Abstract
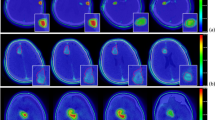
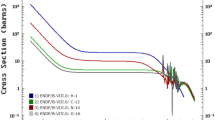
A method based on the cross-sectional relationship between 10B(n, α)7Li and 1H(n, γ)2H was proposed to detect and reconstruct the three-dimensional boron concentration/dose distribution in vivo during boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Factors such as the neutron energy, fluence rate, and degree of non-uniform distribution of the boron concentration in a voxel may affect the results of this method. A theoretical analysis of the accuracy of the method using a Monte Carlo simulation shows that the determining error is generally less than 1% under different tumor locations and neutron source configurations. When the voxel size is larger than 0.4 cm, the determining error might be higher for a non-uniformly distributed boron concentration in the voxel because of the changes in the neutron energy and fluence rate. In conclusion, the proposed method enables an accurate three-dimensional boron determination in vivo during BNCT.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Wittig, J. Michel, R.L. Moss et al., Boron analysis and boron imaging in biological materials for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 68, 66–90 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2008.03.004
R.L. Moss, Critical review, with an optimistic outlook, on boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 88, 2–11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.11.109
S. Hang, X.B. Tang, D.Y. Shu et al., Monte Carlo study of the beam shaping assembly optimization for providing high epithermal neutron flux for BNCT based on D-T neutron generator. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 310, 1289–1298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-5001-4
M. Peng, G.Z. He, Q.W. Zhang et al., Study of neutron production and moderation for sulfur neutron capture therapy. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 30, 2 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-018-0529-3
Y. Gong, X.C. Guan, Q. Wang et al., Design of moderator for boron neutron capture therapy based on D-D neutron source. Nucl. Tech. 43, 090303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11889/j.0253-3219.2020.hjs.43.090303(in Chinese)
G.J. Chen, J.Y. Yang, G. Lu et al., One stone kills three birds: novel boron-containing vesicles for potential BNCT, controlled drug release, and diagnostic imaging. J. Mol. Pharm. 11, 3291–3299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/mp400641u
T. Yamamoto, A. Matsumura, K. Nakai et al., Current clinical results of the Tsukuba BNCT trial. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 61, 1089–1093 (2004)
S.J. González, M.R. Bonomi, G.A. Santa et al., First BNCT treatment of a skin melanoma in Argentina: dosimetric analysis and clinical outcome. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 61, 1101–1105 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2004.05.060
E. Shimosegawa, K. Isohashi, S. Naka et al., Assessment of 10 B concentration in boron neutron capture therapy: potential of image-guided therapy using 18 FBPA PET. Ann. Nucl. Med. 30, 749–755 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149.016.1121.8
T. Watabe, K. Hanaoka, S. Naka et al., Practical calculation method to estimate the absolute boron concentration in tissues using 18 F-FBPA PET. Ann. Nucl. Med. 31, 481–485 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149.017.1172.5
T. Aihara, J. Hiratsuka, N. Morita et al., First clinical case of boron neutron capture therapy for head and neck malignancies using 18 F-BPA PET. Head Neck J. Sci. Spec. Head Neck 28, 850–855 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20418
S. Fatemi, C.H. Gong, S. Bortolussi et al., Innovative 3D sensitive CdZnTe solid state detector for dose monitoring in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Nucl. Instrum Methods Phys. Res. Sect A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 936, 50–51 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2018.09.135
I. Murata, S. Nakamura, M. Manabe et al., Characterization measurement of a thick CdTe detector for BNCT-SPECT–Detection efficiency and energy resolution. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 88, 129–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2014.01.023
X.L. Shen, P. Gong, X.B. Tang et al., Encoding methods matching the 16×16 pixel CZT detector of a coded aperture gamma camera. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 31, 92 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-020-00796-5
I. Murata, T. Mukai, S. Nakamura et al., Development of a thick CdTe detector for BNCT-SPECT. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 69, 1706–1709 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.05.014
S. Fatemi, S. Altieri, S. Bortolussi et al., Preliminary characterization of a CdZnTe photon detector for BNCT-SPECT. . Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 903, 134–139 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2018.06.068
D.M. Minsky, A. Valda, A.J. Kreiner et al., Progress in the development of a tomographic SPECT system for online dosimetry in BNCT. AIP Conf. Proc. 1265, 415–418 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3480218
D.M. Minsky, A.A. Valda, A.J. Kreiner et al., Experimental feasibility studies on a SPECT tomograph for BNCT dosimetry. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 67, 179–182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2009.03.044
M. Kim, B.H. Hong, I. Cho et al., Design of a scintillator-based prompt gamma camera for boron-neutron capture therapy: comparison of SrI2 and GAGG using Monte-Carlo simulation. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 53, 626–636 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2020.07.010
B. Hales, T. Katabuchi, M. Igashira et al., Predicted performance of a PG-SPECT system using CZT primary detectors and secondary Compton-suppression anti-coincidence detectors under near-clinical settings for boron neutron capture therapy. Nucl. Instrum Methods Phys. Res. Sect A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 875, 1–56 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.09.009
C.H. Gong, X.B. Tang, S. Fatemi et al., A Monte Carlo study of SPECT in boron neutron capture therapy for a heterogeneous human phantom. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 16, 33–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.ijrr.16.1.33
M. Patino, A. Prochowski, M.D. Agrawal et al., Material separation using dual-energy CT: current and emerging applications. Radiographics 36, 1087–1105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2016150220
M. Yang, G. Virshup, J. Clayton et al., Theoretical variance analysis of single-and dual-energy computed tomography methods for calculating proton stopping power ratios of biological tissues. Phys. Med. Biol. 55, 1343–1362 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/55/5/006
C.R. Geng, Y. Ai, X.B. Tang et al., Quantum dots enhanced Cerenkov luminescence imaging. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 30, 71 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-019-0599-x
X.D. Zhang, Y.H. Liu, X.B. Tang et al., Strategies for accurate response assessment of radiochromic film using flatbed scanner for beam quality assurance. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 30, 160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-019-0685-0
J.P. He, X.B. Tang, P. Gong et al., Spectrometry analysis based on approximation coefficients and deep belief networks. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 29, 69 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-018-0402-4
G. Chiba, K. Okumura, K. Sugino et al., JENDL-4.0 benchmarking for fission reactor applications. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 48, 172–187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/18811248.2011.9711692
K. Shibata, O. Iwamoto, T. Nakagawa et al., JENDL-4.0: a new library for nuclear science and engineering. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 48, 1–30 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/18811248.2011.9711675
J. Perl, J. Shin, J. Schümann et al., TOPAS: an innovative proton Monte Carlo platform for research and clinical applications. Med. Phys. 39, 6818–6837 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4758060
J. Allison, K. Amako, J.E. Apostolakis et al., Geant4 developments and applications. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53, 270–278 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2006.869826
S. Agostinelli, J. Allison, K. Amako et al., GEANT4—a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 506, 250–303 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9002(03)01368-8
C.R. Geng, X.B. Tang, F.D. Guan et al., GEANT4 calculations of neutron dose in radiation protection using a homogeneous phantom and a Chinese hybrid male phantom. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 168, 433–440 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncv364
S.J. Wu, C.R. Geng, X.B. Tang et al., Dosimetric impact of respiratory motion during boron neutron capture therapy for lung cancer. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108527
X.X. Zhang, C.R. Geng, X.B. Tang et al., Assessment of long-term risks of secondary cancer in pediatric patients with brain tumor after boron neutron capture therapy. J. Radiol. Prot. 39, 838–853 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6498/ab29a3
D.R. White, R.V. Griffith, I.J. Wilson (1992) Report 46. J. Int. Comm. Radiat. Units Meas. 28:NP–NP
W.S. Kiger, S. Sakamoto, O.K. Harling, Neutronic design of a fission converter-based epithermal neutron beam for neutron capture therapy. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 131, 1–22 (1999). https://doi.org/10.13182/NSE99-A2015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Feng Tian, Chang-Ran Geng, and Xiao-Bin Tang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Feng Tian and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11805100 and 11905106) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. NG2020003).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, F., Geng, CR., Tang, XB. et al. Analysis of influencing factors on the method for determining boron concentration and dose through dual prompt gamma detection . NUCL SCI TECH 32, 35 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-021-00873-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-021-00873-3