Abstract
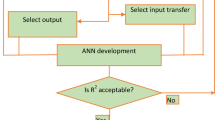
In this study, the multilayer perceptron (MLP) model underwent optimization using evolutionary artificial intelligence algorithms. This optimization was further enhanced by integrating the Evaporation Rate-based Water Cycle Algorithm (ER-WCA). This integrated approach resulted in a refined technique employed to forecast the load-settlement behavior of shallow footings located near slopes. Addressing this intricate engineering challenge necessitates a comprehensive approach, considering various input variables such as unit weight (UW) (kN/m3), elastic modulus (EM) (kN/m2), friction angle (FA), dilation angle (DA), Poisson's ratio (PR) (v), and setback distance (SD) (m). To construct the requisite dataset, finite element analysis was conducted. Throughout the model's implementation, it became apparent that the hybrid model’s performance was notably influenced by the population size parameter in ER-WCA (R2 = 0.9964 and 0.99631, RMSE = 20.4937 and 19.53741). Consequently, the proposed hybrid model demonstrated significant potential in accurately predicting the vertical load necessary to achieve a specific footing settlement.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moayedi H, Moatamediyan A, Nguyen H, Bui XN, Bui DT, Rashid ASA (2020) Prediction of ultimate bearing capacity through various novel evolutionary and neural network models. Eng Comput 36(2):671–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00723-2
Abbaszadeh Shahri A, Shan C, Larsson S (2022) A novel approach to uncertainty quantification in groundwater table modeling by automated predictive deep learning. Nat Resour Res 31(3):1351–1373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-022-10051-w
Meyerhof GG, Hanna AM (1978) Ultimate bearing capacity of foundations on layered soils under inclined load. Can Geotech J 15(4):565–572. https://doi.org/10.1139/t78-060
Florkiewicz A (1989) Upper bound to bearing capacity of layered soils. Can Geotech J 26(4):730–736. https://doi.org/10.1139/t89-084
Lotfizadeh MR, Kamalian M (2016) Estimating bearing capacity of strip footings over two-layered sandy soils using the characteristic lines method. Int J Civ Eng 14:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-016-0015-4
Moayedi H, Nazir R, Ghareh S, Sobhanmanesh A, Tan YC (2018) Performance analysis of a piled raft foundation system of varying pile lengths in controlling angular distortion. Soil Mech Found Eng 55:265–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-018-9535-z
Mosallanezhad M, Moayedi H (2017) Developing hybrid artificial neural network model for predicting uplift resistance of screw piles. Arab J Geosci 10(22):479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3285-5
Mosallanezhad M, Moayedi H (2017) Comparison analysis of bearing capacity approaches for the strip footing on layered soils. Arab J Sci Eng 42(9):3711–3722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2490-6
Nazir R, Moayedi H, Subramaniam P, Gue SS (2018) Application and design of transition piled embankment with surcharged prefabricated vertical drain intersection over soft ground. Arab J Sci Eng 43(4):1573–1582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2628-6
Ghaderi A, Abbaszadeh Shahri A, Larsson S (2022) A visualized hybrid intelligent model to delineate Swedish fine-grained soil layers using clay sensitivity. CATENA 214:106289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106289
Ranjan G and A Rao (2007) Basic and applied soil mechanics: New Age International
Das BM and N.Sivakugan (2018) Principles of foundation engineering. Cengage learning
Moayedi H, Hayati S (2018) Modelling and optimization of ultimate bearing capacity of strip footing near a slope by soft computing methods. Appl Soft Comput 66:208–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.02.027
Moayedi H, Jahed Armaghani D (2018) Optimizing an ANN model with ICA for estimating bearing capacity of driven pile in cohesionless soil. Eng Comput 34:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0545-7
Dehghanbanadaki A, Khari M, Amiri ST, Armaghani DJ (2021) Estimation of ultimate bearing capacity of driven piles in c-φ soil using MLP-GWO and ANFIS-GWO models: a comparative study. Soft Comput 25:4103–4119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05435-0
Moayedi H, Mosallanezhad M (2017) Uplift resistance of belled and multi-belled piles in loose sand. Measurement 109:346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.06.001
Dimitrov D, Abdo H (2019) Tight independent set neighborhood union condition for fractional critical deleted graphs and ID deleted graphs. Discrete Continuous Dyn Syst 12(4&5):711–721. https://doi.org/10.3934/dcdss.2019045
Gao W, Guirao JLG, Abdel-Aty M, Xi W (2019) An independent set degree condition for fractional critical deleted graphs. Discrete Continuous Dyn Syst 12(4&5):877–886. https://doi.org/10.3934/dcdss.2019058
Gao W, Wu H, Siddiqui MK, Baig AQ (2018) Study of biological networks using graph theory. Saudi J Biol Sci 25(6):1212–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.022
Özsoy M, Kaplan O, Akar M (2024) FEM-based analysis of rotor cage material and slot geometry on double air gap axial flux induction motors. Ain Shams Eng J 15(2):102393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2023.102393
Ocak C (2023) A FEM-based comparative study of the effect of rotor bar designs on the performance of squirrel cage induction motors. Energies 16(16):6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16166047
Ai ZY, Chen YF (2020) FEM-BEM coupling analysis of vertically loaded rock-socketed pile in multilayered transversely isotropic saturated media. Comput Geotech 120:103437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103437
Dehghanbanadaki A, Motamedi S, Ahmad K (2020) FEM-based modelling of stabilized fibrous peat by end-bearing cement deep mixing columns. Geomech Eng 20(1):75–86. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2019.20.1.075
Amiri ST, Dehghanbanadaki A, Nazir R, Motamedi S (2020) Unit composite friction coefficient of model pile floated in kaolin clay reinforced by recycled crushed glass under uplift loading. Transp Geotech 22:100313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2019.100313
Ismail A, Jeng DS (2011) Modelling load–settlement behaviour of piles using high-order neural network (HON-PILE model). Eng Appl Artif Intell 24(5):813–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2011.02.008
Abbaszadeh Shahri A, Pashamohammadi F, Asheghi R, Abbaszadeh Shahri H (2022) Automated intelligent hybrid computing schemes to predict blasting induced ground vibration. Eng Comput 38(Suppl 4):3335–3349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01444-1
Sarkar G, Siddiqua S, Banik R, Rokonuzzaman M (2015) Prediction of soil type and standard penetration test (SPT) value in Khulna City, Bangladesh using general regression neural network. Q J Eng GeolHydrogeol 48(3–4):190–203. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2014-108
Abbaszadeh Shahri A, Asheghi R, Khorsand Zak M (2021) A hybridized intelligence model to improve the predictability level of strength index parameters of rocks. Neural Comput Appl 33(8):3841–3854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05223-9
Acharyya R, Dey A, Kumar B (2018) Finite element and ANN-based prediction of bearing capacity of square footing resting on the crest of c-φ soil slope. Int J Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2018.1435022
Padmini D, Ilamparuthi K, Sudheer KP (2008) Ultimate bearing capacity prediction of shallow foundations on cohesionless soils using neurofuzzy models. Comput Geotech 35(1):33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2007.03.001
Alavi AH, Sadrossadat E (2016) New design equations for estimation of ultimate bearing capacity of shallow foundations resting on rock masses. Geosci Front 7(1):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2014.12.005
Asheghi R, Hosseini SA, Saneie M, Shahri AA (2020) Updating the neural network sediment load models using different sensitivity analysis methods: a regional application. J Hydroinf 22(3):562–577. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2020.098
Nguyen H, Mehrabi M, Kalantar B, Moayedi H (2019) Potential of hybrid evolutionary approaches for assessment of geo-hazard landslide susceptibility mapping. Geomat Nat Haz Risk. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2019.1607782
Moayedi H, Raftari M, Sharifi A, Jusoh WAW, Rashid ASA (2020) Optimization of ANFIS with GA and PSO estimating α ratio in driven piles. Eng Comput 36(1):227–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-00694-w
Harandizadeh H, Toufigh MM, Toufigh V (2019) Application of improved ANFIS approaches to estimate bearing capacity of piles. Soft Comput 23:9537–9549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3517-y
Moayedi H, Nguyen H, Rashid ASA (2021) Novel metaheuristic classification approach in developing mathematical model-based solutions predicting failure in shallow footing. Eng Comput 37(1):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00819-9
Moayedi H, Abdullahi MAM, Nguyen H, Rashid ASA (2021) Comparison of dragonfly algorithm and Harris hawks optimization evolutionary data mining techniques for the assessment of bearing capacity of footings over two-layer foundation soils. Eng Comput 37:437–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00834-w
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5(4):115–133
Zahmatkesh S, Karimian M, Chen Z, Ni BJ (2024) Combination of coagulation and adsorption technologies for advanced wastewater treatment for potable water reuse: By ANN, NSGA-II, and RSM. J Environ Manag 349:119429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119429
Wu D, Li S, Moayedi H, Cifci MA, Li BN (2022) ANN-Incorporated satin bowerbird optimizer for predicting uniaxial compressive strength of concrete. Steel Compos Struct 45(2):281–291
Zhao W, Li H, Wang S (2022) An ANN-based generic energy model of cleanroom air-conditioning systems for high-tech fabrication location and technology assessments. Appl Therm Eng 216:119099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.119099
Kolivand H, Joudaki S, Sunar MS, Tully D (2021) A new framework for sign language alphabet hand posture recognition using geometrical features through artificial neural network (part 1). Neural Comput Appl 33(10):4945–4963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05279-7
Kolivand H, Joudaki S, Sunar MS, Tully D (2021) An implementation of sign language alphabet hand posture recognition using geometrical features through artificial neural network (part 2). Neural Comput Appl 33(20):13885–13907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06025-3
Dehghanbanadaki A, Rashid ASA, Ahmad K, Yunus NZM, Said KNM (2022) A computational estimation model for the subgrade reaction modulus of soil improved with DCM columns. Geomech Eng 28(4):385–396. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2022.28.4.385
Keshtkarbanaeemoghadam A, Dehghanbanadaki A, Kaboli MH (2018) Estimation and optimization of heating energy demand of a mountain shelter by soft computing techniques. Sustain Cities Soc 41:728–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.06.008
Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Bahreininejad A, Kim JH (2015) Water cycle algorithm with evaporation rate for solving constrained and unconstrained optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 30:58–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.050
Foong LK, Moayedi H, Lyu Z (2021) Computational modification of neural systems using a novel stochastic search scheme, namely evaporation rate-based water cycle algorithm: an application in geotechnical issues. Eng Comput 37:3347–3358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01000-3
Alweshah M, Al-Sendah M, Dorgham OM, Al-Momani A, Tedmori S (2020) Improved water cycle algorithm with probabilistic neural network to solve classification problems. Clust Comput 23:2703–2718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-03038-5
Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Lee HM, Yoo DG, Kim JH (2016) Water cycle algorithm: a detailed standard code. SoftwareX 5:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2016.03.001
Moayedi H, Mehrab M, Mosallanezhad M, Rashid ASA, Pradhan B (2019) Modification of landslide susceptibility mapping using optimized PSO-ANN technique. Eng Comput 35:967–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0644-0
Dehghanbanadaki A (2021) Intelligent modelling and design of soft soil improved with floating column-like elements as a road subgrade. Transp Geotech 26:100428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2020.100428
Dehghanbanadaki A, Khari M, Arefnia A, Ahmad K, Motamedi S (2019) A study on UCS of stabilized peat with natural filler: a computational estimation approach. KSCE J Civ Eng 23:1560–1572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0343-4
Khari M, Dehghanbanadaki A, Motamedi S, Armaghani DJ (2019) Computational estimation of lateral pile displacement in layered sand using experimental data. Measurement 146:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.04.081
Abbaszadeh Shahri A, Chunling S, Larsson S (2023) A hybrid ensemble-based automated deep learning approach to generate 3D geo-models and uncertainty analysis. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-023-01852-5
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res Atmosph 106(D7):7183–7192. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900719
Prakash S, Kumar S, Rai B (2024) A new technique based on the gorilla troop optimization coupled with artificial neural network for predicting the compressive strength of ultrahigh performance concrete. Asian J Civ Eng 25(1):923–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00822-y
Kassaymeh S, Alweshah M, Al-Betar MA, Hammouri AI (2024) Software effort estimation modeling and fully connected artificial neural network optimization using soft computing techniques. Clust Comput 27(1):737–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-03979-y
Şener R, Koç MA, Ermiş K (2024) Hybrid ANFIS-PSO algorithm for estimation of the characteristics of porous vacuum preloaded air bearings and comparison performance of the intelligent algorithm with the ANN. Eng Appl Artif Intell 128:107460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107460
Dehghanbanadaki A, Motamedi S (2023) Bearing capacity prediction of shallow foundation on sandy soils: a comparative study of analytical, FEM, and machine learning approaches. Multiscale Multidiscip Model Exp Des. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-023-00280-8
Mughal SN, Sood YR, Jarial RK (2024) Techno-economic assessment of photovoltaics by predicting daily global solar radiations using hybrid ANN-PSO model. Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-023-00646-4
Sangdeh MK, Salimi M, Khansar HH, Dokane M, Ranjbar PZ, Payan M, Arabani M (2024) Predicting the precipitated calcium carbonate and unconfined compressive strength of bio-mediated sands through robust hybrid optimization algorithms. Transp Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2024.101235
Bahmed IT, Khatti J, Grover KS (2024) Hybrid soft computing models for predicting unconfined compressive strength of lime stabilized soil using strength property of virgin cohesive soil. Bull Eng Geol Env 83(1):46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03537-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raftari, M., Joudaki, S. Evaluation of load-settlement behavior of shallow footings using hybrid MLP-evolutionary AI approach with ER-WCA optimization. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 9, 203 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-024-01514-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-024-01514-5