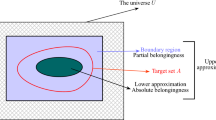
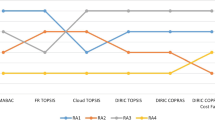
Abstract
Failure Modes and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a significant mathematical technique for the risk assessment of the failure modes in the industrial automation and robotics which are used for various manufacturing process. Due to the existence of uncertainty and diversity in the assessment information, various FMEA techniques depend on fuzziness, rough approximations, and other uncertain theories have been presented. A novel approach to discuss various types of uncertainties and randomness is proposed by integrating the rough numbers clouds and and ELimination and Choice Translating REality (ELECTRE) II method in this research paper. Rough integrated clouds, a form of normal cloud evaluations, have been utilized to deal with ambiguity and randomness with the initial parameters and suppository functions. First, the weights are calculated using objective and subjective aspects of vagueness based on statistical expectation and the maximum deviation method instead of using decision-makers’ preferences. The standard derivation of cloud evaluation is computed from entropy and hyperentropy values instead of existing complicated formula based on central mean value. Second, rough approximation technique is applied on the initial data without additional information which is then transformed into cloud evaluations to deal with fuzziness and randomness using a single mathematical approach. The proposed rough integrated cloud model is a risk assessment approach to recognise the potential risks and their effects. The neutral, weak, and strong discordance and concordance relations are derived to discuss the similarities, differences, and pairwise relations of failure modes. Third, the normalization method is based on two formulae instead of a single formula considering both benefit and cost criteria. Finally, the presented approach is described with a case study to identify the failure modes in automatic robotics. The applications of presented approach have been observed in many research domains like in intelligent manufacturing processes and engineering problems. The comparison of the proposed approach with certain existing techniques is presented to elaborate its out-performance, rationality, and efficacy of findings.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used to support this study.
References
Ahmad S, Khan J, Khan ZA, Asjad M (2023) A comparative assessment of Conventional and Rough-Based Multi-Criteria methods for failure mode and effects analysis of Root canal treatment. Decis Anal J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2023.100170
Akram M, Arshad M (2020) Bipolar fuzzy TOPSIS and bipolar fuzzy ELECTRE-I methods to diagnosis. Comput Appl Math 39(1):1–21
Akram M, Ilyas F, Garg H (2021) ELECTRE-II method for group decision-making in Pythagorean fuzzy environment. Appl Intell 51(12):8701–8719
Akram M, Niaz Z, Feng F (2022) Extended CODAS method for multi-attribute group decision-making based on 2-tuple linguistic Fermatean fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators. Granular Comput 8(3):441–466
Akram M, Noreen U, Deveci M (2023) Enhanced ELECTRE II method with 2-tuple linguistic m-polar fuzzy sets for multi-criteria group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 213:119237
Akram M, Khan A, Luqman A, Senapati T, Pamučar D (2023) An extended MARCOS method for MCGDM under 2-tuple linguistic q-rung picture fuzzy environment. Eng Appl Artif Intell 120:105892
Akram M, Ramzan N, Deveci M (2023) Linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy CRITIC-EDAS method for multiple-attribute group decision analysis. Eng Appl Artif Intell 119:105777
Benayoun R, Roy B, Sussman B (1966) ELECTRE: Une méthode pour guider le choix en présence de points de vue multiples. Note de travail 49:2–120
Brikaa MG, Zheng Z, Ammar ES (2021) Rough set approach to non-cooperative continuous differential games. Granular Comput 6(1):149–162
Chang KH, Cheng CH (2010) A risk assessment methodology using intuitionistic fuzzy set in FMEA. Int J Syst Sci 41(12):1457–1471
Chen Z, Ming X (2020) A rough-fuzzy approach integrating best-worst method and data envelopment analysis to multi-criteria selection of smart product service module. Appl Soft Comput 94:106479
Chen N, Xu Z (2015) Hesitant fuzzy ELECTRE II approach: a new way to handle multi-criteria decision making problems. Inf Sci 292:175–197
El-Bably MK, Fleifel KK, Embaby OA (2022) Topological approaches to rough approximations based on closure operators. Granular Comput 7(1):1–14
Fang H, Li J, Song W (2020) A new method for quality function deployment based on rough cloud model theory. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 69(6):2842–2856
Fattahi R, Khalilzadeh M (2018) Risk evaluation using a novel hybrid method based on FMEA, extended MULTIMOORA, and AHP methods under fuzzy environment. Saf Sci 102:290–300
Feng F, Zhang C, Akram M, Zhang J (2022) Multiple attribute decision making based on probabilistic generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. Granular Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-022-00358-7
Feng F, Zheng Y, Sun B, Akram M (2022) Novel score functions of generalized orthopair fuzzy membership grades with application to multiple attribute decision making. Granular Comput 7(1):95–111
Guowei L, Qiuye S, Huaguang Z (2007) Load modeling of power system based on rough cloud generator. In 2007 8th International Conference on Electronic Measurement and Instruments (pp 1–733). IEEE
Huang G, Xiao L, Zhang G (2021) Assessment and prioritization method of key engineering characteristics for complex products based on cloud rough numbers. Adv Eng Inform 49:101309
Huang G, Xiao L, Zhang G (2021) Decision-making model of machine tool remanufacturing alternatives based on dual interval rough number clouds. Eng Appl Artif Intell 104:104392
Huang G, Xiao L, Pedrycz W, Pamučar D, Zhang G, Martínez L (2022) Design alternative assessment and selection: a novel Z-cloud rough number-based BWM-MABAC model. Inf Sci 603:149–189
Hwang C-L, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making: methods and applications a state-of-the-art survey. Springer, Berlin
Jagtap M, Karande P (2022) Effect of normalization methods on rank performance in single valued m-polar fuzzy ELECTRE-I algorithm. Mater Today 52:762–771
Jasemi M, Ahmadi E (2018) A new fuzzy ELECTRE based multiple criteria method for personnel selection. Scientia Iranica 25(2):943–953
Kahraman C, Yasin Ateş N, Çevik S, Gülbay M, Ayça Erdoğan S (2007) Hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS model for selection among logistics information technologies. J Enterp Inf Manag 20(2):143–168
Li D, Du Y (2017) Artificial intelligence with uncertainty. CRC Press
Li D, Liu C, Gan W (2009) A new cognitive model: cloud model. Int J Intell Syst 24(3):357–375
Li J, Fang H, Song W (2019) Modified failure mode and effects analysis under uncertainty: a rough cloud theory-based approach. Appl Soft Comput 78:195–208
Li J, Fang H, Song W (2019) Sustainable supplier selection based on SSCM practices: a rough cloud TOPSIS approach. J Clean Prod 222:606–621
Liao R, Bian J, Yang L, Grzybowski S (2013) Cloud model based failure mode and effects analysis for prioritization of failures of power transformer in risk assessment. Int Trans Elect Energy Syst 23(7):1172–1190
Liu P, Li Y (2019) An extended MULTIMOORA method for probabilistic linguistic multi-criteria group decision-making based on prospect theory. Comput Ind Eng 136:528–545
Liu HC, You JX, Shan MM, Shao LN (2015) Failure mode and effects analysis using intuitionistic fuzzy hybrid TOPSIS approach. Soft Comput 19:1085–1098
Liu HC, Li Z, Song W, Su Q (2017) Failure mode and effect analysis using cloud model theory and PROMETHEE method. IEEE Trans Reliab 66(4):1058–1072
Liu HC, Shi H, Li Z, Duan CY (2022) An integrated behavior decision-making approach for large group quality function deployment. Inf Sci 582:334–348
Liu Z, Wang D, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Liu P (2023) An improved ELECTRE II based outranking method for MADM with double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets and its application to emergency logistics provider selection. Int J Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01449-y
Mishra AR, Chen SM, Rani P (2022) Multiattribute decision making based on Fermatean hesitant fuzzy sets and modified VIKOR method. Inf Sci 607:1532–1549
Nie RX, Tian ZP, Wang XK, Wang JQ, Wang TL (2018) Risk evaluation by FMEA of supercritical water gasification system using multi-granular linguistic distribution assessment. Knowl-Based Syst 162:185–201
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Pawlak Z (1996) Rough sets, rough relations and rough functions. Fund Inform 27(2–3):103–108
Pawlak Z (1997) Rough set approach to knowledge-based decision support. Eur J Oper Res 99(1):48–57
Rafie M, Namin FS (2015) Prediction of subsidence risk by FMEA using artificial neural network and fuzzy inference system. Int J Min Sci Technol 25(4):655–663
Rahman K (2023) Multiple attribute group decision-making based on generalized interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy Einstein geometric aggregation operators. Granular Comput 8(2):293–310
Sarwar M (2020) Decision-making approaches based on color spectrum and D-TOPSIS method under rough environment. Comput Appl Math 39(4):1–32
Sarwar M (2022) Decision making model for design concept evaluation based on interval rough integrated cloud VIKOR. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 14(4):3875–3897
Sarwar M (2023) Improved assessment model for health-care waste management based on dual 2-tuple linguistic rough number clouds. Eng Appl Artif Intell 123:106255
Sarwar M, Akram M, Liu P (2021) An integrated rough ELECTRE II approach for risk evaluation and effects analysis in automatic manufacturing process. Artif Intell Rev 54(6):4449–4481
Sarwar M, Zafar F, Akram M (2023) Novel group decision making approach based on the rough soft approximations of graphs and hypergraphs. J Appl Math Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-023-01855-x
Sarwar M, Ali G, Chaudhry NR (2023a) Decision-making model for failure modes and effect analysis based on rough fuzzy integrated clouds. Appl Soft Comput 110148
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1963) Mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press Urbana
Sharma V, Sharma V, Karwasra K (2021) A decision framework for green manufacturing indicators using fuzzy AHP-ELECTRE I: a case study of the steering system manufacturer. Int J Sustain Eng 14(6):1332–1341
Singh H, Gupta MM, Meitzler T, Hou ZG, Garg KK, Solo AM, Zadeh LA (2013) Real-life applications of fuzzy logic. Adv Fuzzy Syst 2013 Article ID 581879 3 pages
Song W, Ming X, Wu Z, Zhu B (2014) A rough TOPSIS approach for failure mode and effects analysis in uncertain environments. Qual Reliab Eng Int 30(4):473–486
Song W, Zhu Y, Zhou J, Chen Z, Zhou J (2022) A new rough cloud AHP method for risk evaluation of public-private partnership projects. Soft Comput 26(4):2045–2062
Verma R, Rohtagi B (2022) Novel similarity measures between picture fuzzy sets and their applications to pattern recognition and medical diagnosis. Granular Comput 7(4):761–777
Wan SP, Xu GL, Dong JY (2017) Supplier selection using ANP and ELECTRE II in interval 2-tuple linguistic environment. Inf Sci 385:19–38
Wan N, Li L, Ye C, Wang B (2019) Risk assessment in intelligent manufacturing process: a case study of an optical cable automatic arranging robot. IEEE Access 7:105892–901
Wang YJ, Seggelke S, Hawkins RM, Gibbs J, Lindsay M, Hazlett I, Wang CCL, Rasouli N, Young KA, Draznin B (2016) Impact of glucose management team on outcomes of hospitalizaron in patients with type 2 diabetes admitted to the medical service. Endocr Pract 22(12):1401–1405
Yu J, Zeng Q, Yu Y, Wu S, Ding H, Ma W, Gao H, Yang J (2023) Failure mode and effects analysis based on rough cloud model and MULTIMOORA method: application to single-point mooring system. Appl Soft Comput 132:109841
Zahid K, Akram M, Kahraman C (2022) A new ELECTRE-based method for group decision-making with complex spherical fuzzy information. Knowl-Based Syst 243:108525
Zhai LY, Khoo LP, Zhao-Wei Z (2008) A rough set enhanced fuzzy approach to quality function deployment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37(5–6):613–624
Zhai LY, Khoo LP, Zhong ZW (2009) Design concept evaluation in product development using rough sets and grey relation analysis. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):7072–7079
Zhang R, Xu Z, Gou X (2023) ELECTRE II method based on the cosine similarity to evaluate the performance of financial logistics enterprises under double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 22(1):23–49
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang J (2014) Objective attributes weights determining based on shannon information entropy in hesitant fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Math Prob Eng 2014 Article ID 463930 7 pages
Zhou X, Tang Y (2018) Modeling and fusing the uncertainty of FMEA experts using an entropy-like measure with an application in fault evaluation of aircraft turbine rotor blades. Entropy 20(11):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20110864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and WG: concept, design, analysis, modeling, writing, modifications, and corrections of the manuscript. SA: proof reading of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sarwar, M., Gulzar, W. & Ashraf, S. Improved risk assessment model based on rough integrated clouds and ELECTRE-II method: an application to intelligent manufacturing process. Granul. Comput. 8, 1533–1560 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-023-00385-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-023-00385-y