Abstract
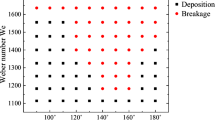
In this paper, the displacement and deformation of a two-dimensional droplet on a vertical wall are examined using a modified pseudopotential model and imposing the multi-relaxation time into the collision term. The selected model guarantees the thermodynamic consistency adjusting proper values for the constant of the potential function k and the weighting factor for the force term, A. Also, it is possible to add adhesion forces and create different contact angles defining the index function for the solid points. Accordingly, non-dimensional parameters of Reynolds number, Weber number, Froude number, and density ratio are defined under the influence of the gravitational force and the uniform vapor flow. Results show that the change of the each dimensionless numbers affects the slip ratio between the droplet and vapor. It is also observed that in addition to the effects of viscous and gravitational forces, the change of the contact angle plays a significant role in the displacement and velocity of the droplet. The results show that reducing the contact angle increases the surface wettability and decreases the droplet velocity. It is seen that by decreasing the intermolecular forces at the Weber number of 62.36 and contact angle of 150°, the droplet begins to decay. Also, it is concluded that the droplet rubbing on the solid surface weakens the slip ratio in all cases.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhardwaj S, Dalal A (2018) Mesoscopic analysis of three-dimensional droplet displacement on wetted grooved wall of a rectangular channel. Eur J Mech-B/Fluids 67:35–53
Binesh A, Mousavi S, Kamali R (2015) Effect of temperature-dependency of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluid properties on the dynamics of droplet impinging on hot surfaces. Int J Mod Phys C 26(9):1550106
Chen L, Kang Q, Mu Y, He Y-L, Tao W-Q (2014) A critical review of the pseudopotential multiphase lattice Boltzmann model: methods and applications. Int J Heat Mass Transf 76:210–236
Gunstensen AK, Rothman DH, Zaleski S, Zanetti G (1991) Lattice Boltzmann model of immiscible fluids. Phys Rev A 43(8):4320
He X, Shan X, Doolen GD (1998) Discrete Boltzmann equation model for nonideal gases. Phys Rev E 57(1):R13
Huang H, Sukop M, Lu X (2015) Multiphase lattice Boltzmann methods: theory and application. Wiley
Kang Q, Zhang D, Chen S (2002) Displacement of a two-dimensional immiscible droplet in a channel. Phys Fluids 14(9):3203–3214
Kang Q, Zhang D, Chen S (2005) Displacement of a three-dimensional immiscible droplet in a duct. J Fluid Mech 545:41–66
Khojasteh D, Mousavi SM, Kamali R (2017) CFD analysis of Newtonian and non-Newtonian droplets impinging on heated hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Indian J Phys 91(5):513–520
Khojasteh D, Manshadi MKD, Mousavi SM, Sotoudeh F, Kamali R, Bordbar A (2020) Electrically modulated droplet impingement onto hydrophilic and (super) hydrophobic solid surfaces. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(4):1–11
Kupershtokh A (2003) Calculations of the action of electric forces in the lattice Boltzmann equation method using the difference of equilibrium distribution functions. In: Proc. 7th int. conf. on modern problems of electrophysics and electrohydrodynamics of liquids. St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg, pp 155–155
Kupershtokh A (2004) New method of incorporating a body force term into the lattice Boltzmann equation. In: Proc. 5th international EHD workshop. University of Poitiers, Poitiers, pp 241–246
Kupershtokh A, Stamatelatos C, Agoris D (2005) Stochastic model of partial discharge activity in liquid and solid dielectrics. In: IEEE international conference on dielectric liquids, 2005. ICDL. IEEE, pp 135–138
Kupershtokh A, Karpov D, Medvedev D, Stamatelatos C, Charalambakos V, Pyrgioti E, Agoris D (2007) Stochastic models of partial discharge activity in solid and liquid dielectrics. IET Sci Meas Technol 1(6):303–311
Kupershtokh A, Medvedev D, Karpov D (2009) On equations of state in a lattice Boltzmann method. Comput Math Appl 58(5):965–974
Kupershtokh AL, Medvedev DA, Gribanov II (2018) Thermal lattice Boltzmann method for multiphase flows. Phys Rev E 98(2):023308
Mazloomi A, Moosavi A (2013) Thin liquid film flow over substrates with two topographical features. Phys Rev E 87(2):022409
Mohamad A (2011) Lattice Boltzmann method. Springer
Nemati M, Abady ARSN, Toghraie D, Karimipour A (2018) Numerical investigation of the pseudopotential lattice Boltzmann modeling of liquid–vapor for multi-phase flows. Phys A 489:65–77
Shabankareh IZ, Mousavi SM, Kamali R (2017) Numerical study of non-Newtonian droplets electrocoalescence. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 39(10):4207–4217
Shan X, Chen H (1993) Lattice Boltzmann model for simulating flows with multiple phases and components. Phys Rev E 47(3):1815
Son S, Chen L, Derome D, Carmeliet J (2015) Numerical study of gravity-driven droplet displacement on a surface using the pseudopotential multiphase lattice Boltzmann model with high density ratio. Comput Fluids 117:42–53
Swift MR, Osborn W, Yeomans J (1995) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of nonideal fluids. Phys Rev Lett 75(5):830
Taghilou M, Rahimian MH (2014) Investigation of two-phase flow in porous media using lattice Boltzmann method. Comput Math Appl 67(2):424–436
Zhang R, Chen H (2003) Lattice Boltzmann method for simulations of liquid-vapor thermal flows. Phys Rev E 67(6):066711
Zhang L-Z, Yuan W-Z (2018) A lattice Boltzmann simulation of coalescence-induced droplet jumping on superhydrophobic surfaces with randomly distributed structures. Appl Surf Sci 436:172–182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taghilou, M., Zarei, S. LBM Investigation of the Droplet Displacement and Rubbing on a Vertical Wall by a Modified Pseudopotential Model. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 45, 755–768 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-021-00435-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-021-00435-3