Abstract
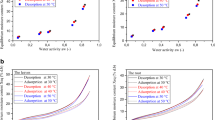
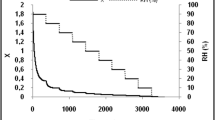
As a result of the growing demand for low-calorie sweeteners, interest in stevia plant has increased. Two methods are applied for the preservation of stevia leaves: freeze drying and gamma irradiation at 1 kGy. Because most studies have focused on sorption characteristics of plants, the present work aims to evaluate the effect of these two technologies on moisture sorption and thermodynamics properties of stevia leaves at 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C using the static gravimetric method. The obtained results indicated that freeze-dried stevia adsorbed more water vapor. According to the adsorption results and for ensuring microbial stability during storage, the moisture content should not be higher than 10.10%, 11.58%, and 13.79% dry weight basis (d.b.) for commercial, irradiated, and freeze-dried stevia leaves, respectively. Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer (GAB) model was fitted to the experimental data. The monolayer moisture content and the surface area of sorption were shown to decrease with increasing temperature. The isosteric heat and differential entropy of sorption were found to decrease with increasing moisture content. The optimal water activities for conservation values were determined and reported as being 0.35, 0.32, and 0.35 for commercial, freeze-dried, and irradiated stevia, respectively. Thus, this study could be used as a reference to specify the adequate storage conditions of stevia leaves.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- X eq = EMC:
-
Equilibrium moisture content (% d.b.)
- Am:
-
Area of a water molecule (1.06 × 10−19 m2)
- N A :
-
Avogadro’s number (6 × 1026 molecules/mol)
- K B :
-
Boltzmann constant (1.38 × 10−23 J K−1)
- MRE:
-
Mean relative error (%)
- \({\text{Xeq}}_{{\text{i,exp}}}\) :
-
Experiment equilibrium moisture content (% d.b.)
- \(Xeq_{i,pred}\) :
-
Predicted equilibrium moisture content (% d.b.)
- GAB:
-
Guggenheim–Anderson–de Boer
- X m :
-
Monolayer moisture content
- \(\Delta H_{d}\) :
-
Isosteric heat of sorption (kJ mol−1)
- \(\Delta h_{d}\) :
-
Net isosteric heat of sorption (kJ mol−1)
- \(\Delta S_{d}\) :
-
Entropy of sorption (J mol−1 K−1)
- R:
-
Universal gas constant (8.3145 J mol−1 K−1)
- aw :
-
Water activity
- \(\theta\) :
-
Temperature (°C)
- d.b.:
-
Dry weight basis
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- N :
-
Number of data points
- \(\varphi\) :
-
Spreading pressure (J m−2)
- C, K, X m :
-
GAB model coefficients
- S :
-
Solid surface area (m2 g−1 dry solids)
- \(M_{{H_{2} O}}\) :
-
Molecular weight of water (18 g mol−1)
- T:
-
Absolute temperature (K)
- \(\Delta H_{vap}\) :
-
Heat of vaporization of water
References
Abdenouri N, Idlimam A, Kouhila M (2010) Sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of powdered milk. Chem Eng Commun 197:1109–1125. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986440903412936
Alonzo Macias M (2013) Comparatives studies of different drying process of strawberry hot air drying freeze-drying and swell-drying : application on the biological compounds preservation. Université de la Rochelle
Argyropoulos D, Müller J (2014) Effect of convective-, vacuum- and freeze drying on sorption behaviour and bioactive compounds of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.). J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 1:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2014.06.001
Arora S, Sharma SR, Kumar S (2011) Thermodynamic models for water sorption by garlic. J Food Sci Technol 48:604–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-010-0144-8
Bahloul N, Boudhrioua N, Kechaou N (2008) Moisture desorption–adsorption isotherms and isosteric heats of sorption of Tunisian olive leaves (Olea europaea L.). Ind Crops Prod 28:162–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2008.02.003
Brunauer S, Deming WE (1940) On a theory of Van der Waals adsorption of gases. J Am Chem 62:1723–1732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2009.02.032
Cassini AS, Marczak LDF, Noreña CPZ (2006) Water adsorption isotherms of texturized soy protein. J Food Eng 77:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.05.059
Dalgıç AC, Pekmez H, Belibağlı KB (2012) Effect of drying methods on the moisture sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of mint leaves. J Food Sci Technol 49:439–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0302-7
Fan K, Chen L, Wei X, He J, Yan F (2015) Moisture adsorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of Auricularia auricula. J Food Process Preserv 39:1534–1541. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12379
Ghanta S, Banerjee A, Poddar A, Chattopadhyay S (2007) Oxidative DNA damage preventive activity and antioxidant potential of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) Bertoni, a natural sweetener. J Agric Food Chem 55:10962–10967
Greenspan L (1977) Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aqueous solutions. J Res Natl Bur Stand Sect A Phys Chem 81:89
Gupta E, Purwar S, Sundaram S, Rai GK (2013) Nutritional and therapeutic values of Stevia rebaudiana: a review. J Med Plant Res 7:3343–3353. https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR2013.5276
Hidar N, Mghazli S, Lahnine L, Ouhammou M, Idlimam A, Jaouad A, Bouchdoug M, Kouhila M, Mahrouz M (2017) Desorption isotherms and solar convective drying kinetics of stevia. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing
Hidar N, Noufid A, Mourjan A, El Adnany EM, Mghazli S, Mouhib M, Jaouad A, Mahrouz M (2021) Effect of preservation methods on physicochemical quality, phenolic content, and antioxidant activity of stevia leaves. J Food Qual 2021:10
Hidar N, Noufid A, Mourjane A, Mghazli S, Idlimam A, Jaouad A, Mahrouz M (2022) Physicochemical and microbiological properties and moisture adsorption isotherms characteristics of commercial steviol glycoside, rebaudioside A. Euro-Mediterranean. J Environ Integr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-022-00309-3
Hidar N, Ouhammou M, Idlimam A, Jaouad A, Bouchdoug M, Lamharrar A, Kouhila M, Mahrouz M (2018) Investigation of water adsorption and thermodynamic properties of stevia powder. J Food Meas Charact 12:2615–2625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9879-0
Hidar N, Ouhammou M, Mghazli S, Idlimam A, Hajjaj A, Bouchdoug M, Jaouad A, Mahrouz M (2020) The impact of solar convective drying on kinetics, bioactive compounds and microstructure of stevia leaves. Renew Energy 161:1176–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.07.124
Horta de Oliveira GH, Corrêa PC, Rodrigues De Oliveira APL, Baptestini FM, Vargas-Elías GA (2016) Roasting, grinding, and storage impact on thermodynamic properties and adsorption isotherms of arabica coffee. J Food Process Preserv. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12779
Horta de Oliveira GH, Corrêa PC, de Santos ES, Treto PC, Diniz MDMS (2011) Evaluation of thermodynamic properties using GAB model to describe the desorption process of cocoa beans. Int J Food Sci Tech. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2011.02719.x
Huang X, Li W, Wang Y, Wan F (2020) Drying characteristics and quality of Stevia rebaudiana leaves by far-infrared radiation. LWT. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110638
Irchad A, Razouk R, Ouaabou R, Mouhib M, Hssaini L (2022) Effect of 60Co γ-rays on dried figs adsorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties. Front Nutr. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.940111
Karam MC, Petit J, Zimmer D, Baudelaire Djantou E, Scher J (2016) Effects of drying and grinding in production of fruit and vegetable powders: a review. J Food Eng 188:32–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.05.001
Koua BK, Koffi PME, Gbaha P, Toure S (2014) Thermodynamic analysis of sorption isotherms of cassava (Manihot esculenta). J Food Sci Technol 51:1711–1723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0687-y
Lahnine L, Idlimam A, Mahrouz M, Jada A, Hanine H, Mouhib M, Zantar S, Kouhila M (2016) Adsorption measurements and modeling of thyme treated with gamma irradiation and thermal-biochemical treatment. Ind Crops Prod 88:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.049
Lemus-Mondaca R, Vega-Galvez A, Moraga NO, Astudillo S (2014) Dehydration of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves: kinetics, modeling and energy features. J Food Process Preserv 39:508–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12256
Lemus-Mondaca R, Vega-Gálvez A, Rojas P, Ah-hen K (2016) Assessment of quality attributes and steviosides of Stevia rebaudiana leaves subjected to different drying methods. J Food Nutr Res 4:720–728
Lemus-Mondaca R, Vega-Gálvez A, Rojas P, Stucken K, Delporte C, Valenzuela-Barra G, Jagus RJ, Agüero MV, Pasten A (2018) Antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory potential of Stevia rebaudiana leaves: effect of different drying methods. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 11:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2018.10.003
Lemus-Mondaca R, Vega-Gálvez A, Zura-Bravo L, Kong AH (2012) Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, source of a high-potency natural sweetener: a comprehensive review on the biochemical, nutritional and functional aspects. Food Chem 132:1121–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.140
Liébanes MD, Aragón JM, Palancar MC, Arévalo G, Jiménez D (2006) Equilibrium moisture isotherms of two-phase solid olive oil by-products: Adsorption process thermodynamics. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 282–283:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.03.025
López-Vidaña EC, Castillo Téllez M, Pilatowsky Figueroa I, Santis Espinosa LF, Castillo-Téllez B (2021) Moisture sorption isotherms, isosteric heat, and Gibbs free energy of stevia leaves. J Food Process Preserv. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15016
Machhour H, Idlimam A, Mahrouz M, El Hadrami I, Kouhila M (2012) Sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of peppermint tea (Mentha piperita) after thermal and biochemical treatment. J Mater Environ Sci 3:232–247
Meng Q, Fan H, Li Y, Zhang L (2018) Effect of drying methods on physico-chemical properties and antioxidant activity of Dendrobium officinale. J Food Meas Charact 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9611-5
Mghazli S, Idlimam A, Mahrouz M, Lahnine L, Hidar N, Ouhammou M, Mouhib M, Zantar S, Bouchdoug M (2016) Comparative moisture sorption isotherms, modelling and isosteric heat of sorption of controlled and irradiated Moroccan rosemary leaves. Ind Crops Prod 88:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.050
Mostafavi HA, Mirmajlessi SM, Fathollahi H (2012) The potential of food irradiation : benefits and limitations. In: Eissa AA (ed) Trends in vital food and control engineering. InTech, pp 43–68
Moussaoui H, Idlimam A, Lamharrar A, Kouhila M, Bahammou Y, Mouhib M, Amamou A (2020) The determination of moisture sorption isotherms and the isosteric heat of sorption for irradiated and non-irradiated durum wheat. Moroccan J Chem 8:866–878
Mrad ND, Bonazzi C, Boudhrioua N, Kechaou N, Courtois F (2012) Moisture sorption isotherms, thermodynamic properties, and glass transition of pears and apples. Dry Technol 30:1397–1406. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2012.683843
Muanda FN, Soulimani R, Diop B, Dicko A (2011) Study on chemical composition and biological activities of essential oil and extracts from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. LWT 44:1865–1872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2010.12.002
Ouaabou R, Ennahli S, Hssaini L, Nabil B, Idlimam A, Lamharrar A, Mahrouz M, Hanine H (2022) Moisture sorption isotherms of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.): comparative study of kinetics and thermodynamic modeling of five varieties. Int J Food Sci 2022:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6786590
Periche A, Castelló ML, Heredia A, Escriche I (2016) Effect of different drying methods on the phenolic, flavonoid and volatile compounds of Stevia rebaudiana leaves. Flavour Fragr J 31:173–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.3298
Rao GN, Rao PP, Balaswamy K, Satyanarayana A (2014) Antioxidant activity of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana L.) leaf powder and a commercial stevioside powder. J Food Pharm Sci 2:32–38
Ruiz-Ruiz JC, Moguel-Ordoñez YB, Segura-Campos MR (2015) Biological activity of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni and their relationship to health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1072083
Seth D, Dash KK, Mishra HN, Deka SC (2018) Thermodynamics of sorption isotherms and storage stability of spray dried sweetened yoghurt powder. J Food Sci Technol 55:4139–4147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3340-6
Simal S, Femenia A, Castell-Palou A, Rossello C (2007) Water desorption thermodynamic properties of pineapple. J Food Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.10.001
Spiess WEL, Wolf W (1983) The results of the COST 90 project on water acitvity. In: Jowitt R (ed) Physical properties of foods. Applied Science Publishers, London, pp 65–91
Thomas JE, Glade MJ (2010) Stevia: it’s not just about calories. Open Obes J 2:101–109
Tsami E (1991) Net isosteric heat of sorption in dried fruits. J Food Eng 14:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/0260-8774(91)90022-K
Yogendrarajah P, Samapundo S, Devlieghere F, De Saeger S, De Meulenaer B (2015) Moisture sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of whole black peppercorns (Piper nigrum L.). LWT 64:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.05.045
Zeng J, Cai W, Yang W, Wu W (2013) Antioxidant abilities, phenolics and flavonoids contents in the ethanolic extracts of the stems and leaves of different Stevia rebaudiana Bert lines. Sugar Tech 15:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-013-0210-4
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the MESRSFC and the CNRST of the Kingdom of Morocco in the priority areas of research valorization scientific and technological by innovation of local products Moroccan: aromatic and medicinal plants in IAA and ICPC (R2BINNOVA) code: PPR-B-R2BINOV-Mahrouz-FSUCA- Marrakech. The authors also would like to acknowledge MOGADOR Cooperative (ESSAOUIRA, Morocco) for kindly providing the stevia plant material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ksibi Mohamed.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hidar, N., Noufid, A., El Adnany, E.M. et al. Sorption behavior and thermodynamic characteristics of stevia leaves as affected by freeze drying and gamma irradiation technologies. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 8, 179–189 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00346-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00346-6