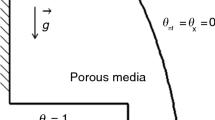
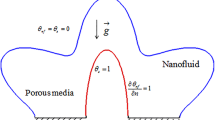
Abstract
Computational modelling for nanoparticle migration inside a permeable space has been reported. Impacts of shape factor and radiation were included in the mathematical model. CVFEM was employed to analyse magnetic force impact. Impacts of magnetic radiative parameters, buoyancy forces and nanoparticle shape on nanomaterial behaviour were demonstrated. Utilizing the Darcy model helps us to predict the behaviour of porous media. Outputs revealed higher convective mode can be achieved with augmenting buoyancy force while opposite outcome appears when magnetic field is imposed. Thermal plume vanishes with the rise of conductive mode which is gained as Hartmann increases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelsalam S, Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Riaz A, Beg OA (2019a) Metachronal propulsion of a magnetized particle-fluid suspension in a ciliated channel with heat and mass transfer. Phys Scr 94(11):1–10
Alkanhal TA, Sheikholeslami M, Usman M, Rizwan-ul Haq, Shafee A, Al-Ahmadi AS, Tlili I (2019a) Thermal management of MHD nanofluid within the porous medium enclosed in a wavy shaped cavity with square obstacle in the presence of radiation heat source. Int J Heat Mass Transf 139:87–94
Alkanhal TA, Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Rizwan-ul Haq, Shafee A, Li Z, Tlili I (2019b) Simulation of convection heat transfer of magnetic nanoparticles including entropy generation using CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf 136:146–156
Bhatti MM, Lu DQ (2019) Analytical study of the head-on collision process between hydroelastic solitary waves in the presence of a uniform current. Symmetry 11(3):333
Bhatti MM, Sheikholeslami M, Shahid A, Hassan M, Abbas T (2019a) Entropy generation on the interaction of nanoparticles over a stretched surface with thermal radiation. Colloids Surf A 570:368–376
Bhatti MM, Yousif MA, Mishra SR, Shahid A (2019b) Simultaneous influence of thermo-diffusion and diffusion-thermo on non-Newtonian hyperbolic tangent magnetised nanofluid with Hall current through a nonlinear stretching surface. Pramana 93(6):88
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. J Heat Transf Trans ASME 128:240–250
Chon CH, Kihm KD, Lee SP, Choi SUS (2005) Empirical correlation finding the role of temperature and particle size for nanofluid (Al2O3) thermal conductivity enhancement. Appl Phys Lett 87(2005):1531071–1531073
Ellahi R, Hassan M, Zeeshan A (2017) Shape effects of spherical and nonspherical nanoparticles in mixed convection flow over a vertical stretching permeable sheet. Mech Adv Mater Struct 24(15):1231–1238
Ellahi R, Sait SM, Shehzad N, Mobin N (2019) Numerical simulation and mathematical modeling of electro-osmotic Couette-Poiseuille flow of MHD power-law nanofluid with entropy generation. Symmetry 11(8):1038
Hamilton RL, Crosser OK (1962) Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. EC Fundam 1:187–191
Hassan M, Marin M, Ellahi R, Alamri SZ (2018) Exploration of convective heat transfer and flow characteristics synthesis by Cu-Ag/water hybrid-nanofluids. Heat Transfer Research 49(18):1837–1848
Hassan M, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Bhatti MM (2019) Analysis of natural convective flow of non-Newtonian fluid under the effects of nanoparticles of different materials. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part E J Process Mech Eng 233(3):643–652
Hedayat M, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Henda MB, Tlili I, Li Z (2019) Investigation of nanofluid conduction heat transfer within a triplex tube considering solidification. J Mol Liq 290:111232
Izadi M, Behzadmehr A, Shahmardan MM (2013) Richardson number ratio effect on laminar mixed convection of a nanofluid flow in an annulus. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech 14(4)
Izadi M, Shahmardan MM, Norouzi M, Rashidi AM, Behzadmehr A (2014) Cooling performance of a nanofluid flow in a heat sink microchannel with axial conduction effect. Appl Phys A 117(4):1821–1833
Izadi M, Mehryan SAM, Sheremet MA (2018a) Natural convection of CuO-water micropolar nanofluids inside a porous enclosure using local thermal non-equilibrium condition. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 88:89–103
Izadi M, Mohebbi R, Chamkha A, Pop I (2018b) Effects of cavity and heat source aspect ratios on natural convection of a nanofluid in a C-shaped cavity using Lattice Boltzmann method. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow 28(8):1930–1955. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-03-2018-0110
Izadi M, Maleki N, Pop I, Mehryan S (2019) Natural convection of a hybrid nanofluid subjected to non-uniform magnetic field within porous medium including circular heater. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 29(4):1211–1231. https://doi.org/10.1108/hff-08-2018-0428
Jeong J, Li C, Kwon Y, Lee J, Kim SH, Yun R (2013) Particle shape effect on the viscosity and thermal conductivity of ZnO nanofluids. Int J Refrig 36(8):2233–2241
Li Z, Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM (2019a) Effect of lorentz forces on nanofluid flow inside a porous enclosure with a moving wall using various shapes of cuo nanoparticles. Heat Transf Res 50(7):697–715
Li F, Sheikholeslami M, Nasir Dara R, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Li Z (2019b) Numerical study for nanofluid behavior inside a storage finned enclosure involving melting process. J Mol Liq 297:111939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111939
Ma X, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Li Z (2019) Solidification inside a clean energy storage unit utilizing phase change material with copper oxide nanoparticles. J Cleaner Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118888
Majeed A, Zeeshan A, Noori FM, Masud U (2019a) Influence of rotating magnetic field on Maxwell saturated ferrofluid flow over a heated stretching sheet with heat generation/absorption. Mech Ind 20(5):502
Majeed A, Zeeshan A, Mubbashir S (2019b) Vibration analysis of carbon nanotubes based on cylindrical shell by inducting Winkler and Pasternak foundations. Mech Adv Mater Struct 26(13):1140–1145
Marin M, Vlase S, Ellahi R, Bhatti MM (2019) On the partition of energies for the backward in time problem of thermoelastic materials with a dipolar structure. Symmetry 11(7):863
Maskeen MM, Zeeshan A, Mehmood OU, Hassan M (2019) Heat transfer enhancement in hydromagnetic alumina–copper/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim 138(2):1127–1136
Mehryan SAM, Izadi M, Chamkha AJ, Sheremet MA (2018) Natural convection and entropy generation of a ferrofluid in a square enclosure under the effect of a horizontal periodic magnetic field. J Mol Liq 263:510–525
Mehryan SAM, Sheremet MA, Soltani M, Izadi M (2019a) Natural convection of magnetic hybrid nanofluid inside a double-porous medium using two-equation energy model. J Mol Liq 277:959–970
Mehryan SAM, Ghalambaz M, Izadi M (2019b) Conjugate natural convection of nanofluids inside an enclosure filled by three layers of solid, porous medium and free nanofluid using Buongiorno’s and local thermal non-equilibrium models. J Therm Anal Calorim 135(2):1047–1067
Mohamed IA, Othmanm M (2017) Marin, effect of thermal loading due to laser pulse on thermoelastic porous medium under G–N theory. Results Phys 7:3863–3872
Mohebbi R, Mohebbi R, Delouei AA, Sajjadi H (2019a) Natural convection of a magnetizable hybrid nanofluid inside a porous enclosure subjected to two variable magnetic fields. Int J Mech Sci 151:154–169
Mohebbi R, Izadi M, Delouei AA, Sajjadi H (2019b) Effect of MWCNT-Fe 3 O 4/water hybrid nanofluid on the thermal performance of ribbed channel with apart sections of heating and cooling. J Therm Anal Calorim 135(6):3029–3042
Nguyen TK, Usman M, Sheikholeslami M, Rizwan-ul Haq, Shafee A, Jilani AK, Tlili I (2020) Numerical analysis of MHD flow and nanoparticle migration within a permeable space containing Non-equilibrium model. Physica A Stat Mech Appl 537, 122459
Nguyen-Thoi T, Bhatti MM, Ali JA, Hamad SM, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Rizwan-ul Haq (2019) Analysis on the heat storage unit through a Y-shaped fin for solidification of NEPCM. J Mol Liq 292, 111378
Patel HE, Das SK, Sundararajan T, Nair AS, George B, Pradeep T (2003) Thermal conductivities of naked and monolayer protected metal nanoparticle based nanofluids: manifestation of anomalous enhancement and chemical effects. Appl Phys Lett 83:2931–2933
Qin Y (2015a) Urban canyon albedo and its implication on the use of reflective cool pavements. Energy Build 96:86–94
Qin Y (2015b) A review on the development of cool pavements to mitigate urban heat island effect. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 52:445–459
Qin Y (2016) Pavement surface maximum temperature increases linearly with solar absorption and reciprocal thermal inertial. Int J Heat Mass Transf 97:391–399
Qin Y, He H (2017) A new simplified method for measuring the albedo of limited extent targets. Solar Energy 157:1047–1055
Qin Y, Liang J, Yang H, Deng Z (2016) Gas permeability of pervious concrete and its implications on the application of pervious pavements. Measurement 78:104–110
Qin Y, He Y, Wu B, Ma S, Zhang X (2017a) Regulating top albedo and bottom emissivity of concrete roof tiles for reducing building heat gains. Energy Build 156(Supplement C):218–224
Qin Y, Zhang M, Hiller JE (2017b) Theoretical and experimental studies on the daily accumulative heat gain from cool roofs. Energy 129:138–147
Qin Y, Luo J, Chen Z, Mei G, Yan L-E (2018a) Measuring the albedo of limited-extent targets without the aid of known-albedo masks. Sol Energy 171:971–976
Qin Y, He Y, Hiller JE, Mei G (2018b) A new water-retaining paver block for reducing runoff and cooling pavement. J Clean Prod 199:948–956
Qin Y, He H, Ou X, Bao T (2019a) Experimental study on darkening water-rich mud tailings for accelerating desiccation. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118235
Qin Y, Hiller JE, Meng D (2019b) Linearity between pavement thermophysical properties and surface temperatures. J Mater Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002890
Qin Y, Zhao Y, Chen X, Wang L, Li F, Bao T (2019c) Moist curing increases the solar reflectance of concrete. Constr Build Mater 215:114–118
Rezaeianjouybari B, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Babazadeh H (2020) A novel bayesian optimization for flow condensation enhancement using nanorefrigerant: a combined analytical and experimental study. Chem Eng Sci 215:115465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.115465
Rudraiah N, Barron RM, Venkatachalappa M, Subbaraya CK (1995) Effect of a magnetic fieldon free convection in a rectangular enclosure. Int J Eng Sci 33:1075–1084
Seyednezhad M, Sheikholeslami M, Ali JA, Shafee A, Nguyen TK (2019) Nanoparticles for water desalination in solar heat exchanger. Rev J Thermal Anal Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08634-6
Shehzad N, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R, Rashidi S (2018) Modelling study on internal energy loss due to entropy generation for non-Darcy Poiseuille flow of silver-water nanofluid: an application of purification. Entropy 20:851
Sheikholeslami M (2015) Effect of uniform suction on nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a cylinder. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 37:1623–1633
Sheikholeslami M (2016) CVFEM for magnetic nanofluid convective heat transfer in a porous curved enclosure. Eur Phys J Plus 131:413. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16413-y
Sheikholeslami M (2017a) Magnetic field influence on CuO-H2O nanofluid convective flow in a permeable cavity considering various shapes for nanoparticles. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:19611–19621
Sheikholeslami M (2017b) Influence of Lorentz forces on nanofluid flow in a porous cavity by means of non-darcy model. Eng Comput 34(8):2651–2667. https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-01-2017-0008
Sheikholeslami M (2017c) Lattice Boltzmann Method simulation of MHD non-Darcy nanofluid free convection. Phys B 516:55–71
Sheikholeslami M (2017d) Influence of magnetic field on nanofluid free convection in an open porous cavity by means of Lattice Boltzmann Method. J Mol Liq 234:364–374
Sheikholeslami M (2017e) Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid forced convection in a porous lid driven cubic cavity using lattice Boltzmann method. J Mol Liq 231:555–565
Sheikholeslami M (2017f) CuO-water nanofluid free convection in a porous cavity considering Darcy law. Eur Phys J Plus 132:55. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11330-3
Sheikholeslami M (2017g) Numerical investigation of MHD nanofluid free convective heat transfer in a porous tilted enclosure. Eng Comput 34(6):1939–1955
Sheikholeslami M (2017h) Magnetic field influence on nanofluid thermal radiation in a cavity with tilted elliptic inner cylinder. J Mol Liq 229:137–147
Sheikholeslami M (2017i) Numerical simulation of magnetic nanofluid natural convection in porous media. Phys Lett A 381:494–503
Sheikholeslami M (2017j) Influence of Lorentz forces on nanofluid flow in a porous cylinder considering Darcy model. J Mol Liq 225:903–912
Sheikholeslami M (2017k) Influence of Coulomb forces on Fe3O4-H2O nanofluid thermal improvement. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:821–829
Sheikholeslami M (2018a) Solidification of NEPCM under the effect of magnetic field in a porous thermal energy storage enclosure using CuO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 263:303–315
Sheikholeslami M (2018b) Investigation of Coulomb forces effects on ethylene glycol based nanofluid laminar flow in a porous enclosure. Appl Math Mech (Engl Ed) 39(9):1341–1352
Sheikholeslami M (2018c) Numerical simulation for solidification in a LHTESS by means of Nano-enhanced PCM. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 86:25–41
Sheikholeslami M (2018d) Numerical modeling of nano enhanced PCM solidification in an enclosure with metallic fin. J Mol Liq 259:424–438
Sheikholeslami M (2018e) Numerical investigation of nanofluid free convection under the influence of electric field in a porous enclosure. J Mol Liq 249:1212–1221
Sheikholeslami M (2018f) CuO-water nanofluid flow due to magnetic field inside a porous media considering Brownian motion. J Mol Liq 249:921–929
Sheikholeslami M (2018g) Numerical investigation for CuO–H2O nanofluid flow in a porous channel with magnetic field using mesoscopic method. J Mol Liq 249:739–746
Sheikholeslami M (2019a) New computational approach for exergy and entropy analysis of nanofluid under the impact of Lorentz force through a porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 344:319–333
Sheikholeslami M (2019b) Numerical approach for MHD Al2O3-water nanofluid transportation inside a permeable medium using innovative computer method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 344:306–318
Sheikholeslami M (2019c) Application of control volume based finite element method (CVFEM) for nanofluid flow and heat transfer. Elsevier. ISBN: 9780128141526
Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM (2017a) Forced convection of nanofluid in presence of constant magnetic field considering shape effects of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 111:1039–1049
Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM (2017b) Active method for nanofluid heat transfer enhancement by means of EHD. Int J Heat Mass Transf 109:115–122
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R (2015) Three dimensional mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 89:799–808
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A (2018) Solidification heat transfer of nanofluid in existence of thermal radiation by means of FEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf 123:418–431
Sheikholeslami M, Mahian O (2019) Enhancement of PCM solidification using inorganic nanoparticles and an external magnetic field with application in energy storage systems. J Clean Prod 215:963–977
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB (2017a) Numerical modeling of nanofluid natural convection in a semi annulus in existence of Lorentz force. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 317:419–430
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB (2017b) Simulation of nanofluid heat transfer in presence of magnetic field: a review. Int J Heat Mass Transf 115:1203–1233
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB (2017c) Nanofluid two phase model analysis in existence of induced magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf 107:288–299
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB (2018a) Numerical simulation for impact of Coulomb force on nanofluid heat transfer in a porous enclosure in presence of thermal radiation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 118:823–831
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB (2018b) Magnetic nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer in a porous cavity considering Brownian motion effects. Phys Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5012517
Sheikholeslami M, Sadoughi M (2017) Mesoscopic method for MHD nanofluid flow inside a porous cavity considering various shapes of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 113:106–114
Sheikholeslami M, Sadoughi MK (2018) Simulation of CuO- water nanofluid heat transfer enhancement in presence of melting surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 116:909–919
Sheikholeslami M, Seyednezhad M (2017) Nanofluid heat transfer in a permeable enclosure in presence of variable magnetic field by means of CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf 114:1169–1180
Sheikholeslami M, Seyednezhad M (2018) Simulation of nanofluid flow and natural convection in a porous media under the influence of electric field using CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf 120:772–781
Sheikholeslami M, Shamlooei M (2017) Fe3O4- H2O nanofluid natural convection in presence of thermal radiation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42(9):5708–5718
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA (2017a) CVFEM for influence of external magnetic source on Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid behavior in a permeable cavity considering shape effect. Int J Heat Mass Transf 115:180–191
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA (2017b) Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid convection in a porous enclosure considering heat flux boundary condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf 106:1261–1269
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA (2018a) CVFEM simulation for nanofluid migration in a porous medium using Darcy model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 122:1264–1271
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA (2018b) Simulation of water based nanofluid convective flow inside a porous enclosure via Non-equilibrium model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 120:1200–1212
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA (2018c) Numerical analysis of Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid flow in permeable media under the effect of external magnetic source. Int J Heat Mass Transf 118:182–192
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K (2017) Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a cavity with variable magnetic field. Appl Math Comput 298:272–282
Sheikholeslami M, Zeeshan A (2017) Analysis of flow and heat transfer in water based nanofluid due to magnetic field in a porous enclosure with constant heat flux using CVFEM. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 320:68–81
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K, Rashidi MM (2016) Forced convection heat transfer in a semi annulus under the influence of a variable magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf 92:339–348
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017a) On simulation of nanofluid radiation and natural convection in an enclosure with elliptical cylinders. Int J Heat Mass Transf 115:981–991
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Abelman S (2017b) Numerical analysis of EHD nanofluid force convective heat transfer considering electric field dependent viscosity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 108:2558–2565
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017c) Numerical study for external magnetic source influence on water based nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 106:745–755
Sheikholeslami M, Li Z, Shafee A (2018a) Numerical modeling for Alumina nanofluid magnetohydrodynamic convective heat transfer in a permeable medium using Darcy law. Int J Heat Mass Transf 127:614–622
Sheikholeslami M, Li Z, Shafee A (2018b) Lorentz forces effect on NEPCM heat transfer during solidification in a porous energy storage system. Int J Heat Mass Transf 127:665–674
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A, Li Z, Shafee A, Saleem S (2018c) Influence of CuO nanoparticles on heat transfer behavior of PCM in solidification process considering radiative source term. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1252–1264
Sheikholeslami M, Darzi M, Li Z (2018d) Experimental investigation for entropy generation and exergy loss of nano-refrigerant condensation process. Int J Heat Mass Transf 125:1087–1095
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z (2018e) Water based nanofluid free convection heat transfer in a three dimensional porous cavity with hot sphere obstacle in existence of Lorenz forces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 125:375–386
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Li Z (2018f) Nanofluid turbulent convective flow in a circular duct with helical turbulators considering CuO nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 124:980–989
Sheikholeslami M, Darzi M, Sadoughi MK (2018g) Heat transfer improvement and pressure drop during condensation of refrigerant-based nanofluid: an experimental procedure. Int J Heat Mass Transf 122:643–650
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Saleem S, Li Z, Shafee A, Jiang Y (2018h) Nanofluid heat transfer augmentation and exergy loss inside a pipe equipped with innovative turbulators. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:156–163
Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Khan I, Shafee A, Li Z (2019a) Impact of Lorentz forces on Fe3O4-water ferrofluid entropy and exergy treatment within a permeable semi annulus. J Clean Prod 221:885–898
Sheikholeslami M, Rezaeianjouybari B, Darzi M, Shafee A, Li Z, Khang Nguyen T (2019b) Application of nano-refrigerant for boiling heat transfer enhancement employing an experimental study. Int J Heat Mass Transf 141:974–980
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Hedayat M, Shafee A, Li Z, Khang Nguyen T, Bakouri M (2019c) Heat transfer and turbulent simulation of nanomaterial due to compound turbulator including irreversibility analysis. Int J Heat Mass Transf 137:1290–1300
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee, Li Z, Rizwan-ul Haq (2019d) Heat transfer of nanoparticles employing innovative turbulator considering entropy generation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 136:1233–1240
Sheikholeslami M, Rizwan-ul Haq, Shafee, Li Z, Elaraki YG, Tlili I (2019e) Heat transfer simulation of heat storage unit with nanoparticles and fins through a heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf 135:470–478
Sheikholeslami M, Rizwan-ul Haq, Shafee A, Li Z (2019f) Heat transfer behavior of nanoparticle enhanced PCM solidification through an enclosure with V shaped fins. Int J Heat Mass Transf 130:1322–1342
Sheikholeslami M, Nematpour Keshteli A, Babazadeh H (2020) Nanoparticles favorable effects on performance of thermal storage units. J Mol Liq 300:112329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112329
Sohail A, Fatima M, Ellahi R, Akram KB (2019) A videographic assessment of Ferrofluid during magnetic drug targeting: an application of artificial intelligence in nanomedicine. J Mol Liq 285:47–57
Soomro FA, Zaib A, Rizwan Ulhaq, Sheikholeslami M (2019) Dual nature solution of water functionalized copper nanoparticles along a permeable shrinking cylinder: FDM approach. Int J Heat Mass Transf 129:1242–1249
Timofeeva EV, Routbort JL, Singh D (2009) Particle shape effects on thermophysical properties of alumina nanofluids. J Appl Phys 106(1):014304
Tlili I, Bhatti MM, Hamad SM, Barzinjy AA, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A (2019) Macroscopic modeling for convection of Hybrid nanofluid with magnetic effects. Physica A Stat Mech Its Appl 534, 122136
Wang R, Sheikholeslami M, Mahmood BS, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T (2019) Simulation of triplex-tube heat storage including nanoparticles, solidification process. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111731
Waqas H, Khan SU, Imran M, Bhatti MM (2019) Thermally developed Falkner-Skan bioconvection flow of a magnetized nanofluid in the presence of a motile gyrotactic microorganism: Buongiorno’s nanofluid model. Phys Scr 94(11):115304
Wen D, Ding Y (2005) Effect of particle migration on heat transfer in suspensions of nanoparticles flowing through minichannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 1(2):183–189
Xuan Y, Roetzel W (2000) Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 43:3701–3707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babazadeh, H., Zeeshan, A., Jacob, K. et al. Numerical Modelling for Nanoparticle Thermal Migration with Effects of Shape of Particles and Magnetic Field Inside a Porous Enclosure. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 45, 801–811 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-020-00354-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-020-00354-9