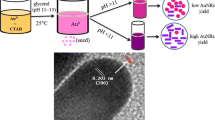
Abstract
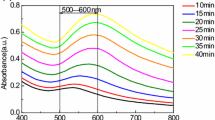
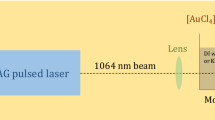
Colloidal gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have attracted more and more attention in areas of materials science, biotechnology and organic chemistry due to their unique functions as molecular markers and their applications in diagnostic imaging and catalysis. The AuNP synthesis approaches have been well developed; however, the solvent effects have not been systematically studied yet. Here we analyzed and compared solvent effects on AuNP formation using UV irradiation of Au(III) without adding any other ligands. By monitoring the surface plasmon resonance absorption of Au(III)-containing solutions, results showed that both ketone and alcohol solvents can induce Au(III) to form gold nanospheres; on the other hand, solvents like ACN and THF can induce Au(III) to form nanostructures with longer dimensions. The possible mechanism was discussed, which could facilitate efficient photochemical synthesis of AuNPs and might apply to other metal NP synthesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Sperling, P. Rivera gil, F. Zhang et al., Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 9, 1896–1908 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/B712170a
F. Zhang, E. Lees, F. Amin et al., Polymer-coated nanoparticles: a universal tool for biolabelling experiments. Small 22, 3113–3127 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201100608
M.L. Marin, K.L. McGilvray, J.C. Scaiano, Photochemical Strategies for the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Au(III) and Au(I) Using Photoinduced Free Radical Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 49, 16572–16584 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja803490n
S. Eustis, H.-Y. Hsu, M.A. El-Sayed, Gold nanoparticle formation from photochemical reduction of Au3+ by continuous excitation in colloidal solutions. A proposed molecular mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 11, 4811–4815 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0441588
K.L. McGilvray, C. Fasciani, C.J. Bueno-Alejo et al., Photochemical strategies for the seed-mediated growth of gold and gold–silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 46, 16148–16155 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/la302814v
C. Zhao, S. Qu, J. Qiu et al., Photoinduced formation of colloidal Au by a near-infrared femtosecond laser. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1710–1714 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0235
K. Kurihara, J. Kizling, P. Stenius et al., Laser and pulse radiolytically induced colloidal gold formation in water and in water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 9, 2574–2579 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00347a011
K. Malone, S. Weaver, D. Taylor et al., Formation kinetics of small gold crystallites in photoresponsive polymer gels. J. Phys. Chem. B 30, 7422–7431 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp020176i
J.M. Zhu, Y.H. Shen, A.J. Xie et al., Photoinduced synthesis of anisotropic gold nanoparticles in room-temperature ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. C 21, 7629–7633 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0711850
H. Qian, Y. Zhu, R. Jin, Size-focusing synthesis, optical and electrochemical properties of monodisperse Au38(SC2H4Ph)24 nanoclusters. ACS Nano 11, 3795–3803 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn901137h
S. Helmi, C. Ziegler, D.J. Kauert et al., Shape-controlled synthesis of gold nanostructures using DNA origami molds. Nano Lett. 11, 6693–6698 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl503441v
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the Program Funded by University for Fostering Distinguished Young Scholars, National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51763019, U1832125), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2018M630937), Inner Mongolia Grassland Talent, Distinguished Young Scholars of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, and Yong Scientist Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, M., Li, YB., Guo, J. et al. Solvent effects on gold nanoparticle formation from photochemical reduction of Au(III) by UV irradiation. NUCL SCI TECH 29, 158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-018-0505-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-018-0505-y