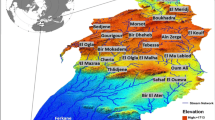
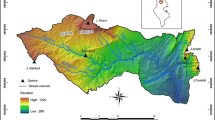
Abstract
Water erosion is a critical factor contributing to soil loss in southern Tunisia and poses a substantial risk to both ecosystems and water/soil conservation. This study employs an analytic hierarchy process (AHP) model integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) to evaluate the potential soil erosion risk and the relative significance of erosion factors within the Oum el Ghram and Bou Said watersheds. Ten factors, including rainfall, land cover/use, slope, elevation, runoff, drainage density, lineament density, lithology, soil type, and support practices, are analyzed. The results highlight land cover/use (27%), elevation (18%), and slope (14%) as the most influential factors. High to very high erosion classes predominantly occur in mountainous areas, covering 5.22% of the study area. Validation using the ROC curve demonstrates a satisfactory accuracy level for the AHP method (AUC = 0.85). To mitigate soil degradation and erosion risks, the findings advocate for implementing sustainable management strategies. Furthermore, this research offers insights for establishing effective soil management strategies under similar conditions in various studies. This work addresses the pressing issue of erosion in southern Tunisia, emphasizing practical solutions and valuable applications for soil conservation efforts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaab N, Zanella A, Akrout D, Mourgues R, Montacer M (2021) Timing and distribution of bedding-parallel veins, in evaporitic rocks, Bouhedma formation, Northern Chotts Tunisia. J Struct Geol 153:104461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2021.104461
Abaoui J, El Ghmari A, El Harti A, Bachaoui EM, Bannari A, El Bouadili A (2005) Cartographie de l’erosion hydrique en zonemontagneuse: cas du bassin versant des Aït Bou Goumez, Haut Atlas, Maroc. Estud Geol 61:33–39
Abbes C, Zargouni F (1986) Anatomie d’un couloir de decrochements: le couloir de Hadifa (Chaine Nord des Chotts—Tunisie). Rev Sci Terre 4:31–37
Abdeljaouad S, Zargouni F (1981) Mise en evidence d’une tectonique intracretace dans le secteur de J. Zemlet El Beida (chaine des Chotts). In: Acte de 1er Congr Nat Sci Terre, Tunis, Tunisia, 28 Sept–4 Oct 1981, p 285
Abdelkarim B, Telahigue F, Agoubi B (2022a) Assessing and delineation of groundwater recharge areas in coastal arid area southern Tunisia. Groundw Sustain Dev 18:100760
Abdelkarim B, Antunes IMHR, Agoubi B (2022b) Groundwater recharge mechanism in a semi-arid region from southern Tunisia—a hydrogeochemical and isotopic contribution. In: Sustain Valencia 2022, Valencia, Spain, 6–8 Oct 2022
Abdelkarim B, Antunes I, Missaoui R, Abaab N, Agoubi, B (2023a) Assessment and modeling of the spatio-temporal variability of recharge in arid zones: the case of the Oued Zegzaou watershed (Southern Tunisia). In: 1st Int Virtual Seminar on Geosciences, Constantine, Algeria, 7–9 Mar 2023, pp 7–9
Abdelkarim B, Antunes IMHR, Agoubi, B (2023b) Spatial variation of groundwater vulnerability to nitrate pollution in semi-arid area. In: XI Congr Nacional de Geologia, Coimbra, Portugal, 17–20 Jul 2023, ISBN: 978-989-98914-8-7
Abdelkarim B, Antunes IMHR, Abaab N, Agoubi B (2023c) Modeling groundwater recharge mechanisms in semi-arid regions: integration of hydrochemical and isotopic data. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00400-3.
Abdelkarim B, Telahigue F, Abaab N, Boudabra B, Agoubi B (2023d) AHP and GIS for assessment of groundwater suitability for irrigation purpose in coastal-arid zone: Gabes region, southeastern Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):15422–15437
Aneseyee AB, Elias E, Soromessa T, Feyisa GL (2020) Land use/land cover change effect on soil erosion and sediment delivery in the Winike watershed, Omo Gibe Basin. Ethiopia Sci Total Environ 728:138776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138776
Aouadj SA, Degdag H, Hasaoui O, Nasrallah Y, Zouidi M, Allam A, Khatir H (2023) Contribution of GIS and remote sensing for the risk mapping of soil water erosion at Saida Province (Western of Algeria). Adv Res Life Sci 7(1):10–21
Arabameri A, Rezaei K, Reza Pourghasemi H, Lee S, Yamani M (2018) GIS-based gully erosion susceptibility mapping: a comparison among three data-driven models and AHP knowledge-based technique. Environ Earth Sci 77:628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7808-5
Arar A, Chenchouni H (2014) A “simple” geomatics-based approach for assessing water erosion hazard at montane areas. Arab J Geosci 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0782-4
Asfaw S, Pallante G, Palma A (2020) Distributional impacts of soil erosion on agricultural productivity and welfare in Malawi. Ecol Econ 177:106764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106764
Aslam B, Maqsoom A, Alaloul WS, Musarat MA, Jabbar T, Zafar A (2021) Soil erosion susceptibility mapping using a GIS-based multi-criteria decision approach: case of district Chitral, Pakistan. Ain Shams Eng J 12:1637–1649
Bayramin I, Dengiz O, Baskan O, Parlak M (2003) Soil erosion risk assessment with ICONA model, case of study: Beypazari Area. Turk J Agric For 27:105–116
Ben Cheikh N, Zouari K, Abidi B (2014) A hydrogeochemical approach for identifying salinization processes in the Cenomanian-Turonian aquifer, south-eastern Tunisia. Carbonates Evaporites 29:193–201
Ben Youssef M, Peybernes B (1993) Donnees micropaleontologiques et biostratigraphiques nouvelles sur le Cretace inferieur marin du Sud tunisien. J Afr Earth Sci 5:217–231
Besser H, Dhaouadi L, Hadji R, Hamed Y, Jemmali H (2021) Ecologic and economic perspectives for sustainable irrigated agriculture under arid climate conditions: an analysis based on environmental indicators for southern Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 177:104134
Blanco H, Lal R (2008) Principles of soil conservation and management, vol 167169. Springer, New York
Blanco H, Lal R (2010) Principles of soil conservation and management. Vadose Zone J. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2009.0110br
Bou Kheir R, Girard MC, Shaban A, Khawlie M, Faour G, Darwich T (2001a) Apport de la télédétection pour la modélisation de l’érosion hydrique des sols dans la région côtière du Liban. Télédétection 2(2):79–90
Bou Kheir R, Girardlzy M-Cl, Khawlielry M, Abadallahlly C (2001b) Erosion hydrique des sols dans les milieux méditerranéens: une revue bibliographique. Etude Gest Sols 8:231–245
Bouaziz S (1995) Study of tectonics in the Saharan platform and Atlas (southern Tunisia): evolution of paleo-fields of constraints and geodynamic implications. PhD thesis. University of Tunis, Tunis
Boufeldja S, Baba Hamed K, Bouanani A, Belkendil A (2020) Identifcation of zones at risk of erosion by the combination of a digital model and the method of multi-criteria analysis in the arid regions: case of the BecharWadi watershed. Appl Water Sci 10:121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01191-6
Boukhalfa K, Li G, Ben Ali W, Soussi M (2015) Early Cretaceous spinicaudatans (“conchostracans”) from lacustrine strata of the Sidi Aich formation in the northern Chotts range, southern Tunisia: taxonomy, biostratigraphy and stratigraphic implication. Cretac Res 56:482–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cretres.2015.06.006
Burollet PF (1965) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. La Rapide, Tunis
Chafai A, Brahim N, Slim Shimi N (2020) Mapping of water erosion by GIS/RUSLE approach: watershed Aydariver Tunisia study. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05774-0
Demirag Turan ID, Dengiz O, Ozkan B (2019) Spatial assessment and mapping of soil quality index for desertification in the semi-arid terrestrial ecosystem using MCDM in interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Comput Electron Agric 164:104933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.104933
Durán Zuazo VH, Rodríguez Pleguezuelo CR (2008) Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 28:65–86. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2007062
Evans KG, Loch RJ (2015) Using the RUSLE to identify factors controlling erosion rates of mine soils. Land Degrad Dev 7(3):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-145X(199609)7:3
Fourati M, Bouaziz R, El Amri A, Majdoub R (2015) Identification des anomalies de fonctionnement des ouvrages de conservation des eaux et du sol du bassin versant Sidi Salah [Identification of the operating anomalies of soil and water conservation works at the watershed Sidi Salah]. Int J Innov Appl Stud 10:428–435. ISSN 2028-9324
Fu B, Zhang L, Xu Z, Zhao Y, Wei Y, Skinner D (2015) Ecosystem services in changing land use. J Soils Sediments 15(4):833–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1082-x
Ganasri BP, Ramesh H (2016) Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—a case study of Nethravathi basin. Geosci Front 7(6):953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007
García-Ruiz JM, Beguería S, Lana-Renault N, Nadal-Romero E, Cerdà A (2017) Ongoing and emerging questions in water erosion studies. Land Degrad Develop 28:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2641
Ghosh A, Rakshit S, Tikle S, Das S, Chatterjee U, Pande CB, Mattar MA (2023) Integration of GIS and remote sensing with RUSLE model for estimation of soil erosion. Land 12(1):116
Ghrabi M (2013) Relationship between the southern Atlas foreland and the eastern margin of Tunisia (Chotts—Gulf of Gabes): Tectono-sedimentary, fault kinematics and balanced cross section approaches. PhD thesis. University of Sfax, Sfax, p 202. http://www.theses.fr/2013AIXM4340/document
Gyssels G, Poesen J, Bochet E, Li Y (2005) Impact of plant roots on the resistance of soils to erosion by water: a review. Prog Phys Geogr 29(2):189–217
Hadji R, Limani Y, Baghem M, Demdoum A (2013) Geologic, topographic and climatic controls in landslide hazard assessment using GIS modeling: a case study of Souk Ahras region, NE Algeria. Quatern Int 302:224–237
Hajjem A (1985) Étude hydrogéologique préliminaire de la nappe de The Chaffar (Sahel Sud de Sfax). Commissariat régional de développement agricole (CRDA), Arrondissement des eaux, Sfax
Halder JC (2023) The integration of RUSLE-SDR lumped model with remote sensing and GIS for soil loss and sediment yield estimation. Adv Space Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2023.01.008
Halefom A, Teshome A (2019) Modelling and mapping of erosion potentiality watersheds using AHP and GIS technique: a case study of Alamata Watershed, South Tigray. Ethiopia Model Earth Syst Environ 5:819–831
Hamed Y, Hadji R, Ahmadi R, Ayadi Y, Shuhab K. Pulido-Bosch A (2023) Hydrogeological investigation of karst aquifers using an integrated geomorphological, geochemical, GIS, and remote sensing techniques (Southern Mediterranean Basin—Tunisia). Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-02994-8
Jamil Anache AA, Edson Wendland C, Paulo Oliveira TS, Dennis Flanagan C, Mark A (2017) Nearing, runoff and soil erosion plot-scale studies under natural rainfall: a meta-analysis of the Brazilian experience. Catena 152:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.01.003
Jemai S (2019) Etude de la variabilité pluviométrique et simulation des crues éclair dans le bassin versant de Gabès (Sud-Est Tunisien). PhD thesis. University of Sfax, Sfax, p 155
Jin Z, Zhao Q, Qin X, Zhang J, Zhang H, Qin J, Wang L (2021) Quantifying the impact of landscape changes on hydrological variables in the alpine and cold region using hydrological model and remote sensing data. Hydrol Process 35:e14392
Kachouri S, Achour H, Abida H, Bouaziz S (2014) Soil erosion hazard mapping using analytic hierarchy process and logistic regression: a case study of Haffouz watershed, Central Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 8:4257–4268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1464-1
Kallel A, Ksibi M, Dhia HB, Khélifi N (2018) Recent advances in environmental science from the Euro-Mediterranean and surrounding regions: proceedings of Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-1), Tunisia 2017. Springer, New York
Kefi M, Yoshino K, Setiawan Y, Zayani K, Boufaroua M (2011) Assessment of the effects of vegetation on soil erosion risk by water: a case of study of the Batta watershed in Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0891-x
Kia MB, Pirasteh S, Pradhan B, Mahmud AR, Sulaiman WNA, Moradi A (2012) An artificial neural network model for flood simulation using GIS: Johor River Basin, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 67:251–264
Kirti P (2007) Criteria for evaluating group decision-making methods. J Math Comput Model. 46(7–8):935–947
Kucuker DM, Giraldo DC (2022) Assessment of soil erosion risk using an integrated approach of GIS and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in Erzurum Turkiye. Ecol Inf 71:101788
Kumar S, David Raj A, Kalambukattu JG, Chatterjee U (2023) Climate change impact on land degradation and soil erosion in hilly and mountainous landscape: sustainability issues and adaptation strategies. Ecological footprints of climate change: adaptive approaches and sustainability. Springer, Cham, pp 119–155
Lee MC (2010) The analytic hierarchy and the network process in multi-criteria decision making: performance evaluation and selecting key performance indicators based on ANP model. In: Crisan M (ed) Convergence and hybrid information technologies. IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/9643
Li G, Boukhalfa K, Teng X, Soussi M, Ali WB, Ouaja M, Houla Y (2017) New Early Cretaceous clam shrimps (Spinicaudata) from uppermost Bouhedma formation of northern Chotts range, southern Tunisia: taxonomy, stratigraphy and palaeoenvironmental implications. Cretac Res 72:124–133
Louhaichi MA, Tlig S (1993) Tectonique synsedimentaire des series post Barremiennes au Nord-Est de la chaine Nord des Chotts (Tunisie meridionale). Geol Mediterr 10(1):53–74
M’Rabet A (1981) Stratigraphie, sedimentation et diagenese carbonatee des series du Cretace inferieur de Tunisie Centrale. PhD thesis. Université Paris-Sud, Paris, p 540
Mahleb A, Hadji R, Zahri F, Boudjellal R, Chibani A, Hamed Y (2022) Water-borne erosion estimation using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model over a semiarid watershed: case study of Meskiana catchment Algerian-Tunisian Border. Geotech Geol Eng 40(8):4217–4230
Mahmoudi S, Srasra E, Zargouni F (2010) Firing behaviour of the Lower Cretaceous clays of Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 58(2):235–241
Majdoub R, Fourati M, Sahtout N, Ben Ammar A, Bouaziz R (2016) Contribution d’un Système d’Information Géographique à l’évaluation de la dégradation du sol et des aménagements antiérosifs au niveau du bassin versant d’Oued Agareb [Contribution of Geographic Information Systems to the evaluation land degradation and anti-erosion management in the watershed of Oued Agareb]. J Mater Environ Sci 7(9):3362–3370. www.researchgate.net/publication/308900220
Mekrazi F (1975) Contribution à l’étude géologique et hydrogéologique de la région de Gabès Nord. PhD thesis. Université de Tunis, Tunis
Mihi A, Benarfa N, Arar A (2019) Assessing and mapping water erosionprone areas in northeastern Algeria using analytic hierarchy process, USLE/RUSLE equation, GIS, and remote sensing. Appl Geom. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518.019.00289.0
Missaoui R, Abdelkarim B, Ncibi K, Hamed Y, Choura A, Essalami L (2022) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability to nitrate contamination using an improved model in the Regueb Basin, Central Tunisia. Water Air Soil Pollut 233(8):1–16
Missaoui R, Ncibi K, Abdelkarim B, Bouajila A, Choura A, Hamdi M, Hamed Y (2023) Assessment of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater: link of AHP and PCA methods using a GIS approach in a semi-arid region Central Tunisia. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 8:1–16
Mnasri H, Sahnoun H, Abdelkarim B, Nunes A, Mahmoudi S (2023) Assessment of water erosion hazard using an integrated approach of geographic information systems and analytic hierarchy process: watersheds of Oum el Ghram and Bou Said (south-eastern Tunisia). In: 1st Int Virtual Seminar on Geosciences, Constantine, Algeria, 7–9 Mar 2023, pp 7–9
Msaddek MH, Merzougui A, Zghibi A, Chekirbane A (2022) Integrated decisional approach for watershed vulnerability prioritization using water and soil hazard index (WSHI) and AHP methods: Chiba watershed, Cap-Bon region, northeast Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 15(12):1148
Ncibi K, Hadji R, Hajji S, Besser H, Hajlaoui H, Hamad A, Hamed Y (2021) Spatial variation of groundwater vulnerability to nitrate pollution under excessive fertilization using index overlay method in central Tunisia (Sidi Bouzid basin). Irrig Drain 70(5):1209–1226
Negese A, Fekadu E, Getnet H (2021) Potential soil loss estimation and erosion-prone area prioritization using RUSLE, GIS, and remote sensing in Chereti Watershed, Northeastern Ethiopia. Air Soil Water Res 14:1178622120985814
Neji N, Ayed RB, Abida H (2021) Cartographie des risques d’érosion hydrique à l’aide du processus de hiérarchie analytique (AHP) et de la modélisation par logique floue: une étude de cas du bassin versant du Chaffar (sud-est de la Tunisie). J Arabe Des Géosci 14:1–15
Nunes AN, Almeida AC, Coelho COA (2011) Impacts of land use and cover type on runoff and soil erosion in a marginal area of Portugal. Appl Geogr 31(2):687–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2010.12.006
Ramesh V, Iqbal SS (2020) Urban flood susceptibility zonation mapping using evidential belief function, frequency ratio and fuzzy gamma operator models in GIS: a case study of Greater Mumbai Maharashtra. India. 37(2):581–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1730448
Saaty T (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty TL, Vargas LG (2012) Models, methods, concepts, and applications of the analytic hierarchy process, vol 175. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3597-6
Sahnoun H, Serbaji MM, Karray B, Medhioub K (2012) GIS and multi-criteria analysis to select potential sites of agro-industrial complex. Environ Earth Sci 66:2477–2489
Sarkar S, Kanungo DP (2004) An integrated approach for landslide susceptibility mapping using remote sensing and GIS. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 70:617–625
Sathiyamurthi S, Ramya M, Saravanan S, Subramani T (2023) Estimation of soil erosion for a semi-urban watershed in Tamil Nadu, India using RUSLE and geospatial techniques. Urban Clim 48:101424
Taguas EV, Arroyo C, Lora A, Guzmán G, Vanderlinden K, Gómez JA (2015) Exploring the linkage between spontaneous grass cover biodiversity and soil degradation in two olive orchard microcatchments with contrasting environmental and management conditions. Soil 1:651–664. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-1-651-2015
Li G, Boukhalfa K, Teng X, Soussi M, Ben Ali W, Ouaja M, Houla Y (2017) New Early Cretaceous clam shrimps (Spinicaudata) from uppermost Bouhedma Formation of northern Chotts range, southern Tunisia: taxonomy, stratigraphy and palaeoenvironmental implications. Cretac Res 72(201):124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cretres.2016.12.014
Vente JD, Poesen J (2005) Predicting soil erosion and sediment yield at the basin scale: scale issues and semi-quantitative models. Earth Ence Rev 71(1–2):95–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.02.002
Wei H, Liu H, Xu Z, Ren J, Lu N, Fan W, Zhang P, Dong X (2018) Linking ecosystem services supply, social demand, and human well-being in a typical mountain–oasis–desert area, Xinjiang China. Ecosyst Serv 31:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.03.012
Wu Q, Wang M (2007) A framework for risk assessment on soil erosion by water using an integrated and systematic approach. J Hydrol 337:11–21
Zhao Q, Chen W, Peng C, Wang D, Xue W, Bian H (2022) Modeling landslide susceptibility using an evidential belief function-based multiclass alternating decision tree and logistic model tree. Environ Earth Sci. 81(15):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-022-10525-3/FIGURES/13
Zouaghi T (2008) Distribution des sequences de depot du Cretace (Aptien-Maastrichtien) en subsurface: role de la deformation tectonique, l’halocinese et evolution geodynamique: Atlas Central Tunisien. PhD thesis. University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Riheb Hadji.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mnasri, H., Nunes, A., Sahnoun, H. et al. Assessment of soil erosion in southern Tunisia using AHP-GIS modeling. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 9, 223–234 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00429-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00429-4