Abstract
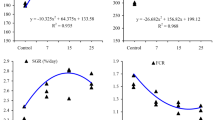
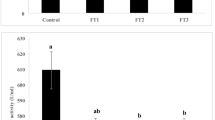
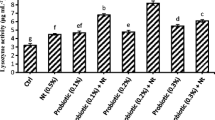
The aim of this study is to evaluate the effects of potassium diformate (KDF) and butyric acid (BA), both separately and in combination, on the growth performance, biochemical parameters, innate immune system, and digestive enzyme activity of Beluga (Huso huso). Fish (average weight of 28.39 ± 1.82 g) were divided into seven groups, each receiving a different diet: control, 2 g/kg− 1 KDF, 5 g/kg− 1 KDF, 10 g/kg− 1 KDF, 2 g/kg− 1 BA, 5 g/kg− 1 BA, 10 g/kg− 1 BA, and 5 g/kg− 1 KDF + 5 g/kg− 1 BA. The fish were fed twice daily at a rate of 2% of their biomass and water parameters were monitored throughout the experiment. At the end of the experiment, 45 fish (6 from each treatment diet) were euthanized, and their weight and blood samples were collected for analysis. The study revealed improved growth performance parameters in Beluga fish fed diets containing KDF and BA, either separately or together. However, there was a significant decrease in Specific Growth Rate (SGR) compared to the control group (P < 0.05).The KDF and BA supplements significantly reduced levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzymes, and increased serum total protein, globulin, albumin, lysozyme enzyme activity, and alternative complement pathway activity. Incorporating KDF and BA supplements also led to a notable increase in digestive enzyme activities (protease, trypsin, chymotrypsin, lipase, and alpha amylase), with the highest levels seen in the KDF 10 and KDF + BA groups (P < 0.05). These findings suggest that diets containing KDF and a combination of KDF and BA have a beneficial effect on the growth, metabolism, and immunity of Beluga fish. The study suggests that the incorporation of a combination of KDF and BA into the diet of Beluga fish can result in improved growth and enhanced immune system.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aalamifar H, Soltanian S, Vazirizadeh A, Akhlaghi M, Morshedi V, Gholamhosseini A, Torfi Mozanzadeh M (2020) Dietary butyric acid improved growth, digestive enzyme activities and humoral immune parameters in Barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Aquacult Nutr 26:156–164
Abdel-Tawwab M, Khattaby ARA, Monier MN (2019) Dietary acidifiers blend enhanced the production of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), striped mullet (Mugil cephalus), and African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) polycultured in earthen ponds. Aquacult Int 27:369–379
Aliko V, Qirjo M, Sula E, Morina V, Faggio C (2018) Antioxidant defense system, immune response and erythron profile modulation in gold fish, Carassius auratus, after acute manganese treatment. Fish Shellfish Immunol 76:101–109
Anuta JD, Buentello A, Patnaik S, Lawrence AL, Mustafa A, Hume ME, Gatlin DM, Kemp MC (2011) Effect of dietary supplementation of acidic calcium sulfate (Vitoxal) on growth, survival, immune response and gut microbiota of the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J World Aquaculture Society 42:834–844
Baruah K, Pal AK, Sahu NP, Jain KK, Mukherjee SC, Debnath D (2005) Dietary protein level, microbial phytase, citric acid and their interactions on bone mineralization of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) juveniles. Aquac Res 36:803–812
Biller-Takahashi JD, Takahashi LS, Marzocchi-Machado CM, Sabbadin Zanuzzo F, Sabioni RE, Urbinati EC (2012) Hemolytic activity of alternative complement pathway as an indicator of innate immunity in pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus). Revi Brasi De Zoot 41:237–241
Castillo S et al (2014) Effects of organic acids on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of juvenile red drum Sciaenops ocellatus. Aquaculture 433:6–12
da Silva BC, Nascimento Vieira F, Mouriño JLP, Ferreira GS, Seiffert WQ (2013) Salts of organic acids selection by multiple characteristics for marine shrimp nutrition. Aquaculture 384:104–110
Hassaan MS, Mohammady EY, Adnan M, Abd Elnabi A, Ayman HE, Soltan MF, El-Haroun MA ER (2020a) Effect of dietary protease at different levels of malic acid on growth, digestive enzymes and haemato-immunological responses of Nile tilapia, fed fish meal free diets. Aquaculture 522:735124
Hassaan MS, El-Sayed AMI, Mohammady EY, Zaki MAA, Elkhyat MM, Jarmołowicz S, El-Haroun ER (2020b) Eubiotic effect of a dietary potassium diformate (KDF) and probiotic (Lactobacillus acidophilus) on growth, hemato-biochemical indices, antioxidant status and intestinal functional topography of cultured Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fed diet free fishmeal. Aquaculture 533:736147
Hoseini SM, Yousefi M, Afzali-Kordmahalleh A, Pagheh E, Mirghaed A (2023) Effects of dietary lactic acid supplementation on the activity of digestive and antioxidant enzymes, gene expressions, and bacterial communities in the intestine of common carp. Cyprinus carpio Animals 13(12):1934
Hoseinifar SH, Zoheiri F, Caipang CM (2016) Dietary sodium propionate improved performance, mucosal and humoral immune responses in Caspian white fish (Rutilus frisii Kutum) fry. Fish Shellfish Immunol 55:523–528
Hoseinifar SH, Sun YZ, Caipang CM (2017) Short-chain fatty acids as feed supplements for sustainable aquaculture: an updated view. Aquac Res 48:1380–1391
Jedi Mostafaloo A, Hedayatifard M, Keshavarz M, Mohammadian T (2021) Effects of different levels of Sodium diformate and formic acid salt on growth performance, digestive enzymes, and innate immunological parameters of Beluga (Huso huso) juveniles. IJFS 20:879–900
Kharat TL, Rokade KB, Shejule KB (2020) Effect of Roundup 41% (glyphosate) on blood serum biochemical parameters of freshwater fish, Rasbora daniconius. Environ Biology 41:222–227
Knudsen KEB, Serena A, Canibe N, Juntunen KS (2003) New insight into butyrate metabolism. Proc of the Nutr Soc 62:81–86
Liebert F, Mohamed K, Lückstädt C (2010) Effects of diformates on growth and feed utilization of all male Nile Tilapia fingerlings (Oreochromis niloticus) reared in tank culture. XIV International symposium on fish nutrition and feeding, Qingdao, China, Book of Abstracts, 2010, pp. 190
Lückstädts C (2006) Acidifiers in aquaculture prove beneficial. Feed Mix 14:11–12
Mirghaed AT, Yarahmadi P, Soltani M, Paknejad H, Hoseini SM (2019) Dietary sodium butyrate (Butirex® C4) supplementation modulates intestinal transcriptomic responses and augments Disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol 92:621–628
Mohammadi G, Hafezieh M, Karimi AA, Azra MN, Doan HV, Tapingkae W, Abdelrahman HA, Dawood MAO (2022) The synergistic effects of plant polysaccharide and Pediococcus acidilactici as a synbiotic additive on growth, antioxidant status, immune response, and resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 120:304–313
Mohtashemipour H, Mohammadian T, Mesbah M, Rezaie A, Torfi Mozanzadeh M (2023) Acidifier supplementation in low-fish meal diets improved growth performance and health indices in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) juveniles. Aquaculture Rep 29:101502
Naderi Farsani M, Bahrami Gorji S, Hoseinifar SH, Rashidian G, Doan HV (2020) Combined and singular effects of dietary PrimaLac® and potassium diformate (KDF) on growth performance and some physiological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12:236–245
Ng WK, Koh CB, Sudesh K, Siti-Zahrah A (2009) Effects of dietary organic acids on growth, nutrient digestibility and gut microflora of red hybrid tilapia, Oreochromis sp., and subsequent survival during a challenge test with Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquac Res 40:1490–1500
Öner M, Atli G, Canli M (2008) Changes in serum biochemical parameters of freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus following prolonged metal (ag, cd, cr, Cu, Zn) exposures. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:360–366
Parveen S (2017) Effect of tannery waste water on lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme activity of fresh water fish, Channa punctatus. Entomol Zool Stud 5:643–647
Pelusio NF, Rossi B, Parma L, Volpe E, Ciulli S, Piva A, Amico F, Scicchitano D, Candela M, Gatta PP, Bonaldo A, Grilli E (2020) Effects of increasing dietary level of organic acids and nature-identical compounds on growth, intestinal cytokine gene expression and gut microbiota of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) reared at normal and high temperature. Fish Shellfish Immunol 107:324–335
Reda RM, Mahmoud R, Selim KM, El-Araby IE (2016) Effects of dietary acidifiers on growth, hematology, immune response and Disease resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 50:255–262
Rimoldi S, Gliozheni E, Ascione C, Gini E, Terova G (2018) Effect of a specific composition of short-and medium-chain fatty acid 1-Monoglycerides on growth performances and gut microbiota of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). PeerJ 6:e5355
Romano N, Koh CB, Ng W (2015) Dietary microencapsulated organic acids blend enhances growth, phosphorus utilization, immune response, hepatopancreatic integrity and resistance against Vibrio harveyi in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 435:228–236
Ross NW, Firth KJ, Wang A, Burka JF, Johnson SC (2000) Changes in hydrolytic enzyme activities of naive Atlantic salmon Salmo salar skin mucus due to Infection with the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis and cortisol implantation. Dis Aquat Organ 41:43–51
Sangari M, Sotoudeh E, Bagheri D, Morammazi S, Torfi Mozanzadeh M (2021) Growth, body composition, and hematology of yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus) given feeds supplemented with organic acid salts (sodium acetate and sodium propionate). Aquacult Int 29:261–273
Shamsaie Mehrgan M, Hosseini Shekarabi SP, Azari A, Yilmaz S, Luckstadt C, Rajabi Islami H (2022) Synergistic effects of sodium butyrate and sodium propionate on the growth performance, blood biochemistry, immunity, and immune-related gene expression of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Aquacult Int 30:3179–3193
Stankus A (2021) State of world aquaculture 2020 and regional reviews: FAO webinar series. FAO Aquaculture Newsletter. 17–18
Taherpour M, Roomiani L, Rajabi Islami H, Shamsaie Mehrgan M (2023) Effect of dietary butyric acid, Bacillus licheniformis (probiotic), and their combination on hemato-biochemical indices, antioxidant enzymes, immunological parameters, and growth performance of Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture Rep 30:101534
Tian L, Zhou X, Jiang W, Liu Y, Wu P, Jiang J, Kuang S, Tang L, Zhang Y, Xie F, Feng L (2017) Sodium butyrate improved intestinal immune function associated with NF-κB and p38MAPK signalling pathways in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol 66:548–563
Tran-Ngoc KT, Huynh ST, Sendao J, Nguyen TH, Roem AJ, Verreth JAJ, Schrama JW (2019) Environmental conditions alter the effect of organic acid salts on digestibility and intestinal morphology in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult Nutr 25:134–144
Xie S, Zhang L, Wang D (2003) Effects of several organic acids on the feeding behavior of Tilapia nilotica. Appl Ichthyol 19:255–257
Xun P, Zhou C, Huang X, Huang Z, Yu W, Yang Y, Li T, Huang J, Wu Y, Lin H (2022) Effects of dietary potassium diformate on growth performance, fillet quality, plasma indices, intestinal morphology and liver health of juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Aquaculture Rep 24:101110
Yousefi M, Abtahi B, Abedian Kenari A (2012) Hematological, serum biochemical parameters, and physiological responses to acute stress of Beluga sturgeon (Huso huso, Linnaeus 1785) juveniles fed dietary nucleotide. Comp Clin Pathol 21:1043–1048
Zahmatkesh A, Karimzadeh K, Faridnia M (2020) Effect of dietary selenium nanoparticles and chitosan oligosaccharide on biochemical parameters of Caspian Roach (Rutilus Caspicus) under malathion stress. Casp J Environ Sci 18:59–71
Zhou C, Lin H, Huang Z, Wang J, Yu W (2019) Effect of dietary sodium butyrate on growth performance, enzyme activities and intestinal proliferation-related gene expression of juvenile golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Aquacult Nutr 25:1261–1271
Zhu Y, Qiu X, Ding Q, Duan M, Wang C (2014) Combined effects of dietary phytase and organic acid on growth and phosphorus utilization of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquaculture 430:1–8
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The Corresponding author is Laleh Roomiani. The initial design of the research was carried out by Behnam Boroumand and Laleh Roomiani. The research was carried out by Laleh Roomiani and Behnam Boroumand. Mehran Javaheri Baboli helped in writing fish diet. Hadide Mabodi was involved in preparing figures and tables of paper. Mojdeh Chelemal Dezfulneghad contributed to the statistical section of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All handling of fish was carried out following the guidelines for control and supervision of experiments on animals by the Government of Iran and approved by Institutional Animal Ethics Committee.
Competing of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Boroumand, B., Roomiani, L., Baboli, M.J. et al. A Comparative Study on the Impact of Potassium Diformate and Butyric acid on Growth, Biochemistry, Innate Immunity, and Digestive Enzyme Activity in Huso huso. Thalassas 40, 183–191 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-023-00640-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-023-00640-8