Abstract
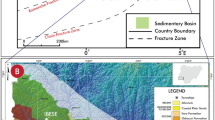
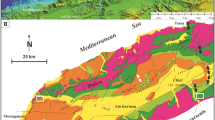
On the southeast Tunisian coast, organic-rich facies were formed at the middle Holocene in a confined Boujmel lagoon bottom (currently Sebkha Boujmel) during the last deglaciation. Sedimentological and organic geochemistry are used to analyze samples from respectively eight and three cores. The total organic carbon (TOC) and humic compounds analysis highlighted the setting of anoxia around 6800 years before present (BP) and its breakdown at about 4000 years BP. Biotic and abiotic anoxic proxies constitute waterproofing of a high degree of confinement occurring under water column stratification. The well-preserved organic-rich material of mixed origin (continental and marine) constitutes a biotic proxy and the abiotic ones are made of polyhalite and magnesian minerals that layer just above the euxinic facies close-fitting water column stratification. The TOC peak registered in the euxinic facies of the Sebkha Boujmel correlates with the highest Holocene sea level change during the transgression of the Mediterranean Sea. Such correlation and the time of the anoxic phase launch the relationship between the Mediterranean sapropel S1 and the euxinic facies of Sabkha Boujmel. It seems that anoxia began early around 9000 years BP in the deepest areas of the Mediterranean Sea and progressively reached its edges around 6000–7000 years BP, recording a diachronism in the installation of the organic-rich facies, which agrees with the marine intrusion highlighted in the Sebkha Boujmel.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert NL, Keiser WE, Szymanski HA (1970) Theory and practice of infrared spectroscopy. Plénum Press, New-York
Ariztegui D, Asioli A, Lowe JJ, Trincardi F, Vigliotti L, Tamburini F, Oldfield F (2000) Palaeoclimate and the formation of sapropel S1: inferences from Late Quaternary lacustrine and marine sequences in the central Mediterranean region. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol. 158(3–4):215–240
Bakrač K, Ilijanić N, Miko S, Hasan O (2015) Evidence of sapropel S1 formation from Holocene lacustrine sequences in Northern Dalmatia (Vrana Lake). In: 5. HRVATSKI GEOLOŠKI KONGRES međunarodnim sudjelovanjem/5th CROATIAN GEOLOGICAL CONGRESS with international participation. p 19–20
Bellamy LJ (1958) The infrared spectra of complex molecules, 2nd edn. Methuen and Co., Ltd., London
Betts JN, Holland HD (1991) The oxygen content of ocean bottom waters, the burial efficiency of organic carbon, and the regulation of atmospheric oxygen. Paleogeogr, Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 97:493
Bouloubassi I, Guehenneux G, Rullkötter J (1998) Biological marker significance of organic matter origin in sapropels from the Mediterranean Ridge, Site 9691. In: Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results Vol. 160. p 261–269
Brown JK (1955) The infrared spectra coals. J Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9550000744
Busson G, Perthuisot JP (1977) Intérêt de la Sebkha el Melah (Sud tunisien) pour l’interprétation des séries évaporitiques anciennes. Sediment Geol 2:139–164
Castañeda IS, Schefuß E, Pätzold J, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Weldeab S, Schouten S (2010) Millennial-scale sea surface temperature changes in the eastern Mediterranean (Nile River Delta region) over the last 27,000 years. Paleoceanography. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009PA001740
Cita MD, Vergnaud-Grazzini CC, Robert C, Chamley H, Ciaranfi N, d’Onofrio S (1977) Paleoclimatic record of a long deep sea core from the Eastern Mediterranean. Quat Res 8:205–235
Clarkson MO, Hennekam R, Sweere TC, Andersen MB, Reichart GJ, Vance D (2021) Carbonate associated uranium isotopes as a novel local redox indicator in oxidatively disturbed reducing sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 311:12–28
Demaison GJ, Moore GT (1980) Anoxic environments and oil source bed genesis. AAPG Bull 64:1179–1209
Espitalie J, Durand B, Roussel JC, Souron C (1973) Etude de la matière organique insoluble (kérogène) des argiles du Toarcien du Bassin de Paris II. Etude en spectroscopie infrarouge, en analyse thermique différentielle et en analyse thermogravimétrique. Rev. Inst. Français Pétrole, XXVIII.
Filippidi A, De Lange GJ (2019) Eastern Mediterranean deep water formation during sapropel S1: a reconstruction using geochemical records along a bathymetric transect in the Adriatic outflow region. Paleoceanogr Paleoclimatol 34(3):409–429
Filippidi A, Triantaphyllou MV, De Lange GJ (2016) Eastern-Mediterranean ventilation variability during sapropel S1 formation, evaluated at two sites influenced by deep-water formation from Adriatic and Aegean Seas. Quatern Sci Rev 144:95–106
Fontes JCh, Perthuisot JP (1971) Faciès minéralogiques et isotopiques des carbonates de la Sabkhael Melah (Zarzis, Tunisie): les variations du niveau de la Méditerranée orientale depuis 40.000ans. Revue et de Géographie Physique et de Géologie Dynamique(2). 4:299
Grazzini CV, Devaux M, Znaidi J (1986) Stable isotope “anomalies” in Mediterranean Pleistocene records. Mar Micropaleontol 10(1–3):35–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8398(86)90024-1
Hennekam R, Jilbert T, Schnetger B, de Lange GJ (2014) Solar forcing of Nile discharge and sapropel S1 formation in the early to middle Holocene eastern Mediterranean. Paleoceanography 29(5):343–356
Huc AY, Durand BM (1977) Occurrence and significance of humic acids in ancient sediments. Fuel 56:73–80
Huc AY, Durand, B, Monin JC (1978) Humic compounds and kerogens in core from Black Sea Sediments Legs 42 B, Sites 379 A, B and 380 A. U.S. Government Printing Office.
Lakhdar R (2009) Sédimentologie des dépôts holocènes et des tapis microbiens récents de la de Sebkha Boujmel et de ses environs (Sud-Est de la Tunisie): Faciès et paléoenvironnements Doctorat en sciences géologiques. Université de Sfax, Faculté des sciences de Sfax, p 207p
Lakhdar R, Soussi M, Ben Ismail MH, M’Rabet A (2006) A Mediterranean Holocene restricted coastal lagoon under arid climate: case of the sedimentary record of the Sabkha Boujmel (SE Tunisia). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 241:177–191
Lakhdar R, Talbi R, Soussi M, Jedoui Y, Jaouadi S, Anzidei M (2022) Sedimentary record from Holocene to present-day Southeastern Tunisia: facies, paleoenvironments and climate changes. Arab J Geosci. 15:954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09964-w
Lourens LJ, Hilgen FJ, Zachariasse WJ, Van Hoof AAM, Antonarakou A, Vergaud-Grazzini C (1996) Evaluation of the PlioPleistocene astronomical timescale. Paleoceanography 11:391–413
Matthews A, Azrieli-Tal I, Benkovitz A, Bar-Matthews M, Vance D, Poulton SW, Archer C (2017) Anoxic development of sapropel S1 in the Nile Fan inferred from redox sensitive proxies, Fe speciation, Fe and Mo isotopes. ChemicalGeology 475:24–39
Meyer KM, Kump LR (2008) Oceanic euxinia in Earth history: causes and consequences. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 36:251–288
Nijenhuis IA, Bosch HJ, Damsté JS, Brumsack HJ, De Lange GJ (1999) Organic matter and trace element rich sapropels and black shales: a geochemical comparison. Earth Planet Sci Lett 169(3–4):277–290
Olausson E (1991) A post-Cromerian rise in sea level. In: Weller G, Wilson CL, Severin BAB (Eds), International Conference on the Role of Polar Regions in Global Change: Proceedings of a Conference Held Jun 11–15, 1990 at the University of Alaska Fairbanks vol. II. Geophysical Inst. Univ. of Alaska Fairbanks. p 496–498
Paskoff R, Sanlaville P (1983) Les cotes de la Tunisie. Variations du niveau de la mer depuis le Tyrrhénien. Maison de l'Orient Méditerranéen, Lyon University. p 192
Pastouret L (1970) Étude sédimentologique et paléoclimatique de carottes prélevées en Méditerranée orientale. Tethys 2(1):227–266
Pavlovska M, Prekrasna I, Dykyi E, Zotov A, Dzhulai A, Frolova A, Stoica E (2021) Niche partitioning of bacterial communities along the stratified water column in the Black Sea. Microbiologyopen. 10(3):e1195
Pomar L (2020) Carbonate systems. Regional geology and tectonics. Elsevier, New York, pp 235–311
Purser BH (1980) Sédimentation et diagenèse des carbonates néritiques récents. Tome, vol. 1. Editions Technip, Paris. 366 pp. Geo-Eco-Trop, 2007. 31: 171–214
Reimer PJ, Baillie MGL, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck AJW, Blackwell PJ, Buck CE, Burr GS, Cutler KB, Damon PE, Edwards RL, Fairbanks RG, Friedrich M, Guilderson TP, Herring C, Hughen KA, Kromer B, Mccormac G, Manning S, Bronk Ramsey C, Reimer RW, Remmele S, Southon JR, Stuiver M, Talamo S, Taylor FW, Van Der Plicht J, Weyhenmeyer CE (2013) INTACAL04 terrestrial radiocarbon age calibration. Radiocarbon 46:1029–1058
Richards FA, Redfield AC (1954) A correlation between the oxygen content of seawater and the organic content of marine sediments. Deep Sea Res. 1:279–281
Robin PL (1978) Rouxhet PG (1978) Characterization of kerogens and study of their evolution by infrared spectroscopy carbonyl and carboxyl groups. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42(9):1341–1349
Rodríguez-López JP, Liesa CL, Pardo G, Meléndez N, Soria AR, Skilling I (2016) Glacial dropstones in the western Tethys during the late Aptian–early Albian cold snap: palaeoclimate and palaeogeographic implications for the mid-Cretaceous. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 452:11–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.04.004
Rohling EJ, Jorissen FJ, De Stigter HC (1997) 200 year interruption of Holocene sapropel formation in the Adriatic Sea. J Micropalaeontol 16(2):97–108
Rossignol-Strick M, Nesteroff W, Olive P, Vergnaud-Grazzini C (1982) After the deluge: Mediterranean stag-nation and sapropel formation. Nature 295:105–110
Schlanger SO, Jenkyns HC (1976) Cretaceous oceanic anoxic events: causes and consequences. Geologie Mijnbow 55(3–4):179–184
Slomp CP, Thomson J, de Lange GJ (2002) Enhanced regeneration of phosphorus during formation of the most recent eastern Mediterranean sapropel (S1). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66(7):1171–1184
Smith KL (1978) Benthic community respiration in the NW Atlantic Ocean: in situ measurements from 40 to 5299m. Marine Biol. 47:337–347
Sohlenius G, Emeis KC, Andrén E, Andrén T, Kohly A (2001) Development of anoxia during the Holocene fresh–brackish water transition in the Baltic Sea. Mar Geol 177(3–4):221–242
Stanford JD, Hemingway R, Rohling EJ, Challenor PG, Medina-Elizalde M, Lester AJ (2011) Sea-level probability for the last deglaciation: a statistical analysis of far-field records. Glob Planet Chang 79:193–203
Stanley DJ, Maldonado A (1977) Mud-facies definition for paleoenvironmental interpretation. In: Program and Abstracts, AAPG-SEPM Meeting, June 1977, Washington. pp. 106–107
Stevenson FJ, Goh KM (1971) Infrared spectra of humic acids and related substances. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 35:471–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(71)90044-5
Stewart K, Kassakian S, Krynytzky M, DiJulio D, Murray JW (2007) Oxic, suboxic, and anoxic conditions in the Black Sea. The Black Sea flood question: Changes in coastline, climate, and human settlement. p 1–21
Suess E (1980) Particulate organic carbon flux in the oceans-surface productivity and oxygen utilization. Nature. 288:260–263
Talbi R, Lakhdar R, Smati A, Spiller R, Levey R (2018) Aptian-Albian shale oil unconventional system as registration of Cretaceous oceanic anoxic sub-events in the southern Tethys (Bir M’Cherga basin, Tunisia). J Pet Explor Prod Technol 9(2):1007–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-018-0577-6
Thomson J, Mercone D, De Lange GJ, Van Santvoort PJM (1999) Review of recent advances in the interpretation of eastern Mediterranean sapropel S1 from geochemical evidence. Mar Geol 153(1–4):77–89
Troelstra SR, Ganssen GM, Der Borg KV, De Jong AFM (1991) A late quaternary stratigraphic framework for eastern mediterranean sapropel is based on ams 14c dates and stable oxygen isotopes. Radiocarbon. 33(1):15–21
Van Santvoort PJM, De Lange GJ, Thomson J, Cussen H, Wilson TRS, Krom MD, Ströhle K (1996) Active post-depositional oxidation of the most recent sapropel (S1) in sediments of the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60(21):4007–4024
Vergnaud-Grazzini C, Ryan WB, Cita MB (1977) Stable isotopic fractionation, climate change and episodic stagnation in the eastern Mediterranean during the late Quaternary. Mar Micropaleontol 2:353–370
Zanchetta G, Drysdale RN, Hellstrom JC, Fallick AE, Isola I, Gagan MK, Pareschi MT (2007) Enhanced rainfall in the Western Mediterranean during deposition of sapropel S1: stalagmite evidence from Corchia cave (Central Italy). Quatern Sci Rev 26(3–4):279–286
Zirks E, Krom MD, Zhu D, Schmiedl G, Goodman-Tchernov BN (2019) Evidence for the presence of oxygen-depleted sapropel intermediate water across the Eastern Mediterranean during Sapropel S1. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry 3(10):2287–2297
Znaidi-Rivault J (1982) Les grands évènements climatiques du Quaternaire récent en Méditerranée Orientale: La réponse sédimentaire, microfaunique et isotopique (Doctoral dissertation, PhD Thesis, University of Paris).
Zonneveld KA, Versteegh GJ, Kasten S, Eglinton TI, Emeis KC, Huguet C, Wakeham SG (2010) Selective preservation of organic matter in marine environments; processes and impact on the sedimentary record. Biogeosciences. 7(2):483–511
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted with the support of the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Tunisia and was funded by the Research Laboratory: LR18 ES07 (Sedimentary Basins and Petroleum Geology). The authors thank Professor Mohamed Ksibi Editor-in-Chief for its insightful comments and Dr. Nabil Khelifi, Senior Editor, Springer, MENA, for judicious recommendations; they are both greatly acknowledged. Professor Marlone H. Hünnig Bom, Itt OCEANEON—UNISINOS University, Brazil and two anonymous reviewers are also thanked for their constructive remarks and comments, which really improved the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was fnancially supported by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientifc Research of Tunisia, and was funded by the Research Laboratory: LR18 ES07 (Sedimentary Basins and Petroleum Geology).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ahmed El-Kenawy.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lakhdar, R., Talbi, R. Ephemeral signature of anoxia in the southwest Mediterranean coastal lagoon (southeast Tunisia) similar to the sapropel S1. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-024-00505-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-024-00505-3