Abstract
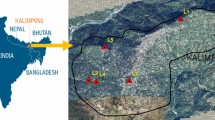
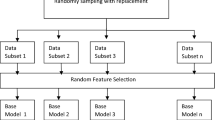
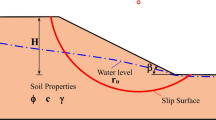
Slope stability assessment is necessary to evaluate the safety of natural or man-made slopes. This analysis is crucial for determining the potential risk that could result in landslides or other hazardous situations. This research investigates the landslide predictability of crucial locations in Kalimpong, Darjeeling Himalayas, which are characterized by complicated geology in tough terrains. The study concentrated on the factor of safety determination process for dry and saturated conditions utilizing the GeoStudio commercial software “SLOPE/W” based on limit equilibrium method and provide an analytical comparison using computational intelligence and machine learning approaches. Support vector machine, decision tree, random forest, logistic regression, naïve Bayes, k-nearest neighbors algorithm, and AdaBoost are used as machine learning classifiers having a strong capability of predicting slope failures and perils. Five parameters, namely cohesion, internal friction angle, unit weight, slope angle, and slope height, are chosen as random variables and stability condition as output. Inter-criteria correlation (CRITIC)-based method is utilized to perform sensitivity analysis denoting the greatest impacting parameter, i.e., slope height. Novel ensemble approach R-Boost is identified to give maximum accuracy in comparison to all seven machine learning methods. By multifold cross-validation, R-Boost has the greatest forecasting skill, with an average classification accuracy of 0.725 and in terms of area under the curve, random forest (RF) represents an average value of 0.81, followed by R-Boost at 0.798. Among all predictive models, particularly R-Boost followed by RF provides quite similar results as obtained by SLOPE/W. This technique will be particularly beneficial in preventing, anticipating, and reducing the impact of these sorts of catastrophic disasters, which function as substantial barriers to the nation's socioeconomic progress

(Source: USGS)


(Source: USGS)

(Source: USGS)










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla JA, Attom MF, Hawileh R (2015) Prediction of minimum factor of safety against slope failure in clayey soils using artificial neural network. Environ Earth Sci 73:5463–5477
Abraham MT, Satyam N, Pradhan B, Alamri AM (2020) IoT-based geotechnical monitoring of unstable slopes for landslide early warning in the Darjeeling Himalayas. Sensors 20(9):2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092611
Agam M, Hashim M, Murad M, Zabidi H (2016) Slope sensitivity analysis using Spencer's method in comparison with general limit equilibrium method. Procedia Chem 19:651–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2016.03.066
Ahangari Nanehkaran Y, Pusatli T, Chengyong J, Chen J, Cemiloglu A, Azarafza M, Derakhshani R (2022) Application of machine learning techniques for the estimation of the safety factor in slope stability analysis. Water 14(22):3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223743
Alejano L, Ferrero AM, Ramírez-Oyanguren P, Fernández MÁ (2011) Comparison of limit-equilibrium, numerical and physical models of wall slope stability. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48(1):16–26
Armaghani DJ, Mamou A, Maraveas C, Roussis PC, Siorikis VG, Skentou AD, Asteris PG (2021) Predicting the unconfined compressive strength of granite using only two non-destructive test indexes. Geomech Eng 25(4):317–330
Asteris PG, Cavaleri L, Ly HB, Pham BT (2021a) Surrogate models for the compressive strength mapping of cement mortar materials. Soft Comput 25(8):6347–6372
Asteris PG, Koopialipoor M, Armaghani DJ, Kotsonis EA, Lourenço PB (2021b) Prediction of cement-based mortars compressive strength using machine learning techniques. Neural Comput Appl 33(19):13089–13121
Asteris PG, Skentou AD, Bardhan A, Samui P, Pilakoutas K (2021c) Predicting concrete compressive strength using hybrid ensembling of surrogate machine learning models. Cement Concr Res 145:106449
Asteris PG, Lourenço PB, Roussis PC, Adami CE, Armaghani DJ, Cavaleri L, Chalioris CE, Hajihassani M, Lemonis ME, Mohammed AS, Pilakoutas K (2022) Revealing the nature of metakaolin-based concrete materials using artificial intelligence techniques. Constr Build Mater 322:126500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126500
Azarafza M, Hajialilue Bonab M, Derakhshani R (2022) A novel empirical classification method for weak rock slope stability analysis. Sci Rep 12(1):14744. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-19246-w
Azarafza M, Nikoobakht S, Asghari-Kaljahi E, Moshrefy-Far M (2014) Stability analysis of jointed rock slopes using block theory (case study: gas flare site in phase 7 of South Pars Gas Complex). In: Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 32th National & 1st International Geosciences Congress of Iran
Begum N, Maiti A, Chakravarty D, Das BS (2021) Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy based rapid coal rank estimation: a machine learning enabled framework. Spectroch Acta Part a: Molec Biomol Spectroscopy 263:120150
Bhagat NK, Mishra AK, Singh RK, Sawmliana C, Singh P (2022) Application of logistic regression, CART and random forest techniques in prediction of blast-induced slope failure during reconstruction of railway rock-cut slopes. Eng Fail Anal 137:106230
Bui XN, Nguyen H, Choi Y, Nguyen-Thoi T, Zhou J, Dou J (2020) Prediction of slope failure in open-pit mines using a novel hybrid artificial intelligence model based on decision tree and evolution algorithm. Sci Rep 10(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66904-y
Chawla A, Chawla S, Pasupuleti S, Rao A, Sarkar K, Dwivedi R (2018) Landslide susceptibility mapping in Darjeeling Himalayas, India. Adv Civil Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6416492
Chen J, Huang H, Cohn AG, Zhang D, Zhou M (2022) Machine learning-based classification of rock discontinuity trace: SMOTE oversampling integrated with GBT ensemble learning. Int J Min Sci Technol 32(2):309–322
Cheng MY, Hoang ND (2016) Slope collapse prediction using Bayesian framework with k-nearest neighbor density estimation: case study in Taiwan. J Comput Civ Eng 30(1):04014116
Cheng YM, Lansivaara T, Wei WB (2007) Two-dimensional slope stability analysis by limit equilibrium and strength reduction methods. Comput Geotech 34(3):137–150
Cohen I, Huang Y, Chen J, Benesty J, Benesty J, Chen J, Huang Y, Cohen I (2009) Pearson Correlation Coefficient. In: Noise Reduction in Speech Processing. Springer Topics in Signal Processing, vol 2. Springer, Berlin and Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00296-0_5
Collins BD, Znidarcic D (2004) Stability analyses of rainfall induced landslides. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 130(4):362–372
Cui W, Wang XH, Zhang GK, Li HB (2021) Identification of unstable bedrock promontory on steep slope based on UAV photogrammetry. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:7193–7211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02333-z
Das S, Sarkar S, Kanungo DP (2022) GIS-based landslide susceptibility zonation mapping using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method in parts of Kalimpong Region of Darjeeling Himalaya. Environ Monitor Assess 194(4):234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09851-7
Dikshit A, Satyam DN (2018) Estimation of rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrences in Kalimpong, India. Innovat Infrastr Solut 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-018-0132-9
Erzin Y, Cetin T (2012) The use of neural networks for the prediction of the critical factor of safety of an artificial slope subjected to earthquake forces. Scientia Iranica 19(2):188–194
Feng X, Li S, Yuan C, Zeng P, Sun Y (2018) Prediction of slope stability using naive Bayes classifier. KSCE J Civ Eng 22:941–950
Ferentinou M, Sakellariou M (2007) Computational intelligence tools for the prediction of slope performance. Comput Geotech 34(5):362–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2007.06.004
Gupta S, Mishra U, Singh VP (2016) Design of minimum cost earthen channels having side slopes riveted with different types of riprap stones and unlined bed by using particle swarm optimization. Irrigat Drain 65(3):319–333. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.1965
Harandizadeh H, Armaghani DJ, Asteris PG, Gandomi AH (2021) TBM performance prediction developing a hybrid ANFIS-PNN predictive model optimized by imperialism competitive algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 33:16149–16179
Huang CZ, Cao YH, Sun WH (2012) Generalized limit equilibrium method for slope stability analysis. In: Paper presented at the Applied Mechanics and Materials
Hwang S, Guevarra IF, Yu B (2009) Slope failure prediction using a decision tree: a case of engineered slopes in South Korea. Eng Geol 104(1–2):126–134
Johari A, Fooladi H (2020) Comparative study of stochastic slope stability analysis based on conditional and unconditional random field. Comput Geotech 125:103707
Johari A, Rahmati H (2019) System reliability analysis of slopes based on the method of slices using sequential compounding method. Comput Geotech 114:103116
Johari A, Javadi AA, Najafi H (2016) A genetic-based model to predict maximum lateral displacement of retaining wall in granular soil. Scientia Iranica 23(1):54–65
Kabir MU, Islam MS, Nazrul FB, Shahin HM (2023) Comparative stability and behaviour assessment of a hill slope on Clayey sand hill tracts. Int J Eng Trends Technol 71:11–24. https://doi.org/10.14445/22315381/ijett-v71i1p202
Kalantari AR, Johari A, Zandpour M, Kalantari M (2023) Effect of spatial variability of soil properties and geostatistical conditional simulation on reliability characteristics and critical slip surfaces of soil slopes. Transport Geotech 39:100933
Kalatehjari R, Rashid ASA, Ali N, Hajihassani M (2014) The contribution of particle swarm optimization to three-dimensional slope stability analysis. The Scient World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/973093
Kardani N, Bardhan A, Samui P, Nazem M, Zhou A, Armaghani DJ (2021) A novel technique based on the improved firefly algorithm coupled with extreme learning machine (ELM-IFF) for predicting the thermal conductivity of soil. Engineering with Computers, 1–20
Khanna K, Martha TR, Roy P, Kumar KV (2021) Effect of time and space partitioning strategies of samples on regional landslide susceptibility modelling. Landslides 18:2281–2294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01627-3
Krishnan AR, Kasim MM, Hamid R, Ghazali MF (2021) A modified CRITIC method to estimate the objective weights of decision criteria. Symmetry 13(6):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13060973
Li J, Wang F (2010) Study on the forecasting models of slope stability under data mining. In: Earth and space: engineering, science, construction, and operations in challenging environments, pp. 765–776
Li Y, Yang X (2019) Soil-slope stability considering effect of soil-strength nonlinearity. Int J Geomech 19(3):04018201. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0001355
Lin S, Zheng H, Han C, Han B, Li W (2021) Evaluation and prediction of slope stability using machine learning approaches. Front Struct Civil Eng 15(4):821–833
Liu Z, Shao J, Xu W, Chen H, Zhang Y (2014) An extreme learning machine approach for slope stability evaluation and prediction. Nat Hazards 73:787–804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1106-7
Liu SY, Shao LT, Li HJ (2015) Slope stability analysis using the limit equilibrium method and two finite element methods. Comput Geotech 63:291–298
Lu P, Rosenbaum M (2003) Artificial neural networks and grey systems for the prediction of slope stability. Nat Hazards 30:383–398. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:nhaz.0000007168.00673.27
Mafi R, Javankhoshdel S, Cami B, Jamshidi Chenari R, Gandomi AH (2021) Surface altering optimisation in slope stability analysis with non-circular failure for random limit equilibrium method. Georisk: Assess Manag Risk Eng Sys Geohaz 15(4):260–286. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2020.1771739
Mathe L, Ferentinou M (2021) Rock slope stability analysis adopting Eurocode 7, a limit state design approach for an open pit. IOP Conf: Series Earth Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/833/1/012201
Matthews C, Farook Z, Helm P (2014) Slope stability analysis–limit equilibrium or the finite element method. Ground Eng 48(5):22–28
Mohamed T, Kasa A (2014) Application of fuzzy set theory to evaluate the stability of slopes. Appl Mech Mater. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.580-583.566
Morgenstern NU, Price VE (1965) The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces. Geotechnique 15(1):79–93. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1965.15.1.79
Mukherjee A, Mitra A (2001) Geotechnical study of mass movements along the Kalimpong approach road in the Eastern Himalayas. Indian J Geol 73(4):271–280
Phong TV, Phan TT, Prakash I, Singh SK, Shirzadi A, Chapi K, Ly HB, Ho LS, Quoc NK, Pham BT (2021) Landslide susceptibility modeling using different artificial intelligence methods: a case study at Muong Lay district, Vietnam. Geocarto Int 36(15):1685–1708. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1665715
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed. Iran Natural Haz 63:965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0217-2
Qi C, Tang X (2018) Slope stability prediction using integrated metaheuristic and machine learning approaches: a comparative study. Comput Ind Eng 118:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.02.028
Raschka S, Patterson J, Nolet C (2020) Machine learning in python: Main developments and technology trends in data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Information 11(4):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040193
Roy P, Ghosal K, Paul PK (2022) Landslide susceptibility mapping of Kalimpong in Eastern Himalayan Region using a Rprop ANN approach. J Earth Syst Sci 131(2):130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01877-2
Sah NK, Sheorey PR, Upadhyaya LN (1994) Maximum likelihood estimation of slope stability. In: International journal of rock mechanics and mining sciences & geomechanics abstracts, Vol. 31, No. 1, pp. 47–53. Pergamon
Sakellariou M, Ferentinou M (2005) A study of slope stability prediction using neural networks. Geotech Geol Eng 23:419–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-004-8680-5
Samui P (2008) Slope stability analysis: a support vector machine approach. Environ Geol 56:255–267
Samui P (2013) Support vector classifier analysis of slope. Geomat, Nat Haz Risk 4(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2012.684725
Schmidhuber J (2015) Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw 61:85–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
Tao Y, Xue Y, Zhang Q, Yang W, Li B, Zhang L, Qu C, Zhang K (2021) Risk assessment of unstable rock masses on high-steep slopes: an attribute recognition model. Soil Mech Found Eng 58(2):175–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-021-09724-0
Verma A, Singh T, Chauhan NK, Sarkar K (2016) A hybrid FEM–ANN approach for slope instability prediction. J Instit Eng: Series A 97:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-016-0168-9
Wang Z, Lin M (2021) Finite element analysis method of slope stability based on fuzzy statistics. Earth Sci Res J 25(1):123–130. https://doi.org/10.15446/esrj.v25n1.93320
Wang Y, Cao Z, Au SK (2011) Practical reliability analysis of slope stability by advanced Monte Carlo simulations in a spreadsheet. Can Geotech J 48(1):162–172
Wei W, Li X, Liu J, Zhou Y, Li L, Zhou J (2021a) Performance evaluation of hybrid WOA-SVR and HHO-SVR models with various kernels to predict factor of safety for circular failure slope. Appl Sci 11(4):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041922
Wei X, Zhang L, Yang HQ, Zhang L, Yao YP (2021b) Machine learning for pore-water pressure time-series prediction: Application of recurrent neural networks. Geosci Front 12(1):453–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.011
Xie H, Dong J, Deng Y, Dai Y (2022) Prediction model of the slope angle of rocky slope stability based on random forest algorithm. Math Probl Eng 2022:1–10
Yan G, Hu R, Luo J, Weiss M, Jiang H, Mu X, Xie D, Zhang W (2019) Review of indirect optical measurements of leaf area index: recent advances, challenges, and perspectives. Agricult Forest Meteorol 265:390–411
Yang H, Wang Z, Song K (2020) A new hybrid grey wolf optimizer-feature weighted-multiple kernel-support vector regression technique to predict TBM performance. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01217-2
Yue ZQ, Kang XY (2021) Different contributions of two shear strength parameters to soil slope stability with limit equilibrium method based slice techniques. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 861(6):062009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/861/6/062009
Zhang H, Nguyen H, Bui XN, Pradhan B, Asteris PG, Costache R, Aryal J (2021) A generalized artificial intelligence model for estimating the friction angle of clays in evaluating slope stability using a deep neural network and Harris Hawks optimization algorithm. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01272-9
Zhao J, Nguyen H, Nguyen-Thoi T, Asteris PG, Zhou J (2021) Improved Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation neural network by particle swarm and whale optimization algorithms to predict the deflection of RC beams. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01267-6
Zhou J, Li X, Mitri HS (2016) Classification of rockburst in underground projects: comparison of ten supervised learning methods. J Comput Civ Eng 30(5):04016003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0000553
Zhou J, Li E, Yang S, Wang M, Shi X, Yao S, Mitri HS (2019) Slope stability prediction for circular mode failure using gradient boosting machine approach based on an updated database of case histories. Saf Sci 118:505–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.05.046
Zhou J, Qiu Y, Khandelwal M, Zhu S, Zhang X (2021) Developing a hybrid model of Jaya algorithm-based extreme gradient boosting machine to estimate blast-induced ground vibrations. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 145:104856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104856
Zhou J, Shen X, Qiu Y, Li E, Rao D, Shi X (2021b) Improving the efficiency of microseismic source locating using a heuristic algorithm-based virtual field optimization method. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 7(3):89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00285-y
Zhou KP, Chen ZQ (2009) Stability prediction of tailing dam slope based on neural network pattern recognition. In: 2009 Second international conference on environmental and computer science, IEEE, pp. 380–383
Zhu D, Lee C, Jiang H (2003) Generalised framework of limit equilibrium methods for slope stability analysis. Geotechnique 53(4):377–395. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.53.4.377.37322
Zhu DY, Lee CF, Qian QH, Chen GR (2005) A concise algorithm for computing the factor of safety using the Morgenstern Price method. Can Geotech J 42(1):272–278
Zou S, Abuduwaili J, Duan W, Ding J, De Maeyer P, Van De Voorde T, Ma L (2021) Attribution of changes in the trend and temporal non-uniformity of extreme precipitation events in Central Asia. Scient Reports 11(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94486-w
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
I certify that the information given is true and complete to the best of my knowledge. I understand that if I have deliberately given any false information or have withheld any information regarding any situation, I am liable for prosecution for fraud and/or perjury.
Consent for Publication
This manuscript has not been submitted for any other purpose.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, V., Sarkar, R. Prophetical Modeling Using Limit Equilibrium Method and Novel Machine Learning Ensemble for Slope Stability Gauging in Kalimpong. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 48, 411–430 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01156-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01156-0