Abstract
This paper explores the feasibility of using 100% recycled fine aggregate in concrete to meet strength requirements for various applications in sustainable construction. The physical and mechanical characteristics including: aggregate strength, gradation, absorption, specific gravity, shape and texture, play crucial roles in determining concrete strength. The quality of recycled aggregate is generally influenced by the loading and exposure conditions of demolished structures. The experimental program focused on assessing the mechanical properties of recycled aggregate over a 3-month period, incorporating cement of OPC 53 grade, Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS), and Novel Additive (NA).
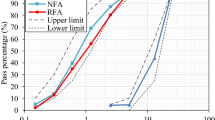
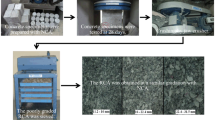
The study evaluated concrete properties when utilizing both fine and coarse recycled aggregate. Various concrete mixes were formulated, featuring 100% recycled fine aggregate (RFA) with varying proportions of recycled coarse aggregate (RCA) from 0 to 100%. These results were compared to those of a control mix. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) was employed to analyze the microstructure of selected mixes. The findings indicated that concrete with satisfactory strength could be achieved through the partial replacement of RCA with Natural Coarse Aggregate (NCA) using 10% NA in the 100% RFA concrete mix in Rheodynamic flowable concrete (Rd-FC).
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Provided in the manuscript.
References
Nedeljkovic M, Visser J, Savija B, Valcke S, Schlangen E (2021) Use of fine recycled concrete aggregates in concrete: A critical review. J Build Eng 38:102196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102196
Djelloul OK, Menadi B, Wardehand G, Kenai S (2018) Performance of self-compacting concrete made with coarse and fine recycled concrete aggregates and ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Adv Concr Constr 6(2):103. https://doi.org/10.12989/acc.2018.6.2.103
Ahmed S, El-Zohairy A, Eisa AS, Mohamed MAEB, Abdo A (2023) Experimental Investigation of Self-Compacting Concrete with Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Buildings. 13(4):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13040856 (https://www.mdpi.com/journal/buildings)
Kumar P, Singh N (2023) Performance of recycled concrete aggregates based self-compacting concrete containing coal combustion ashes and silica fume. Eur J Environ Civil Eng 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2023.2293816
Gandhi S, Dutta AK, Prakash Arul Jose J, Thenmozhi S, Senthil kumar SP, Balkrishna Gorade S (2023) Mechanical Properties of Self Compacting Concrete with Recycled Coarse Aggregate. Eur Chem Bull 2023. https://www.eurchembull.com/uploads/paper/efca874b345a43cde12a7a2593a7c9df.pdf
Revilla-Cuesta V, Ortega-Lóppez V, Skaf M, Khan AR, Manso JM (2022) Deformational behavior of self-compacting concrete containing recycled aggregate, slag cement and green powders under compression and bending: Description and prediction adjustment. J Build Eng 54:104611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104611
Zaid O, Zamir Hashmi SR (2021) Experimental Study on Mechanical Performance of Recycled Fine Aggregate Concrete Reinforced with Discarded Carbon Fibres. Front Mater 8:771423. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2021.771423
Singh RB, Kapoor K, Singh A, Singh B (2023) Rheology of self-compacting concrete containing silica fume and recycled aggregates. Eur J Environ Civil Eng 28(7):1483–1500. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2023.2259965
Wang Y, Zhao B, Yang G, Jia Y, Yang L, Li M, Tang X, Huang Z, Sun J, Shen W (2019) Effect of recycled coarse aggregate on the properties of C40 self-compacting concrete. Adv Compos Lett. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963693519885128
Tang WC, Ryan PC, Cui HZ, Liao W (2016) Properties of self-compacting concrete with recycled coarse aggregate. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2016:11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2761294
Pandaa KC, Balb PK (2013) Properties of Self Compacting Concrete Using Recycled Coarse Aggregate. Procedia Eng 51:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROENG.2013.01.023
Boudali S, Kerdal DE, Ayed K, Soliman AM (2016) Performance of self-compacting concrete incorporating recycled concrete fines and aggregate exposed to sulphate attack. Constr Build Mater 124:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.058
Martínez-García R, Guerra-Romero MI, Morán-Del Pozo JM, Brito J, Juan-Valdés A (2020) Recycling Aggregates for Self-Compacting Concrete Production: A Feasible Option. Materials (Basel) 13:868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040868
Señas L, Priano C, Marfil S (2016) Influence of recycled aggregates on properties of self-consolidating concretes. Constr Build Mater 113:498–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.079
Kapoor K, Singh SP, Singh B (2016) Durability of self-compacting concrete made with Recycled Concrete Aggregates and mineral admixtures. Constr Build Mater 128:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.10.026
Mane KM, Kulkarni DK (2020) Prediction of shear strength of concrete produced by using pozzolanic materials and partly replacing NFA by MS using ANN. J Eng Des Technol 19:578–587. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEDT-12-2019-0346
Karri SK, Ponnada MR, Veerni L (2021) Durability and microstructure study of alkali-activated slag concrete with quartz sand subjected to different exposure conditions. J Eng Des Technol 22:42–59. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEDT-09-2021-0477
Albostami AS, Al-Hamd RKS, Alzabeebee S, Minto A, Keawsawasvong S (2023) Application of soft computing in predicting the compressive strength of self-compacted concrete containing recyclable aggregate. Asian J Civil Eng 25:183–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00767-2
Bostanci SC, Limbachiya M, Kew H (2016) Portland-composite and Composite cement concrete made with coarse recycled and recycled glass sand aggregates: Engineering and durability properties. Elsevier (http://creativecommons.org/about/downloads)
Ali B, Qureshi LA, Nawaz MA, Aslam HMU (2019) Combined Influence of Fly Ash and Recycled Coarse Aggregates on Strength and Economic Performance of Concrete. Civil Eng J 5(4):832–844. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2019-03091292
Rahal K (2007) Mechanical properties of concrete with recycled coarse aggregate. Build Environ 42:407–415
Yehia S, Helal K, Abusharkh A, Zaher A, Istaitiyeh H (2015) Strength and Durability Evaluation of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Int J Concr Struct Mater 9:219–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40069-015-0100-0
Nawaz MA, Qureshi LA, Ali B (2021) Enhancing the Performance of Recycled Aggregate Mortars Using Alkali-Activated Fly Ash. KSCE J Civil Eng 25(2):552–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0260-6
Funding
No.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
1. Experiment.
2. Methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval is obtained.
Consent to participate
Consent to participate is obtained from all.
Consent to publish
Consent to participate is obtained from all.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
M, A., Mourougane, R. Microscale investigation of mechanical characteristics: enhancing sustainable strength in concrete through the use of recycled aggregates. J Build Rehabil 9, 87 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41024-024-00435-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41024-024-00435-1