Abstract
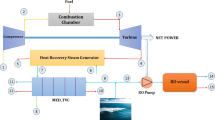
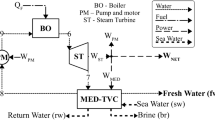
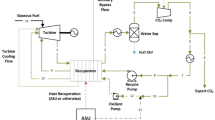
Multi-effect distillation desalination system with thermal vapor compression is one of the systems of producing fresh water based on distillation desalination. This type of desalination system is one of the most appropriate and economic types of desalination systems for low to high capacities of seawater and brackish water in which evaporation and distillation have occurred in a vacuum and in temperature below 70 °C. This research provides a mathematical model in the steady-state conditions for multi-effect distillation desalination system with thermal vapor compression in Bandar Abbas thermal power plant in south of Iran. The genetic algorithm is used for maximizing the produced fresh water and minimizing total exergy destruction rate. Exergy analysis shows that the thermo-compressor and effects are the main sources of exergy destruction in the system (more than 80%). The actual operating data in summer and winter were used for the exergy destruction study. The results show that the exergy destruction in winter is more than summer. Parametric analysis for studying the effects of key parameters shows that increasing the top brine temperature leads to increase in the total exergy destruction of the system. The optimization of the system with two-target genetic algorithm causes distillate production to increase by 16.62%, and the total exergy destruction rate decreases by 3.58%.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Million imperial gallons per day.
Abbreviations
- \( B \) :
-
Brine flow rate (kg/s)
- BPE:
-
Boiling point elevation (°C)
- \( C \) :
-
Specific heat capacity of water (kJ/kgK)
- \( {\text{CR}} \) :
-
Compression ratio
- D i :
-
Distillate (kg/s)
- d ′ i :
-
Flash vapor flow rate (kg/s)
- E :
-
Exergy
- \( E_{{{\text{D}},{\text{c}}}} \) :
-
Exergy destruction rate of component (kW)
- \( E_{{{\text{D}},{\text{t}}}} \) :
-
Total exergy destruction rate (kW)
- \( E_{\text{SD}} \) :
-
Specific exergy destruction (kJ/kg)
- \( {\text{ER}} \) :
-
Expansion ratio
- F i :
-
Feed water flow rate (kg/s)
- \( {\text{GOR}} \) :
-
Gain output ratio
- \( h_{\text{d}} \) :
-
Enthalpy of the discharge steam (kJ/kg)
- \( h_{\text{fs}} \) :
-
Saturated liquid enthalpy (kJ/kg)
- \( h_{\text{ev}} \) :
-
Enthalpy of the Entrained vapor (kJ/kg)
- \( h_{\text{m}} \) :
-
Motive steam enthalpy (kJ/kg)
- \( h_{\text{s}} \) :
-
Input steam enthalpy to first effect (kJ/kg)
- \( h_{\text{w}} \) :
-
Enthalpy of Spray water (kJ/kg)
- h 0 :
-
Environment state enthalpy (kJ/kg)
- L :
-
Latent heat (kJ/kg)
- \( M_{\text{c}} \) :
-
Condenser vapor flow rate (kg/s)
- \( M_{\text{cw}} \) :
-
Cooling water flow rate (kg/s)
- \( M_{\text{d}} \) :
-
Discharge steam flow rate (kg/s)
- \( M_{\text{ev}} \) :
-
Entrained vapor flow rate (kg/s)
- \( M_{\text{m}} \) :
-
Motive steam flow rate (kg/s)
- M s :
-
Input steam flow rate to first effect (kg/s)
- \( M_{\text{sw}} \) :
-
Seawater flow rate (kg/s)
- NEA:
-
Non-equilibrium allowance
- n :
-
Number of effects
- PCF:
-
Pressure correction factor
- \( P_{\text{d}} \) :
-
Discharged vapor pressure (kPa)
- \( P_{\text{ev}} \) :
-
Entrained vapor pressure (kPa)
- \( P_{\text{m}} \) :
-
Motive steam pressure (kPa)
- \( P_{\text{s}} \) :
-
Input steam pressure to first effect (kPa)
- \( Q_{\text{d}} \) :
-
Specific heat consumption (kJ/kg)
- Ra:
-
Entertainment ratio
- \( s_{\text{ev}} \) :
-
Entrained vapor entropy (kJ/kgK)
- \( s_{\text{fs}} \) :
-
Condensate vapor entropy (kJ/kgK)
- s s :
-
Input steam entropy to first effect (kJ/kgK)
- TBT:
-
Top brine temperature
- TCF:
-
Temperature correction factor
- \( T_{\text{d}} \) :
-
Discharge steam temperature (°C)
- \( T_{\text{ev}} \) :
-
Entrained vapor temperature (°C)
- \( T_{\text{f}} \) :
-
Feed water temperature (°C)
- Ti:
-
Effect temperature (°C)
- \( T_{\text{m}} \) :
-
Motive steam temperature (°C)
- \( T_{\text{s}} \) :
-
Input steam temperature to first effect (°C)
- \( T_{\text{sw}} \) :
-
Seawater temperature (°C)
- \( T_{{{\text{v}},i}} \) :
-
Output vapor temperature from effect (°C)
- T 0 :
-
Dead state temperature (K)
- \( \Delta T \) :
-
Temperature difference per effect (°C)
- \( X_{{{\text{b}},i}} \) :
-
Brine salinity (g/kg)
- \( X_{\text{f}} \) :
-
Seawater salinity (g/kg)
- ψ :
-
Exergy efficiency
- δ :
-
Exergy destruction rate
- b:
-
Brine
- c:
-
Condenser
- D:
-
Destruction
- d:
-
Discharge steam
- de:
-
Desuperheater
- dis:
-
Distillate
- e:
-
Effect
- ej:
-
Ejector
- ev:
-
Entrained vapor
- f:
-
Feed
- in:
-
Input
- m:
-
Motive steam
- out:
-
Output
- rej:
-
Rejection
- s:
-
Input vapor to first effect
References
Abed FM, Kassim MS, Rahi MR (2017) Performance improvement of a passive solar still in a water desalination. Environ Sci Technol 14:1277–1284
Al-Najem NM, Darwish MA, Youssef FA (1997) Thermo-vapor compression desalination: energy and availability analysis of single and multi-effect systems. Desalination 110(3):223–238
Ameri M, Mokhtari H, Bahrami M (2016) Energy, exergy, exergoeconomic and environmental (4E) optimization of a large steam power plant: a case study. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 40:11–20
Binamer A (2013) Second law and sensitivity analysis of large ME-TVC desalination units. Desalin Water Treat 1–12
Choi H, Lee T, Kim Y, Song S (2005) Performance improvement of multiple-effect distiller with thermal vapor compression system by exergy analysis. Desalination 182:239–249
Darwish MA (1995) Desalination process: a technical comparison. IDA World Congr Desalin Water Sci 1:149–173
El-Dessouky HT, Ettouney HM (1999) Multiple-effect evaporation desalination systems thermal analysis. Desalination 125(1):259–276
El-Dessouky HT, Ettouney HM (2002) Fundamental of salt-water desalination. Elsevier, Amsterdam
El-Dessouky HT, Ettouney HM, Al-Juwayhel F (2000) Multiple effect evaporation-vapor compression desalination processes. Chem Eng Res Des 78(4):662–676
Ettouney HM, El-Dessouky HT (1999) Understand thermal desalination. Chem Eng Prog 95(9):43–54
Franz C, Seifert B (2015) Thermal analysis of a multi effect distillation plant powered by a solar tower plant. Energy Proc 69:1928–1937
Geankoplis CJ (2003) Transport processes and separation process principle. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Hamed OA, Zamamiri AM, Aly S, Lior N (1996) Thermal performance and exergy analysis of a thermal vapor compression desalination system. Energy Convers Manag 37(4):379–387
Hong W, Yulong L, Jiang C (2013) Analysis of an evaporator-condenser-separated mechanical vapor compression system. Therm Sci 22:152–158
Mazini MT, Yazdizadeh A, Ramezani MH (2014) Dynamic modeling of multi-effect desalination with thermal vapor compressor plant. Desalination 353:98–108
Michels T (1993) Recent achievements of low-temperature multiple effect desalination in the western area of Abu Dhabi. Desalination 93(1):111–118
Miyatake O, Murakami K, Kawata Y, Fujii (1973) Fundamental experiments with flash evaporation. Heat Transf 2:89–100
Naserian MM, Farahat S, Sarhaddi F (2016) Exergoeconomic analysis and genetic algorithm power optimization of an irreversible regenerative Brayton cycle. Energy Equip Syst 4:188–203
Naserian MM, Farahat S, Sarhaddi F (2017) New exergy analysis of a regenerative closed Brayton cycle. Energy Convers Manag 134:116–124
Ophir A, Lokiec F (2005) Advanced MED process for most economical sea water desalination. Desalination 182:187–198
Sarhaddi F, Farhat S, Alavi MA, Sobhnamayan F (2011) Non-sensitive solutions in multi-objective optimization of a solar photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) air collector. Mech Aerosp Ind Mechatron Manuf Eng 5:320–325
Sharaf MA, Nafey AS, García-Rodríguez L (2011) Exergy and thermo-economic analyses of a combined solar organic cycle with multi effect distillation (MED) desalination process. Desalination 272:135–147
Sharifishourabi M, Ratlamwala TAH, Alimoradiyan H, Sadeghizadeh E (2017) Performance assessment of a multi-generation system based on organic rankine cycle. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 41:225–232
Tadeusz JK (1985) The exergy method of thermal plant analysis. Butterworth
Utomo T, Ji M, Kim P, Jeong H, Chung H (2008) CFD analysis of influence of converging duct angle on the steam ejector performance. In: Proceeding of the international conference on engineering optimization
Zarei T, Behyad R, Abedini E (2017) Study on parameters effective on the performance of a humidification-dehumidification seawater greenhouse using support vector regression. Desalination
Zhao D, Xue J, Li S, Sun H, Zhang Q-D (2011) Theoretical analyses of thermal and economical aspects of multi-effect distillation desalination dealing with high-salinity wastewater. Desalination 273:292–298
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khorshidi, J., Pour, N.S. & Zarei, T. Exergy Analysis and Optimization of Multi-effect Distillation with Thermal Vapor Compression System of Bandar Abbas Thermal Power Plant Using Genetic Algorithm. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 43 (Suppl 1), 13–24 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-017-0136-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-017-0136-7