no statistically significant modulation of mind wandering. However, a median-split of the data into two subgroups defined by high versus low mind wandering during silence, revealed an effect of stimulation on mind wandering across all conditions in the high mind wandering subgroup, as well as a significantly reduced propensity to mind wander during 5 Hz monaural beats vs. silence. Levels of meta-awareness were unaffected by the stimulation. These findings tentatively suggest that application of auditory beat stimulation may lead to a reduction in levels of mind wandering in subjects who show a greater tendency towards mind wandering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AI-Therapy, Statistics for Psychologists, Sample size calculator [WWW Document] (2019). URL https://www.ai-therapy.com/psychology-statistics/sample-size-calculator (accessed 5.3.19).
Axelrod, V., Rees, G., Lavidor, M., & Bar, M. (2015). Increasing propensity to mind-wander with transcranial direct current stimulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, 3314–3319. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1421435112.
Axelrod, V., Zhu, X., & Qiu, J. (2018). Transcranial stimulation of the frontal lobes increases propensity of mind-wandering without changing meta-awareness. Scientific Reports, 8, 15975. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34098-z.
Baird, B., Smallwood, J., Mrazek, M. D., Kam, J. W. Y., Franklin, M. S., & Schooler, J. W. (2012). Inspired by distraction: Mind wandering facilitates creative incubation. Psychological Science, 23, 1117–1122. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797612446024.
Becher, A.-K., Höhne, M., Axmacher, N., Chaieb, L., Elger, C. E., & Fell, J. (2015). Intracranial electroencephalography power and phase synchronization changes during monaural and binaural beat stimulation. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 41, 254–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12760.
Bertossi, E., Peccenini, L., Solmi, A., Avenanti, A., & Ciaramelli, E. (2017). Transcranial direct current stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex dampens mind-wandering in men. Scientific Reports, 7, 16962. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17267-4.
Boayue, N. M., Csifcsák, G., Aslaksen, P., Turi, Z., Antal, A., Groot, J., Hawkins, G. E., Forstmann, B., Opitz, A., Thielscher, A., & Mittner, M. (2019). Increasing propensity to mind-wander by transcranial direct current stimulation? A registered report. The European Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14347.
Chaieb, L., & Fell, J. (2017). Binaural beat stimulation. In L. Colzato (Ed.), Theory-driven approaches to cognitive enhancement (pp. 167–181). Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57505-6_12.
Chaieb, L., Wilpert, E. C., Hoppe, C., Axmacher, N., & Fell, J. (2017). The impact of monaural beat stimulation on anxiety and cognition. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 251. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00251.
Christoff, K., Gordon, A. M., Smallwood, J., Smith, R., & Schooler, J. W. (2009). Experience sampling during fMRI reveals default network and executive system contributions to mind wandering. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 8719–8724. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900234106.
Christoff, K., Irving, Z. C., Fox, K. C. R., Spreng, R. N., & Andrews-Hanna, J. R. (2016). Mind-wandering as spontaneous thought: A dynamic framework. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 17, 718–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.113.
Colzato, L. S., Barone, H., Sellaro, R., & Hommel, B. (2017a). More attentional focusing through binaural beats: Evidence from the global-local task. Psychological Research, 81, 271–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-015-0727-0.
Colzato, L. S., Steenbergen, L., & Sellaro, R. (2017b). The effect of gamma-enhancing binaural beats on the control of feature bindings. Experimental Brain Research, 235, 2125–2131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-4957-9.
Derner, M., Chaieb, L., Surges, R., Staresina, B. P., & Fell, J. (2018). Modulation of item and source memory by auditory beat stimulation: A pilot study with intracranial EEG. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 500. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00500.
Ellamil, M., Fox, K. C. R., Dixon, M. L., Pritchard, S., Todd, R. M., Thompson, E., & Christoff, K. (2016). Dynamics of neural recruitment surrounding the spontaneous arising of thoughts in experienced mindfulness practitioners. Neuroimage, 136, 186–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.04.034.
Ezzyat, Y., Kragel, J. E., Burke, J. F., Levy, D. F., Lyalenko, A., Wanda, P., O’Sullivan, L., Hurley, K. B., Busygin, S., Pedisich, I., Sperling, M. R., Worrell, G. A., Kucewicz, M. T., Davis, K. A., Lucas, T. H., Inman, C. S., Lega, B. C., Jobst, B. C., Sheth, S. A., Zaghloul, K., Jutras, M. J., Stein, J. M., Das, S. R., Gorniak, R., Rizzuto, D. S., & Kahana, M. J. (2017). Direct brain stimulation modulates encoding states and memory performance in humans. Current Biology, 27, 1251–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.028.
Fell, J. (2018). Is the hippocampus a potential target for the modulation of mind wandering in major depression? Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9, 363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00363.
Fox, K. C. R., & Christoff, K. (2015). Transcranial direct current stimulation to lateral prefrontal cortex could increase meta-awareness of mind wandering. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, E2414. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504686112.
Garcia-Argibay, M., Santed, M. A., & Reales, J. M. (2018). Efficacy of binaural auditory beats in cognition, anxiety, and pain perception: A meta-analysis. Psychological Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-018-1066-8.
Hoffmann, F., Banzhaf, C., Kanske, P., Bermpohl, F., & Singer, T. (2016). Where the depressed mind wanders: Self-generated thought patterns as assessed through experience sampling as a state marker of depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 198, 127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.03.005.
Isik, B. K., Esen, A., Büyükerkmen, B., Kilinç, A., & Menziletoglu, D. (2017). Effectiveness of binaural beats in reducing preoperative dental anxiety. The British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, 55, 571–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2017.02.014.
Kajimura, S., & Nomura, M. (2015). Decreasing propensity to mind-wander with transcranial direct current stimulation. Neuropsychologia, 75, 533–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.07.013.
Kajimura, S., Kochiyama, T., Nakai, R., Abe, N., & Nomura, M. (2016). Causal relationship between effective connectivity within the default mode network and mind-wandering regulation and facilitation. Neuroimage, 133, 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.03.009.
Kajimura, S., Kochiyama, T., Abe, N., & Nomura, M. (2018). Challenge to unity: Relationship between hemispheric asymmetry of the default mode network and mind wandering. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy086.
Killingsworth, M. A., & Gilbert, D. T. (2010). A wandering mind is an unhappy mind. Science, 330, 932. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1192439.
Kirk, U., Wieghorst, A., Nielsen, C. M., & Staiano, W. (2018). On-the-spot binaural beats and mindfulness reduces behavioral markers of mind wandering. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-018-0114-z.
Leszczynski, M., Chaieb, L., Reber, T. P., Derner, M., Axmacher, N., & Fell, J. (2017). Mind wandering simultaneously prolongs reactions and promotes creative incubation. Scientific Reports, 7, 10197. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10616-3.
Marchetti, I., Koster, E. H. W., Klinger, E., & Alloy, L. B. (2016). Spontaneous thought and vulnerability to mood disorders: The dark side of the wandering mind. Clinical Psychological Science: A Journal of the Association for Psychological Science, 4, 835–857. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702615622383.
McCormick, C., Rosenthal, C. R., Miller, T. D., & Maguire, E. A. (2018). Mind-wandering in people with hippocampal damage. The Journal of Neuroscience, 38, 2745–2754. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1812-17.2018.
Medea, B., Karapanagiotidis, T., Konishi, M., Ottaviani, C., Margulies, D., Bernasconi, A., Bernasconi, N., Bernhardt, B. C., Jefferies, E., & Smallwood, J. (2018). How do we decide what to do? Resting-state connectivity patterns and components of self-generated thought linked to the development of more concrete personal goals. Experimental Brain Research, 236, 2469–2481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-016-4729-y.
Mooneyham, B. W., & Schooler, J. W. (2013). The costs and benefits of mind-wandering: A review. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology, 67, 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031569.
Mrazek, M. D., Phillips, D. T., Franklin, M. S., Broadway, J. M., & Schooler, J. W. (2013). Young and restless: Validation of the Mind-Wandering Questionnaire (MWQ) reveals disruptive impact of mind-wandering for youth. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 560. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00560.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2000). The role of rumination in depressive disorders and mixed anxiety/depressive symptoms. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109, 504–511.
Padmanabhan, R., Hildreth, A. J., & Laws, D. (2005). A prospective, randomised, controlled study examining binaural beat audio and pre-operative anxiety in patients undergoing general anaesthesia for day case surgery. Anaesthesia, 60, 874–877. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2005.04287.x.
Robertson, I. H., Manly, T., Andrade, J., Baddeley, B. T., & Yiend, J. (1997). “Oops!”: Performance correlates of everyday attentional failures in traumatic brain injured and normal subjects. Neuropsychologia, 35, 747–758.
Ruby, F. J. M., Smallwood, J., Sackur, J., & Singer, T. (2013). Is self-generated thought a means of social problem solving? Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 962. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00962.
Schooler, J. W., Smallwood, J., Christoff, K., Handy, T. C., Reichle, E. D., & Sayette, M. A. (2011). Meta-awareness, perceptual decoupling and the wandering mind. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15, 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.05.006.
Scouarnec, L., Poirier, R. M., Owens, J. E., Gauthier, J., Taylor, A. G., & Foresman, P. A. (2001). Use of binaural beat tapes for treatment of anxiety: A pilot study of tape preference and outcomes. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, 7, 58–63.
Seli, P., Risko, E. F., Smilek, D., & Schacter, D. L. (2016). Mind-wandering with and without intention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20, 605–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2016.05.010.
Seli, P., Beaty, R. E., Cheyne, J. A., Smilek, D., Oakman, J., & Schacter, D. L. (2018a). How pervasive is mind wandering, really? Consciousness and Cognition, 66, 74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2018.10.002.
Seli, P., Kane, M. J., Smallwood, J., Schacter, D. L., Maillet, D., Schooler, J. W., & Smilek, D. (2018b). Mind-wandering as a natural kind: A family-resemblances view. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 22, 479–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2018.03.010.
Smallwood, J., & Schooler, J. W. (2015). The science of mind wandering: Empirically navigating the stream of consciousness. Annual Review of Psychology, 66, 487–518. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015331.
Smallwood, J., McSpadden, M., & Schooler, J. W. (2007). The lights are on but no one’s home: Meta-awareness and the decoupling of attention when the mind wanders. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 14, 527–533.
Smallwood, J., Fitzgerald, A., Miles, L. K., & Phillips, L. H. (2009). Shifting moods, wandering minds: Negative moods lead the mind to wander. Emotion, 9, 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014855.
Weiland, T. J., Jelinek, G. A., Macarow, K. E., Samartzis, P., Brown, D. M., Grierson, E. M., & Winter, C. (2011). Original sound compositions reduce anxiety in emergency department patients: A randomised controlled trial. The Medical Journal of Australia, 195, 694–698.
Wernick, J. S., & Starr, A. (1968). Binaural interaction in the superior olivary complex of the cat: An analysis of field potentials evoked by binaural-beat stimuli. Journal of Neurophysiology, 31, 428–441. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.428.
Wiwatwongwana, D., Vichitvejpaisal, P., Thaikruea, L., Klaphajone, J., Tantong, A., Wiwatwongwana, A., & Medscape. (2016). The effect of music with and without binaural beat audio on operative anxiety in patients undergoing cataract surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Eye (London, England), 30, 1407–1414. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.160.
Zedelius, C. M., & Schooler, J. W. (2015). Mind wandering “Ahas” versus mindful reasoning: Alternative routes to creative solutions. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 834. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00834.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Roy Cox and Dr. Christian Hoppe for their helpful comments regarding the statistical analysis, and Dr. Thomas Reber for his insightful comments regarding the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study and all experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty of the University of Bonn and were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Data Availability Statement
All data and accompanying analyses are archived at the Department of Epileptology, University of Bonn, Germany. Data and analyses can be made available upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaieb, L., Derner, M., Leszczyński, M. et al. Modulation of Mind Wandering Using Auditory Beat Stimulation: a Pilot Study. J Cogn Enhanc 4, 40–48 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-019-00137-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-019-00137-4