Abstract
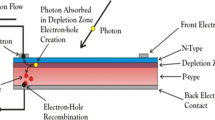
This paper introduces a novel photovoltaic (PV) modeling approach that combines the power law model (PLM), the single diode model (SDM), and a genetic algorithm (GA). The proposed method leverages the simplicity of the PLM and the utility of the SDM to establish two expressions for the PLM parameters. These expressions are formulated as functions of three physical parameters: the ideality factor, series resistance, and shunt resistance. Furthermore, a GA is employed to optimize these physical parameters. The primary objective of this proposed approach is to enhance the optimization of the current–voltage characteristics and the maximal power of PV modules using the PLM model across various environmental conditions, including temperature and irradiation. To assess the effectiveness of the proposed approach, experimental validation is performed using various types of PV modules. The experiments are carried out at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in Florida, specifically at the Cocoa site. The results obtained under different conditions are then compared with those generated by traditional methods. The comparative analysis reveals that the proposed approach exhibits improved agreement with the experimental data, further highlighting its efficacy in accurately optimizing the behavior and performance of PV modules under real operating conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
We declared in the acknowledgements that the data is sent by the NREL laboratory by e-mail.
Abbreviations
- I (A):
-
PV module current
- I sc (A):
-
Short-circuit current
- I ph (A):
-
Photogenerated current
- I s (A):
-
Reverse saturation current of the diode
- R s (Ω):
-
Series resistance
- R sh (Ω):
-
Parallel resistance
- n :
-
Ideality factor
- V (V):
-
PV module voltage
- V oc (V):
-
Open circuit voltage
- V th (A):
-
Thermal voltage
- N s :
-
Number of PV cells connected in series
- T (K):
-
PV module’s temperature
- k (J/K):
-
Boltzmann’s constant
- q (C):
-
Electron charge
- m and g :
-
Shape parameters
- i :
-
Index symbolizing the real time t
- N :
-
Total number of data points
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- NREL:
-
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
- PV:
-
Photovoltaic
- PLM:
-
Power law model
- SDM:
-
Single diode model
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
References
Abbassi A, Ben Mehrez R, Touaiti B et al (2022) Parameterization of photovoltaic solar cell double-diode model based on improved arithmetic optimization algorithm. Optik (Stuttg) 253:168600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168600
Abdulrazzaq AK, Bognár G, Plesz B (2022) Accurate method for PV solar cells and modules parameters extraction using I–V curves. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 34:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2020.07.008
Ait Salah FE, Maouhoub N, Tifidat K et al (2023) An efficient analytical approach for forecasting the peak power of PV panels working in outdoor conditions based on explicit model. Energy Convers Manag X 20:100423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecmx.2023.100423
Anani N, Ibrahim H (2020) Adjusting the single-diode model parameters of a photovoltaic module with irradiance and temperature. Energies 13:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123226
Ang TZ, Salem M, Kamarol M et al (2022) A comprehensive study of renewable energy sources: classifications, challenges and suggestions. Energy Strateg Rev 43:100939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2022.100939
Askarzadeh A, Rezazadeh A (2012) Parameter identification for solar cell models using harmony search-based algorithms. Sol Energy 86:3241–3249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.08.018
Batzelis EI, Papathanassiou SA (2016) A method for the analytical extraction of the single-diode PV model parameters. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 7:504–512. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2015.2503435
Benahmida A, Maouhoub N, Tifidat K, Sahsah H (2022) Extraction of photovoltaic generator parameters through combination of an analytical and iterative approach. Int J Electr Comput Eng 12:4529–4537. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v12i5.pp4529-4537
Boutana N, Mellit A, Haddad S et al (2017) An explicit I–V model for photovoltaic module technologies. Energy Convers Manag 138:400–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.02.016
El-Naggar KM, AlRashidi MR, AlHajri MF, Al-Othman AK (2012) Simulated annealing algorithm for photovoltaic parameters identification. Sol Energy 86:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2011.09.032
El-Sehiemy R, Shaheen A, El-Fergany A, Ginidi A (2023) Electrical parameters extraction of PV modules using artificial hummingbird optimizer. Sci Rep 13:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36284-0
Harrag A, Messalti S (2017) Three, five and seven PV model parameters extraction using PSO. Energy Procedia 119:767–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.07.104
Herbazi R, Kharchouf Y, Amechnoue K et al (2020) Solar photovoltaic cell parameters extraction using differential evolution algorithm. Proceedings 63:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020063043
Laudani A, Fulginei FR, Salvini A (2012) Identification of the one-diode model for photovoltaic modules from datasheet values. Sol Energy 108:432–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2014.07.024
Li S, Gu Q, Gong W, Ning B (2020) An enhanced adaptive differential evolution algorithm for parameter extraction of photovoltaic models. Energy Convers Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112443
Li L, Xiong G, Yuan X et al (2021) Parameter extraction of photovoltaic models using a dynamic self-adaptive and mutual-comparison teaching-learning-based optimization. IEEE Access 9:52425–52441. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3069748
Liang J, Ge S, Qu B et al (2020) Classified perturbation mutation based particle swarm optimization algorithm for parameters extraction of photovoltaic models. Energy Convers Manag 203:112138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112138
Liu L, Liu W, Zhang X, Ingenho J (2019) Research on the novel explicit model for photovoltaic I–V characteristic of the single diode model under different splitting spectrum. Results Phys 12:662–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.12.021
Lu H, Zhang Y, Hao P et al (2022) Output performance prediction of PV modules based on power-law model from manufacturer datasheet. J Renew Sustain Energy 14:033501. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0088190
Lun S, Du C, Yang G et al (2013) An explicit approximate I-V characteristic model of a solar cell based on padé approximants. Sol Energy 92:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2013.02.021
Lun S, Du C, Sang J et al (2014) An improved explicit I–V model of a solar cell based on symbolic function and manufacturer’s datasheet. Sol Energy 110:603–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2014.09.032
Marion W, Anderberg A, Deline C et al (2014) User’s manual for data for validating models for PV module performance. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden
Oliva D, Cuevas E, Pajares G (2014) Parameter identification of solar cells using artificial bee colony optimization. Energy 72:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.05.011
Prakash SB, Singh G, Singh S (2021) Modeling and performance analysis of simplified two-diode model of photovoltaic cells. Front Phys 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2021.690588
Reis LRD, Camacho JR, Novacki DF (2017) The Newton Raphson method in the extraction of parameters of PV modules. Renew Energy Power Qual J 1:634–639. https://doi.org/10.24084/repqj15.416
Ridha HM, Hizam H, Mirjalili S et al (2022) On the problem formulation for parameter extraction of the photovoltaic model: novel integration of hybrid evolutionary algorithm and Levenberg Marquardt based on adaptive damping parameter formula. Energy Convers Manag 256:115403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2022.115403
Saleem H, Karmalkar S (2009) An analytical method to extract the physical parameters of a solar cell from four points on the illuminated J–V curve. Electron Device Lett IEEE 30:349–352
Senthilkumar S, Mohan V, Mangaiyarkarasi SP, Karthikeyan M (2022) Analysis of single-diode PV model and optimized MPPT model for different environmental conditions. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4980843
Tifidat K, Maouhoub N, Benahmida A, Ait Salah FE (2022) An accurate approach for modeling I–V characteristics of photovoltaic generators based on the two-diode model. Energy Convers Manag X 14:100205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecmx.2022.100205
Tifidat K, Maouhoub N, Ait Salah FE (2023a) Modeling approach for extracting the single-diode model. AIP Conf Proc 040006:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0148726
Tifidat K, Maouhoub N, Askar SS, Abouhawwash M (2023b) Numerical procedure for accurate simulation of photovoltaic modules performance based on the identification of the single-diode model parameters. Energy Rep 9:5532–5544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2023.04.378
Yu K, Chen X, Wang X, Wang Z (2017) Parameters identification of photovoltaic models using self-adaptive teaching-learning-based optimization. Energy Convers Manag 145:233–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.04.054
Yu K, Liang JJ, Qu BY et al (2018) Multiple learning backtracking search algorithm for estimating parameters of photovoltaic models. Appl Energy 226:408–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.06.010
Zagrouba M, Sellami A, Bouaïcha M, Ksouri M (2010) Identification of PV solar cells and modules parameters using the genetic algorithms: application to maximum power extraction. Sol Energy 84:860–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2010.02.012
Zaimi M, El Achouby H, Zegoudi O et al (2020) Numerical method and new analytical models for determining temporal changes of model-parameters to predict maximum power and efficiency of PV module operating outdoor under arbitrary conditions. Energy Convers Manag 220:113071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113071
Zaimi M, El Ainaoui K, Assaid EM (2023) Mathematical models to forecast temporal variations of power law shape parameters of a PV module working in real weather conditions: prediction of maximum power and comparison with single-diode model. Sol Energy 266:112197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2023.112197
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Su J et al (2020) Modeling and prediction of PV module performance under different operating conditions based on power-law I–V model. IEEE J Photovolt 10:1816–1827. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOTOV.2020.3016607
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the NREL and in particular Mr. Bill Marion for sending the experimental data by email.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ksibi Mohamed.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ait Salah, F.E., Maouhoub, N. & Tifidat, K. Performance optimization of PV panels operating under varying environmental conditions using a genetic algorithm and power law model. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-024-00474-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-024-00474-7