Abstract
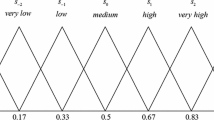
Hospital performance evaluation is vital for effective hospital management as it provides valuable information about a hospital’s condition and enables adaptable implementation based on various attributes. In this research, a multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) method using a 2-tuple linguistic T-spherical fuzzy set (2TLT-SFS) is proposed in the context of the cognitive information presented in the hospital evaluation process. The T-spherical fuzzy set is the most advanced generalization of the q-rung orthopair fuzzy set (q-ROFS) which is capable of handling the uncertainty, fuzziness and ambiguity in terms of four parameters: positivity (yes), negativity (no), impartiality (abstain), and denial (non-acceptance). The 2-tuple linguistic terminology is used to measure the validity of ambiguous data. We propose the 2TLT-SF Hamy mean (2TLT-SFHM) operator, 2TLT-SF weighted Hamy mean (2TLT-SFWHM) operator, 2TLT-SF dual Hamy mean (2TLT-SFDHM) operator and 2TLT-SF weighted dual Hamy mean (2TLT-SFWDHM) operator by combining the 2TLT-SFS and HM operator. Then, based on the proposed maximizing deviation method, a new optimization model is built that is able to exploit expert preference to find the best objective weights among attributes. Next, we extend the TOPSIS (technique for establishing order preference by similarity to the ideal solution) method to the 2TLT-SF-TOPSIS version which not only accounts for human cognition’s inherent uncertainty but also allows experts a wider context to express their decision. Finally, we give a case study about the selection of key performance indicators for hospital performance evaluation to support our proposed method. The findings from parameter analysis and comparative analysis demonstrate the method’s efficacy and reliability. The outcomes demonstrate that our approach successfully handles the assessment and choice of key performance indicators for hospital performance evaluation and captures the relationship between any number of attributes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Akram M, Bibi R (2023) Multi-criteria group decision-making based on an integrated PROMETHEE approach with 2-tuple linguistic Fermatean fuzzy sets. Granul Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-022-00359-6
Akram M, Naz S, Edalatpanah SA, Mehreen R (2021) Group decision-making framework under linguistic \(q\)-rung orthopair fuzzy Einstein models. Soft Comput 25(15):10309–10334
Akram M, Naz S, Santos-Garcia G, Saeed MR (2022) Extended CODAS method for MAGDM with 2-tuple linguistic \(T\)-spherical fuzzy sets. AIMS Math 8(2):3428–3468
Akram M, Khan A, Ahmad U (2023) Extended MULTIMOORA method based on 2-tuple linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy sets for multi-attribute group decision-making. Granul Comput 8(2):311–332
Alahmadi RA, Ganie AH, Al-Qudah Y, Khalaf MM, Ganie AH (2023) Multi-attribute decision-making based on novel Fermatean fuzzy similarity measure and entropy measure. Granul Computi. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-023-00378-x
Atanassov KT (1999) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Physica (Heidelberg) 35:1–137
Chang KH, Chang YC, Lee YT (2014) Integrating TOPSIS and DEMATEL methods to rank the risk of failure of FMEA. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 13(06):1229–1257
Chen SM, Cheng SH, Lin TE (2015) Group decision making systems using group recommendations based on interval fuzzy preference relations and consistency matrices. Inf Sci 298:555–567
Deng X, Wang J, Wei G (2019) Some 2-tuple linguistic Pythagorean Heronian mean operators and their application to multiple attribute decision-making. J Exp Theoret Artif Intell 31(4):555–574
Garg H, Naz S, Ziaa F, Shoukat Z (2021) A ranking method based on Muirhead mean operator for group decision-making with complex interval-valued \(q\)-rung orthopair fuzzy numbers. Soft Comput 25(22):14001–14027
Gou X, Liao H, Xu Z, Herrera F (2017) Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and MULTIMOORA method: a case of study to evaluate the implementation status of haze controlling measures. Inf Fusion 38:22–34
Guleria A, Bajaj RK (2020) \(T\)-spherical fuzzy graphs: operations and applications in various selection processes. Arab J Sci Eng 45(3):2177–2193
Hadi-Vencheh A, Mirjaberi M (2014) Fuzzy inferior ratio method for multiple attribute decision making problems. Inf Sci 277:263–272
Hara T, Uchiyama M, Takahasi SE (1998) A refinement of various mean inequalities. J Inequal Appl 4:932025
Herrera F, Martinez L (2000a) An approach for combining linguistic and numerical information based on the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model in decision-making. Internat J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 8(05):539–562
Herrera F, Martinez L (2000b) A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(6):746–752
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981a) Methods for multiple attribute decision making, vol 186. Springer, Berlin, pp 58–191
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981b) Multiple attributes decision making methods and applications, vol 444. Springer, Berlin, pp 445–446
Ju Y, Wang A, Ma J, Gao H, Santibanez Gonzalez ED (2020) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy 2-tuple linguistic Muirhead mean aggregation operators and their applications to multiple-attribute group decision making. Int J Intell Syst 35(1):184–213
Krylovas A, Zavadskas EK, Kosareva N, Dadelo S (2014) New KEMIRA method for determining criteria priority and weights in solving MCDM problem. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 13(06):1119–1133
Kumar K, Chen SM (2022a) Group decision making based on advanced intuitionistic fuzzy weighted Heronian mean aggregation operator of intuitionistic fuzzy values. Inf Sci 601:306–322
Kumar K, Chen SM (2022b) Group decision making based on weighted distance measure of linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy sets and the TOPSIS method. Inf Sci 611:660–676
Li Z, Gao H, Wei G (2018a) Methods for multiple attribute group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy dombi hamy mean operators. Symmetry 10(11):574
Li Z, Wei G, Lu M (2018b) Pythagorean fuzzy hamy mean operators in multiple attribute group decision making and their application to supplier selection. Symmetry 10(10):505
Liang Z (2020) Models for multiple attribute decision making with fuzzy number intuitionistic fuzzy Hamy mean operators and their application. IEEE Access 8:115634–115645
Liang D, Xu Z (2017) The new extension of TOPSIS method for multiple criteria decision making with hesitant Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Appl Soft Comput 60:167–179
Liu P, Chen SM, Wang Y (2020a) Multiattribute group decision making based on intuitionistic fuzzy partitioned Maclaurin symmetric mean operators. Inf Sci 512:830–854
Liu P, Zhu B, Wang P, Shen M (2020b) An approach based on linguistic spherical fuzzy sets for public evaluation of shared bicycles in China. Eng Appl Artif Intell 87:103295
Liu P, Naz S, Akram M, Muzammal M (2022) Group decision-making analysis based on linguistic \(q\)-rung orthopair fuzzy generalized point weighted aggregation operators. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13(4):883–906
Mahmood T, Ullah K, Khan Q, Jan N (2019) An approach toward decision-making and medical diagnosis problems using the concept of spherical fuzzy sets. Neural Comput Appl 31(11):7041–7053
Mohammadkarim B, Jamil S, Pejman H, Seyyed MH, Mostafa N (2011) Combining multiple indicators to assess hospital performance in Iran using the Pabon Lasso Model. Australas Med J 4(4):175–179
Naz S, Akram M, Al-Shamiri MA, Khalaf MM, Yousaf G (2022a) A new MAGDM method with 2-tuple linguistic bipolar fuzzy Heronian mean operators. Math Biosci Eng 19(4):3843–3878
Naz S, Akram M, Muhiuddin G, Shafiq A (2022b) Modified EDAS method for MAGDM based on MSM operators with 2-tuple linguistic-spherical fuzzy sets. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5075998
Naz S, Akram M, Muzammal M (2022c) Group decision-making based on 2-tuple linguistic T-spherical fuzzy COPRAS method. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07644-1
Naz S, Akram M, Saeid AB, Saadat A (2022d) Models for MAGDM with dual hesitant q-rung orthopair fuzzy 2-tuple linguistic MSM operators and their application to COVID-19 pandemic. Expert Syst 39(8):e13005
Naz S, Akram M, Sattar A, Al-Shamiri MMA (2022e) 2-tuple linguistic q-rung orthopair fuzzy CODAS approach and its application in arc welding robot selection. AIMS Math 7(9):17529–17569
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2004) Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156(2):445–455
Quek SG, Selvachandran G, Munir M, Mahmood T, Ullah K, Son LH, Priyadarshini I (2019) Multi-attribute multi-perception decision-making based on generalized \(T\)-spherical fuzzy weighted aggregation operators on neutrosophic sets. Mathematics 7(9):780
Rong Y, Liu Y, Pei Z (2020) Complex q-rung orthopair fuzzy 2-tuple linguistic Maclaurin symmetric mean operators and its application to emergency program selection. Int J Intell Syst 35(11):1749–1790
Sadeghifar J, Ashrafrezaee N, Hamouzadeh P, Taghavi Shahri M, Shams L (2011) Relationship between performance indicators and hospital evaluation score at hospitals affiliated to Urmia University of Medical Sciences. Nurs Midwifery J 9(4):10
Salsabeela V, Athira TM, John SJ, Baiju T (2023) Multiple criteria group decision making based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy soft sets. Granul Computi. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-023-00369-y
Taslimi MS, Zayandeh M (2013) Challenges of hospital performance assessment system development: Literature review. Hakim Res J 16(1):35–41
Ullah K, Mahmood T, Jan N (2018) Similarity measures for \(T\)-spherical fuzzy sets with applications in pattern recognition. Symmetry 10(6):193
Ullah K, Mahmood T, Garg H (2020) Evaluation of the performance of search and rescue robots using \(T\)-spherical fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22(2):570–582
Verma R, Aggarwal A (2021) On matrix games with 2-tuple intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic payoffs. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 18(4):149–167
Wang WP (2009) Evaluating new product development performance by fuzzy linguistic computing. Expert Syst Appl 36(6):9759–9766
Wang J, Wei G, Lu J, Alsaadi FE, Hayat T, Wei C, Zhang Y (2019) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Hamy mean operators in multiple attribute decision-making and their application to enterprise resource planning systems selection. Int J Intell Syst 34(10):2429–2458
Wang W, Tian G, Zhang T, Jabarullah NH, Li F, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Li Z (2021) Scheme selection of design for disassembly (DFD) based on sustainability: a novel hybrid of interval 2-tuple linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and regret theory. J Clean Prod 281:124724
Wei C, Ren Z, Rodríguez RM (2015) A hesitant fuzzy linguistic TODIM method based on a score function. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8(4):701–712
Wu S, Wang J, Wei G, Wei Y (2018) Research on construction engineering project risk assessment with some 2-tuple linguistic neutrosophic Hamy mean operators. Sustainability 10(5):1536
Wu L, Wang J, Gao H (2019) Models for competiveness evaluation of tourist destination with some interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy Hamy mean operators. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 36(6):5693–5709
Xu Z, Zhang X (2013) Hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute decision making based on TOPSIS with incomplete weight information. Knowl Based Syst 52:53–64
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(4):958–965
Yager RR (2016) Generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(5):1222–1230
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning UI. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Zeb A, Khan MSA, Ibrar M (2019) Approaches to multi-attribute decision making with risk preference under extended Pythagorean fuzzy environment. J Intelli Fuzzy Syst 36(1):325–335
Zhao H, Xu Z, Wang H, Liu S (2017) Hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute decision-making based on the minimum deviation method. Soft Comput 21(12):3439–3459
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naz, S., Hassan, M.M.u., Fatima, A. et al. A decision-making mechanism for multi-attribute group decision-making using 2-tuple linguistic T-spherical fuzzy maximizing deviation method. Granul. Comput. 8, 1659–1687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-023-00388-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-023-00388-9