Abstract
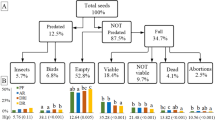
This study aimed to (i) determine the influence of the factors “aspect” and “cone orientation within the tree crown” on cone morphometric traits of Atlas cedar, (ii) determine the relationship between these traits and seed production; and (iii) estimate the damage caused by insects to cones and seeds and the spatial distribution of cone and seed infestations. Within each of the four selected stations, 25 cones were randomly collected from five trees. The parameters determined were: cone morphometric traits, seed yield per cone, number of bores per cone, healthy and infested seeds, and seed damage rates. Despite the variation observed, aspect and orientation had no significant effect (p > 0.05) on cone morphometric traits (length, width, weight and volume); nor on seed production, number of insect exit holes and resin exudation levels. Generalized linear models (GLM) revealed that the number of seeds per cone varied significantly and differently according to cone morphometric traits, site aspect, cone orientation and their interactions. Seed production increased significantly (p < 0.001) with increasing cone length, width, volume and weight in south-facing versus north-facing sites. This increase varied with tree crown position. The variation in seed cropping size among aspects and cone orientations was not significant. The number of healthy seeds per cone was significantly higher (p < 0.001) than the number of infested seeds. GLM showed that seed infestation rates responded positively to southern exposure and infestation indicators (number of holes per cone and level of resin exudation). Seed damage rates were not influenced by cone length, width, volume and cone orientation. The variations observed in seed damage seem to be related to intraspecific variation, tree age, and site-specific trophic conditions. While aspect and cone orientation had limited impacts, the research highlighted significant links between seed yield, cone traits, and site characteristics. Seed damage showed intricate relationships with the studied variables. These insights offer valuable guidance for forest management and suggest avenues for investigating genetic and ecological variations to enhance conservation strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelhamid D, Marniche F, Allal-Benfekih L, Benadjroud N, Mouna M (2017) Importance des Coléoptères sylvatiques associés au cèdre de l’Atlas au niveau du parc national de Theniet El Had (Algérie). Rev Agrobiologia 7(1):297‒311. https://www.asjp.cerist.dz/en/downArticle/255/7/1/119417. Accessed Sept 2023
Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, Mc Dowell N, Vennetier M et al (2010) A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag 259(4):660–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001
Arar A, Tabet S, Nouidjem Y, Bounar R, Chenchouni H (2019) Projected small-scale range reductions of Cedrus atlantica forests due to climate change at the Belezma National Park (Algeria). In: Chenchouni H et al (eds) Exploring the nexus of geoecology, geography, geoarcheology and geotourism. Springer, Cham, pp 15–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01683-8_4
Arya SR, Bhagat S, Singh O (1994) Seed fertility in relation to tree size of Abies pindrow and Picea smithiana. Indian For 120:677–681
Ayari A, Khouja ML (2014) Ecophysiological variables influencing Aleppo pine seed and cone production: A review. Tree Physiol 34(4):426–437. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpu022
Ayari A, Zubizarreta-Gerendiain A, Tome M, Tome J, Garchi S, Henchi B (2012) Stand, tree and crown variables affecting cone crop and seed yield of Aleppo pine forests in different bioclimatic regions of Tunisia. For Syst 21(1):128–140. https://doi.org/10.5424/fs/2112211-11463
Baraclini M, Benedettelli S, Croci F, Terreni P, Tiberi R, Panzavolta T (2013) Cone and seed pests of Pinus pinea: assessment and characterization of damage. J Econ Entomol 106(1):229–234. https://doi.org/10.1603/ec12293
Bates SL, Strong WB, Borden JH (2002) Abortion and seed set in lodgepole and western white pine conelets following feeding by Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heteroptera: Coreidae). Environ Entomol 31(6):1023–1029. https://doi.org/10.1603/0046-225X-31.6.1023
Beghami R, Bertella N, Laamari M, Bensaci AO (2020) Bark beetle and woodborer insects’ outbreak as a potent driver of Atlas cedar (Cedrus atlantica (Endl.) Carriere) forests dieback in Aures-East Algeria. For Sci Technol 16(2):75–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2020.1756929
Benras H, Guezoul O, Neffar S, Chenchouni H (2023) Disclosing the determinants, drivers and predictors of bird depredation on date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) production. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 22(4):231–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2022.12.003
Ben-Said M, Linares JC, Carreira JA, Taïqui L (2022) Spatial patterns and species coexistence in mixed Abies marocana-Cedrus atlantica forest in Talassemtane National Park. For Ecol Manag 506:119967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119967
Berthonnet A (2010) Parcs nationaux et tourisme en Algérie dans les années 1920, une expérience coloniale effacée par l’histoire. Pour Mémoire 9:164–169
Bhattacharya A (2021) Effect of soil water deficit on growth and development of plants: a review. In: Soil water deficit and physiological issues in plants. Springer, Singapore, pp 393–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6276-5_5
Boivin T, Auger-Rozenberg MA (2016) Native fruit, cone and seed insects in the Mediterranean Basin. In: Paine TD, Lieutier F (eds) Insects and diseases of Mediterranean forest systems. Springer, Cham, pp 47–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24744-1_4
Bracalini M, Benedettelli S, Croci F, Terreni P, Tiberi R, Panzavolta T (2013) Cone and seed pests of Pinus pinea: assessment and characterization of damage. J Econ Entomol 106(1):229–234. https://doi.org/10.1603/ec12293
Bréda N, Huc R, Granier DE (2006) Temperate forest trees and stands under severe drought: a review of ecophysiological responses, adaptation processes and long-term consequences. Ann For Sci 63(6):625–644. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2006042
Calama R, Montera G (2007) Cone and seed production from stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) stands in Central Range (Spain). Eur J For Res 126:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-005-0100-8
Calama R, Fortin M, Pardos M, Manso R (2017) Modelling spatiotemporal dynamics of Pinus pinea cone infestation by Dioryctria mendacella. For Ecol Manag 389:136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.12.015
Camarero JJ, Sánchez-Salguero R, Sangüesa-Barreda G, Lechuga V, Viñegla B, Seco JI et al (2021) Drought, axe and goats. More variable and synchronized growth forecasts worsening dieback in Moroccan Atlas cedar forests. Sci Total Environ 765:142752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142752
Chafaa S, Biche M, Chenchouni H, Sellami M, Si Bachir A (2013) Effet du climat et de l’exposition sur la dynamique des populations de la cochenille violette, Parlatoria oleae Colvée (Hemiptera: Diaspididae), en conditions arides. Ann Soc Entomol Fr 49(3):291–297. https://doi.org/10.1080/00379271.2013.856203
Chenchouni H (2010) Drought-induced mass mortality of Atlas Cedar forest (Cedrus atlantica) in Algeria. In: Parrota JA, Carr MA (eds) The International Forestry Review, Proc 33th IUFRO World Congress, Seoul, Korea, 23–28 August 2010
Chenchouni H, Zanati K, Rezougui A, Briki A, Arar A (2010) Population monitoring of pine processionary moth (Thaumetopoea pityocampa) by pheromone trapping at the southern limit of distribution of Pinus halepensis in Eastern Algeria. Forest Sci Technol 6(2):67–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2010.9671974
Chouaki S, Bessedik F, Chebouti A, Maamri F, Oumata S, Kheldoun S et al (2006) Deuxième rapport national sur l’état des ressources phytogénétiques. INRAA. https://www.fao.org/pgrfa-gpa-archive/dza/algerie.pdf. Accessed Sept 2023
Copes-Gerbitz K, Fletcher W, Lageard JGA, Rhanem M, Harrison SP (2019) Multidecadal variability in Atlas cedar growth in Northwest Africa during the last 850 years: Implications for dieback and conservation of an endangered species. Dendrochronologia 56:125599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2019.05.003
Curt T, Coll L, Prévosto B, Balandier P, Kunstler G (2005) Plasticity in growth, biomass allocation and root morphology in beech seedlings as induced by irradiance and herbaceous competition. Ann For Sci 62(1):51–60. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2004092
Derridj A (1990) Etude des populations de Cedrus atlantica en Algérie. PhD thesis. Univ. Toulouse, Toulouse
Dormont RA, Trosset L (1996) Insect damage to cones and other mortality factors limiting natural regeneration potential of Swiss stone pine (Pinus cembra L.) in the northern French Alpes. Ann Sci Forest 53:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:19960112
Durkaya A, Durkaya B, Dail S (2009) The effects of the pine processionary moth on the increment of crimean pine trees in Bartin. Turkey Afr J Biotechnol 8(10):2356–2361. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajb.v8i10.60598
Gachi M, Démolin G, Zamoum M, Khemici M (2005) An evaluation of the radial growth losses of Atlas cedar following defoliation by Thaumetopoea bonjeani in the Belezma massif (Aurès, Algeria). In: Lieutier F, Ghaioule D (eds) Entomological research in Mediterranean forest ecosystems. INRA Editions, Paris, pp 117‒122
Himanen K, Helenius P, Ylioja T, Nygren M (2015) Intracone variation explains most of the variance in Picea abies seed weight: implications for seed sorting. Can J For Res 46:470–477. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2015-0379
Hódar JA, Castro J, Zamora R (2003) Pine processionary caterpillar Thaumetopoea pityocampa as a new threat for relict Mediterranean Scots pine forests under climatic warming. Biol Conserv 110(1):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3207(02)00183-0
Huang Z, Liu Q, Tigabu M, Jin S, Ma X, Liu B (2022) Plastic responses in growth, morphology, and biomass allocation of five subtropical tree species to different degrees of shading. Forests 13(7):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13070996
Idder MA, Ighili H, Mitiche B, Chenchouni H (2015) Influence of date fruit biochemical characteristics on damage rates caused by the Carob moth (Ectomyelois ceratoniae) in Saharan oases of Algeria. Sci Hortic 190:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.04.015
Iwaizumi MG, Ubukata M, Yamada H (2008) Within-crown cone production patterns dependent on cone productivities in Pinus densiflora: Effects of vertically differential, pollination-related, cone growing conditions. Botany 86(6):576–586. https://doi.org/10.1139/b08-024
Iwaizumi MG, Ohtani M, Takahashi M (2019) Geographic cline and climatic effects on cone characteristics of natural populations of Pinus densiflora throughout the Japanese archipelago. J For Res 24(3):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/13416979.2019.1603666
Jacquet JS, Orazio C, Jactel H (2012) Defoliation by processionary moth significantly reduces tree growth: a quantitative review. Ann For Sci 69(8):857–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-012-0209-0
Jacquet JS, Bosc A, O’Grady AP, Jactel H (2013) Pine growth response to processionary moth defoliation across a 40-year chronosequence. For Ecol Manag 293:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.12.003
Kacha S, Adamou-Djerbaoui M, Marniche F, De Prins W (2017) The richness and diversity of Lepidoptera species in different habitats of the national Park Theniet El Had (Algeria). J Fundam Appl Sci 9(2):746–769. https://doi.org/10.4314/jfas.v9i2
Kelly D, Sork VL (2002) Mast seeding in perennial plants: Why, how, where? Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:427–447. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.020602.095433
Kherchouche D, Kalla M, Gutierrez E, Briki A, Hamchi A (2013) La sécheresse et le dépérissement du cèdre de l’Atlas (Cedrus atlantica Manetti) dans le massif du Belezma. Secheresse 24:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1684/sec.2013.0384
Khoudja L (2020) Le Pin d’Alep en Tunisie: Ecologie, gestion et usages. INRGREF, Tunis. https://onagrihome.files.wordpress.com/2021/01/pin_dalep.pdf. Accessed Sept 2023
Krouchi F, Derridj A, Lefèvre F (2004) Year and tree effect on reproductive organisation of Cedrus atlantica in a natural forest. For Ecol Manag 197(1–3):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.05.013
Lavoie J, Montoro Girona M, Morin H (2019) Vulnerability of conifer regeneration to spruce budworm outbreaks in the eastern Canadian boreal forest. Forests 10(10):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100850
Leal DB, Thomas SC (2003) Vertical gradients and tree-to-tree variation in shoot morphology and foliar nitrogen in an old-growth Pinus strobus stand. Can J For Res 33(7):1304–1314. https://doi.org/10.1139/x03-064
Leal-Sáenz A, Waring KM, Álvarez-Zagoya R, Hernández-Díaz JC, López-Sánchez CA, Martínez-Guerrero JH, Wehenkel C (2021) Assessment and models of insect damage to cones and seeds of Pinus strobiformis in the Sierra Madre Occidental, Mexico. Front Plant Sci 12:628795. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.628795
Linares JC, Taïqui L, Camarero JJ (2011) Increasing drought sensitivity and decline of Atlas cedar (Cedrus atlantica) in the Moroccan Middle Atlas forests. Forests 2(3):777–796. https://doi.org/10.3390/f2030777
Liu B, Liu QQ, Daryanto S, Guo S, Huang ZJ, Wang ZN, Wang LX, Ma XQ (2018) Responses of Chinese fir and Schima superba seedlings to light gradients: Implications for the restoration of mixed broadleaf-conifer forests from Chinese fir monocultures. For Ecol Manag 419–420:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.03.033
Lobo N (2014) Conifer seed predation by terrestrial small mammals: a review of the patterns, implications, and limitations of top-down and bottom-up interactions. For Ecol Manag 328:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2014.05.019
Loewe-Muñoz V, Delard C, Del Río R, Balzarini M (2021) Western conifer seed bug (Leptoglossus occidentalis) challenging stone pine cropping in the Southern Hemisphere. For Ecol Manag 496:119434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119434
Long RL, Gorecki MJ, Renton M, Scott JK, Colville L, Goggin DE et al (2015) The ecophysiology of seed persistence: a mechanistic view of the journey to germination or demise. Biol Rev 90(1):31–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12095
M’hirit O (2008) Etude des causes de dépérissement de la cédraie du Moyen Atlas. Rapport de synthèse. FAO, Rome. http://www.eauxetforets.gov.ma/Publications/Dépérissement_Cédraie_lb.pdf. Accessed Sept 2023
Mamo N, Mihretu M, Fekadu M, Tigabu M, Teketay D (2006) Variation in seed and germination characteristics among Juniperus procera populations in Ethiopia. For Ecol Manag 225(1–3):320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2006.01.026
McDowell NG, Williams AP, Xu C, Pockman WT, Dickman LT, Sevanto S et al (2016) Multi-scale predictions of massive conifer mortality due to chronic temperature rise. Nat Clim Change 6(3):295–300. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2873
Messaoudène M, Loukkas A, Janin G, Tafer M, Dilem A, Gonçalez J (2004) Propriétés physiques du bois d’éclaircie des cèdres (Cedrus atlantica), contenant du bois de compression, provenant de l’Atlas du Djurdjura (Algérie). Ann For Sci 61(6):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2004054
Mouna M (2009) Phaenops marmottani Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), xylophage primaire pour le cèdre de l’Atlas (Cedrus atlantica Man). Bull Inst Sci Sect Sci Terre 31:85–90
Mouna M, Fabre JP (2005) Pest insect of cedars: Cedrus atlantica Manetti, C. libani A. Richard and C. brevifolia Henry in Mediterranean area. In: Lieutier F, Ghaioule D (eds) Entomological research in Mediterranean forest ecosystems. INRA, Paris, pp 89–103
Mutke S, Gordo J, Gil L (2005) Variability of Mediterranean Stone pine cone production: Yield loss as response to climate change. Agric For Meteorol 132:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.08.002
Navarro-Cerrilo R, Sarmoum M, Gazol A, Abdoun F, Camarero JJ (2019) The decline of Algerian Cedrus atlantica forests is driven by a climate shift towards drier conditions. Dendrochronologea 55:60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dendro.2019.04.003
Nie Z, Maclean DA, Taylor AR (2019) Disentangling variables that influence growth response of balsam fir regeneration during a spruce budworm outbreak. For Ecol Manag 433:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.10.050
UNDP (2015) Etude diagnostique sur la biodiversité et les changements climatiques en Algérie. Final Report, PROJET MATE-PNUD-FEM, Algeria. https://info.undp.org/docs/pdc/Documents/DZA/Rapport-AtelierBiodiv-CC.pdf. Accessed Sept 2023
Politi PI, Georghiou K, Arianoutsou M (2011) Reproductive biology of Abies cephalonica Loudon in Mount Aenos National Park, Cephalonia, Greece. Trees 25:655–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-011-0542-1
Poncet BN, Garat P, Manel S, Roques A, Despres L (2009) The effect of climate on masting in the European larch and on its specific seed predators. Oecologia 159:527–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1233-5
Pureswaren DS, Roques A, Battisti A (2018) Forest insects and climate change. Curr For Rep 4:35–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s.40725-018-0075-6
R Core Team (2023) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-project.org. Accessed Sept 2023
Rahim N, Chakali G, Battisti A (2021) Natural enemies of the cedar processionary moth, Thaumetopoea bonjeani (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae) in Algeria. Afr Entomol 29(2):674–677. https://doi.org/10.4001/003.029.0674
Rhanem M (2012) Gradients et causes de mortalité du cèdre de l’Atlas (Cedrus atlantica Man.) en marge supérieure de l’écotone infra-forestier limitrophe de la haute plaine de Midelt. L’exemple de la forêt d’Aït-Oufella dans le Moyen-Atlas méridional du Maroc. Bull Soc Bot Cent-Ouest 43:185–204
Roland CA, Schmidt JH, Johnstone JF (2014) Climate sensitivity of reproduction in a mast-seeding boreal conifer across its distributional range from lowland to treeline forests. Oecologia 174:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2821-6
Ros ND, Ostermeyer R, Roques A, Raimbault JP (1993) Insect damage to cones of exotic conifer species introduced in arboreta: I. Interspecific variations within the genus Pices. J Appl Entomol 115(1–5):113–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0418.1993.tb00371.x
Sarmoum M, Navarro-Cerrilo R, Guibal F, Abdoun F (2018) Structure, tree growth dynamics and management of Atlas cedar stands in Theniet El Had National Park (N-W Algeria). Open J Ecol 8:432–446. https://doi.org/10.4236/oje.2018.88026
Sarmoum M, Navarro-Cerrilo R, Guibal F (2019a) Bilan actuel et rétrospectif du dépérissement du cèdre d’Atlas dans le Parc National de Theniet El Had (Algérie). Bois Forets Trop 342(4):29–40. https://doi.org/10.19182/bft2019.342.a31636
Sarmoum M, Navarro-Cerrilo R, Guibal F, Abdoun F (2019b) Impact of drought and site characteristics on vitality and radial growth of Cedrus atlantica Manetti in the Ouarsenis massif (Algeria). AGROFOR Int J 3(4):42–52. https://doi.org/10.7251/agreng1903042s
Sbabdji M, El Hadi O, Haddad A, Kadik B, Lambs L (2009) Cedar tree growth (Cedrus atlantica Manetti) in Chréa national park, Algeria, and the influence of defoliation by the pine processionary caterpillar (Thaumetopoea pityocampa Schiff.). Rev Ecol Terre Vie 64:323–332. https://doi.org/10.3406/revec.2009.1495
Sbabdji M, Lambs L, Haddad A, Kadik B (2015) Effect of periodic defoliations by Thaumetopoea pityocampa Schiff. on radial growth in cedar woodland in Chréa, Algeria. Rev Ecol Terre Vie 70(4):371–386. https://doi.org/10.3406/revec.2015.1798
Schmid JM, Mitchell JC, Carlin KD, Wagner MR (1984) Insect damage, cone dimensions, and seed production in crown levels of ponderosa pine. Great Basin Nat 44(4):5. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/gbn/vol44/iss4/5. Accessed Sept 2023
Sevillano I, Short I, Grant J, O’Reilly C (2016) Effects of light availability on morphology, growth and biomass allocation of Fagus sylvatica and Quercus robur seedlings. For Ecol Manag 374:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.04.048
Slobodník B, Gutternberger H (2000) Ovule, megaspores and female gametophyte formation in Larix decidua Mill (Pinaceae). Acta Biol Crac Ser Bot 42:93–100
Strong WB, Bates SL, Stoehr MU (2001) Feeding by Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera: Coreidae) reduces seed set in lodgepole pine (Pinaceae). Can Entomol 133(6):857–865. https://doi.org/10.4039/Ent133857-6
Tallamy DW, Shropshire KJ (2009) Ranking lepidopteran use of native versus introduced plants. Conserv Biol 23(4):941–947. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2009.01202.x
Turgeon JJ, Roques A, Groot PD (1994) Insect fauna of coniferous seed cones: diversity, host plant interactions, and management. Annu Rev Entomol 39(1):179–212. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.39.010194.001143
Vennetier M, Ripert C, Brochiéro F, Rathgeber C, Chandioux O, Estève R (2010) Évaluation de la croissance du pin d'Alep en région méditerranéenne française. Rev For Fr 57(5):503–524. https://hal.science/hal-00593706. Accessed Sept 2023
Wang L, Zhang FX, Li LP, Wang CJ, Wan JZ (2023) Effects of habitat heterogeneity and topographic variation on insect pest risks in Alpine regions. Land 12(7):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071314
Wenhui Z, Xiaobo X, Jianyun Z (2006) Study on reproduction ecology of endangered species Abies chensiensis. Acta Ecol Sin 26:2417–2424. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2032(06)60036-X
Wion AP, Weisberg PJ, Pearse IS, Redmond MD (2020) Aridity drives spatiotemporal patterns of masting across the latitudinal range of a dryland conifer. Ecography 43(4):569–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.04856
Zherikhin VV (2002) Pattern of insect burial and conservation. In: Rasnitsyn AP, Quicke DLJ (eds) History of insects. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 17–64
Acknowledgements
We address our gratitude to Dr. Alain Roques (Forest Zoology Station of Orléans, France) for helping us to analyze the seeds using X-ray radiography.
Funding
This study was not funded by any source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DA: conceptualization, methodology, resources, and investigation; SN: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing; HC: formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Giulia Guerriero.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelhamid, D., Neffar, S. & Chenchouni, H. Decoding the interplay between tree traits, seed production, and cone-boring insect damage using advanced modeling to unveil the intricacies of Atlas cedar (Cedrus atlantica) forests. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 8, 875–891 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00419-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00419-6