Abstract
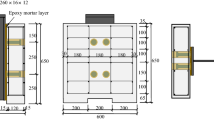
Headed stud is well-known shear connector, which is usually welded to the steel beam of the composite beams to connect the steel beam to the concrete slab to achieve the required composite action and limits the interface slip. Despite the efficiency of using the headed studs for Hot-Rolled Steel beams and steel plate girders, the application of headed studs may not be practical for very thin beam section such as cold-formed steel (CFS) sections due to the limitation of welding of the thin-walled steel sections. Thus, this study proposes innovative shear connector systems for composite cold-formed steel–concrete beams. The behaviour of the shear connector systems, including embedded CFS beam with/without holes, U-shaped steel bar embedded from top, embedded CFS beam and steel bar at the sides, embedded CFS beam with Bent-up tabs, and brackets at the top and bottom, were experimentally investigated through push-out tests in accordance with Eurocode 4 using 8 specimens of composite beam using different orientation. Experimental tests were aimed to determining the maximum resistance of the proposed shear connectors. The results indicated that the strength of a shear connector was very reliant on its deformation and the crushing of concrete. The ductile behaviour of most of the tested shear connectors satisfied the ductility requirements of Eurocode 4. In this study, it was concluded that the proposed shear connectors are suitable for the construction of composite beams with CFS.





















































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hancock GJ, Murray T, Ellifrit DS, Cold-formed steel structures to the AISI specification. CRC, 2001
Tahir MM et al (2011) Finite element analysis of flush end-plate connections connected to column web. Int J Steel Struct 11(3):247
Lawan MM, Tahir MM, Osman MH (2015) Composite construction of cold-formed steel (CFS) section with high strength bolted shear connector. Jurnal Teknologi 77(16):171–179
Yu WW, LaBoube RA, Chen H (2019) Cold-formed steel design. Wiley.
Bamaga SO et al (2013) Feasibility of developing composite action between concrete and cold-formed steel beam. J Central South Univ 20(12):3689–3696
Lakkavalli BS, Liu Y (2006) Experimental study of composite cold-formed steel C-section floor joists. J Constr Steel Res 62(10):995–1006
Bamaga SO et al (2019) Push-out tests on three innovative shear connectors for composite cold-formed steel concrete beams. Constr Build Mater 223:288–298
Salih MN et al (2018) Behavior of boxed cold-formed steel as composite beam with rebar as shear connector. In International congress and exhibition. Sustainable civil infrastructures: innovative infrastructure geotechnology. Springer.
Lawan MM, Tahir MM, Mirza J (2016) Bolted shear connectors performance in self-compacting concrete integrated with cold-formed steel section. Latin Am J Solids Struct 13(4):731–749
Kam CZ et al (2012) Flexural performance of laminated composite plates with diagonally perturbed localized delamination. Adv Sci Lett 14(1):455–457
Mohamad M et al (2015) Friction and cohesion coefficients of composite concrete-to-concrete bond. Cement Concr Compos 56:1–14
Mazoz A, Benanane A, Titoum M (2013) Push-out tests on a new shear connector of I-shape. Int J Steel Struct 13(3):519–528
Titoum M et al (2016) Experimental study and finite element modelling of push-out tests on a new shear connector of I-shape. Adv Steel Construct 12:487–506
Lawson R, Popo-Ola S, Varley D. Innovative development of light steel composite in buildings. In: International symposium on connections between steel and concrete. 2001.
Hanaor A (2000) Tests of composite beams with cold-formed sections. J Constr Steel Res 54(2):245–264
Bezerra LM et al (2018) V-shaped shear connector for composite steel-concrete beam. J Constr Steel Res 150:162–174
Lawan MM, Tahir MM, Hosseinpour E (2016) Feasibility of using bolted shear connector with cold-formed steel in composite construction. J Teknol 78:6–12
Nguyen RP (1991) Thin-walled, cold-formed steel composite beams. J Struct Eng 117(10):2936–2952
Anwar Hossain K (2005) Designing thin-walled composite-filled beams. Proc Institut Civil Eng-Struct Build 158(4):267–278
Irwan J et al (2011) Large-scale test of symmetric cold-formed steel (CFS)–concrete composite beams with BTTST enhancement. J Constr Steel Res 67(4):720–726
Irwan J, Hanizah A, Azmi I (2009) Test of shear transfer enhancement in symmetric cold-formed steel–concrete composite beams. J Constr Steel Res 65(12):2087–2098
Irwan M, et al (2008) Shear transfer enhancement in precast cold-formed steel-concrete composite beams: effect of bent-up tabs types and angles. in Technology and Innovation for Sustainable Development Conference, (28–29 January, Thailand).
Saggaff A et al (2015) Experimental and analytical study of various shear connectors used for cold-formed steel-ferrocement composite beam. In: Applied Mechanics and Materials. Trans Tech Publ.
Wehbe N et al (2011) Development of concrete/cold formed steel composite flexural members. In: Structures Congress.
Standardization ECF (2004) Eurocode 4: design of composite steel and concrete structures. European Committee For Standardization, Brussels
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Institute of Smart Infrastructure and Innovative Construction (ISIC) at Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. The author gratefully acknowledges the support provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Ahmed Almassri reports financial support was provided by University of Technology Malaysia. Ahmed Almassri reports a relationship with University of Technology Malaysia that includes: funding grants.
Ethical statement
This material is the authors' own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Almassri, A.N.M., Tahir, M.M., Saggaff, A. et al. Shear connector systems for composite beam with cold-formed steel of lipped C-channel section. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 8, 91 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-023-01040-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-023-01040-w