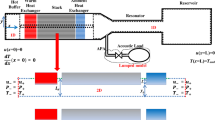
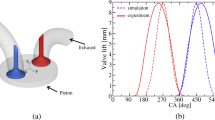
Abstract
A three-dimensional CFD–CHT simulation method is presented and validated with a turbocharged single cylinder SI engine. Various ignition time and lambda strategies as well as variations of boost pressure are investigated with regard to cycle averaged component temperatures. This complements existing published works which experimentally studied crank angle resolved heat fluxes or temperature swings rather than averaged temperatures. Cyclical fluctuations in the pressure curves were measured and processed statistically using probability density functions for the heat transfer coefficient and the cylinder gas temperature. The corresponding joint probability density function considers their strong correlation. The interpretation as random variables enables a time-scale separation with a low-pass filter function. The thermomechanical problem of heat transfer is addressed with simplified models according to Woschni, Eichelberg, and Hohenberg. Previous investigations primarily focused on their predictive quality of instantaneous in-cylinder heat fluxes. In this paper, their effect on cycle averaged component temperatures is investigated and the corresponding different sensitivities to specific engine settings are presented and compared with measurements. It is shown that, by choosing the right model, the suggested simulation approach is an alternative to prevailing experimental methods in temperature analysis: all thermodynamic variations examined are in good agreement with theoretical predictions.













Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 September 2023
Original version of this article corrected for ORCID.
References
Yokomori, T.: Super-lean burn technology for high thermal efficiency SI engines in FVV 2017 Autumn Conf. Leipzig (2017)
Liu, L., Li, Z., Liu, S., Shen, B.: Effect of exhaust gases of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) coupling lean-burn gasoline engine on NOx purification of Lean NOx trap (LNT). Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 87, 195–213(2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.12.029
Robinson, J.S., Cudd, R.L., Evans, J.T.: Creep resistant aluminium alloys and their applications. Mater. Sci. Technol. 19(2), 143–155 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1179/026708303225009373
Golloch, R.: Downsizing bei Verbrennungsmotoren, 1st edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg (2005)
Warnatz, J., Maas, U., Dibble, R.W.: Combustion, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2006)
Eichelberg, G.: Engineering, Some investigations on old combustion-engine problems. Parts I and II. 148, 463 (1939)
Woschni, G.: In A Universally Applicable Equation for the Instantaneous Heat Transfer Coefficient in the Internal Combustion Engine. SAE Tech. Pap. 670931 (1967). https://doi.org/10.4271/670931
Hohenberg, G.F.: Advance approaches for heat transfer calculation. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 790825 (1979). https://doi.org/10.4271/790825
Bargende, M.: Ein Gleichungsansatz zur Berechnung der instationären Wandwärmeverluste im Hochdruckteil von Ottomotoren. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University Darmstadt (1991)
Schubert, C., Wimmer, A., Chmela, F.: Advanced Heat Transfer Model for CI Engines. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 2005–01-0695. SAE International (2005). https://doi.org/10.4271/2005-01-0695
Lee, T.K., Filipi, Z.S.: Improving the Predictiveness of the Quasi-D Combustion Model for Spark Ignition Engines with Flexibles Intake Systems. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 12(1), 1–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-011-0001-4
Payri, F., Margot, X., Gil, A., Martin, J.: Computational Study of Heat Transfer to the Walls of a DI Diesel Engine. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 2005–01-0210. SAE International (2005). https://doi.org/10.4271/2005-01-0210
Mohammadi, A., Yaghoubi, M., Rashidi, M.: Analysis of local convective heat transfer in a spark ignition engine. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 35(2), 215–224 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2007.06.008
Mohammadi, A., Yaghoubi, M.: Estimation of instantaneous local heat transfer coefficient in spark-ignition engines. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49(7), 1309–1317 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2009.12.010
Chiodi, M., Bargende, M.: Improvement of engine heat transfer calculation in the three-dimensional simulation using a phenomenological heat transfer model. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 2001–01-3601. SAE International (2001). https://doi.org/10.4271/2001-01-3601
Broekaert, S., Cuyper, T.D., Paepe, M.D., Verhelst, S.: Evaluation of empirical heat transfer models for HCCI combustion in a CFR engine. Appl. Energy 205, 1141–1150 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.100
Soyhan, H.S., Yasar, H., Walmsley, H., Head, B., Kalghatgi, G.T., Sorusbay, C.: Evaluation of heat transfer correlations for HCCI engine modeling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 29(2–3), 541–549 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2008.03.014
Chang, J., Güralp, O., Filipi, Z., Assanis, D.N., Kuo, T.W., Najt, P., Rask, R.: New Heat Transfer Correlation for an HCCI Engine Derived from Measurements of Instantaneous Surface Heat Flux, in SAE Tech. Pap. 2004–01-2996. SAE International (2004). https://doi.org/10.4271/2004-01-2996
Michl, J., Neumann, J., Rottengruber, H., Wensing, M.: Derivation and validation of a heat transfer model in a hydrogen combustion engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 98, 502–512 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.12.062
Demuynck, J., Paepe, M.D., Huisseune, H., Sierens, R., Vancoillie, J., Verhelst, S.: Investigation of the in fluence of engine settings on the heat flux in a hydrogen- and methane-fueled spark ignition engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 31, 1220–1228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.12.023
Shudo, T., Nakajima, Y., Futakuchi, T.: Thermal efficiency analysis in a hydrogen premixed combustion engine. JSAE Rev. 21(2), 177–182 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0389-4304(99)00091-0
Broekaert, S., Demuynck, J., Cuyper, T.D., Paepe, M.D., Verhelst, S.: Heat transfer in premixed spark ignition engines part I : Identification of the factors influencing heat transfer. Energy 116, 380–391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.08.065
Cuyper, T.D., Demuynck, J., Broekaert, S., Paepe, M.D., Verhelst, S.: Heat transfer in premixed spark ignition engines part II: Systematic analysis of the heat transfer phenomena. Energy 116, 851–860 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.032
LeFeuvre, T., Myers, P.S., Uyehara, O.A.: Experimental instantaneous heat fluxes in a diesel engine and their correlation. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 690464. SAE International (1969). https://doi.org/10.4271/690464
Gilaber, P., Pinchon, P.: Measurements and multidimensional modeling of gas-wall heat transfer in a S.I. Engine. In: SAE Int. Congr. Expo. SAE International (1988). https://doi.org/10.4271/880516
Wimmer, A., Pivec, R., Sams, T.: Heat Transfer to the Combustion Chamber and Port Walls of IC Engines-measurement and prediction. SAE Tech. Pap. 2000-01-0568. SAE International (2000). https://doi.org/10.4271/2000-01-0568
Sanli, A., Ozsezen, A.N., Kilicaslan, I., Canekci, M.: The influence of engine speed and load on the heat transfer between gases and in-cylinder walls at fired and motored conditions of an IDI diesel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 28, 1395–1404 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2007.10.005
Sanli, A., Sayin, C., Gumus, M., Kilicaslan, I., Canakci, M.: Numerical evaluation by models of load and spark timing effects on the in-cylinder heat transfer of a SI engine. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 56(5), 444–458 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/10407780903244312
Sharief, A., Chandrashekar, T.K., Antony, A.J., Samaga, B.S.: Study on heat transfer correlation in IC engines. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 2008–01-1816. SAE International (2008). https://doi.org/10.4271/2008-01-1816
Wang, X., Price, P., Stone, C.R., Richardson, D.: Heat release and heat flux in a spray-guided direct-injection gasoline engine. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 221, 1441–1452 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1243/09544070JAUTO586
Enomoto, Y., Furuhama, S.: Study on thin film thermocouple for measuring instantaneous temperature on surface of combustion chamber wall in internal combustion engine. Bull. JSME 28(235), 108–116 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1299/jsme1958.28.108
Enomoto, Y., Furuhama, S.: Study on thin film thermocouple measuring instantaneous temperature on surface of combustion chamber wall in internal combustion engine—2nd report, study on thin film thermocouples embedded in combustion chamber wall. Bull. JSME 29(256), 3434–3441 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1299/jsme1958.29.3434
Enomoto, Y., Furuhama, S.: A study of the local heat transfer coefficient on the combustion chamber walls of a four-stroke gasoline engine. JSME Int. Journal. Ser. 2 32(1), 107–114 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1299/jsmeb1988.32.1_107
Luo, X., Yu, X., Jansons, M.: Simultaneous in-cylinder surface temperature measurements with thermocouple, laser-induced phosphorescence, and dual wavelength infrared diagnostic techniques in an optical engine. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 2005–01-1658. SAE International (2015). https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-1658.Copyright
Kenningley, S., Morgenstern, R.: Thermal and mechanical loading in the combustion bowl region of light vehicle diesel AlSiCuNiMg pistons; reviewed with emphasis on advanced finite element analysis and instrumented engine testing techniques. In SAE Tech. Pap. 2012–01-1330. SAE International (2012). https://doi.org/10.4271/2012-01-1330
Sugihara, T., Suzuki, Y., Shimano, K., Enomoto, Y., Emi, M.: Direct heat loss to combustion chamber walls in a D.I. Diesel Engine. In SAE Tech. Pap. 2007–24-0006. SAE International (2007). https://doi.org/10.4271/2007-24-0006
Choi, G.H., Choi, K.H., Lee, J.T., Song, Y.S., Ryu, Y., Cho, J.W.: Analysis of combustion chamber temperature and heat flux in a DOHC engine. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 970895. SAE International (1997). https://doi.org/10.4271/970895
Tillock, B.R., Martin, J.K.: Measurement and modeling of thermal flows in an air-cooled engine. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 961731. SAE International (1996). https://doi.org/10.4271/961731
Caton, J., Heywood, J.: An experimental and analytical study of heat transfer in an engine exhaust port. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 24(4), 581–595 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(81)90003-X
Yang, L.C., Hamada, A., Ohtsubo, K.: Engine valve temperature simulation system. In: SAE Tech. Pap. 2000–01-0564. SAE International (2000). https://doi.org/10.4271/2000-01-0564
Fieberg, C., Korthäuer, M.: Forschungsvereinigung Verbrennungskraftmaschinen, Kontaktwärmeübergang—Vorhaben Nr. 828, Kontaktdruckabhängiger Wärmeübergang im motorischen Umfeld, vol. 821 (2006)
Shojaefard, M.H., Noorpoor, A.R., Bozchaloe, D.A., Ghaffarpour, M.: Transient thermal analysis of engine exhaust valve. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 48(7), 627–644 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/10407780590959943
Menter, F.R.: Two-equation Eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 32(8), 1598–1605 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12149
Siemens: STAR-CCM+ User Manual, v11.06 (2018)
Finol, C.A., Robinson, K.: Thermal modelling of modern engines: a review of empirical correlations to estimate the in-cylinder heat transfer coefficient. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 220(12), 1765–1781 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1243/09544070JAUTO202
Adair, R.P., Qvale, E.B., Pearson, J.T.: Instantaneous heat transfer to cylinder wall in reciprocating compressors. Int. Compress. Eng. Conf, pp. 521–526 (1972)
Kleinschmidt, W.: Zur Theorie und Berechnung der instationären Wärmeübertragung in Verbrennungsmotoren. In: 4. Tagung “Der Arbeitsprozess des Verbrennungsmotors”. Graz (1993)
Acknowledgements
P. Hölz would like to thank Tobias Möllenhof and Christian Eifrig, both Porsche Motorsport, for their experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hölz, P., Böhlke, T. & Krämer, T. CFD–CHT calculation method using Buckingham Pi-Theorem for complex fluid–solid heat transfer problems with scattering boundary conditions. Automot. Engine Technol. 3, 45–60 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41104-018-0026-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41104-018-0026-z