Abstract
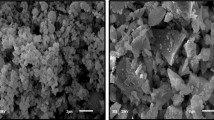
The novelty of this study is to investigate the effect of ferrochrome slag (FS) replacement on the high temperature resistance of alkali-activated granulated blast furnace slag (AAS). The alkali-activated mortar samples were prepared by granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS) and FS at rates of 100/0, 80/20, 70/30, and 60/40 wt.%. A mixture of Na2SiO3 and NaOH was used as the activator. Alkali dosage was determined as 6 wt.% for all mixtures. The ratio of total SiO2 to total Na2O of the activator mixture was 1.5. Prepared samples were exposed to temperatures of 200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 °C. The effect of high temperature on the compressive strength and ultrasonic pulse velocity was investigated. The changes in the microstructure after high temperature exposure were investigated using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The impact of the substitution level of FS on the setting time of AAS was also investigated. The results revealed that the FS substitution increased the high temperature performance of the AAS. At 23 °C, the compressive strength of the sample containing 100% GBFS was 5.4% higher than the sample containing 20% FS substitution. However, after temperatures above 200 °C, the 20% FS substituted sample showed higher compressive strength. Another contribution of the use of FS was the prolongation of the setting time, which is one of the obstacles to the practical use of AAS. The final setting time was prolonged from 119 to 164 min with the lowest substitution rate of 20% FS. It was concluded that FS could partially replace GBFS in AAS production by increasing the high temperature resistance as well as prolonging the setting time.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almutairi AL, Tayeh BA, Adesina A et al (2021) Potential applications of geopolymer concrete in construction: a review. Case Stud Constr Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00733
Amin M, Zeyad AM, Tayeh BA, Agwa IS (2021) Effect of high temperatures on mechanical, radiation attenuation and microstructure properties of heavyweight geopolymer concrete. Struct Eng Mech 80(2):181–199. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2021.80.2.181
ASTM C109/C109M A (2007) compressive strength of hydraulic cement mortars ( Using 2-in . or [ 50-mm ] Cube Specimens ) 1. Am Soc Test Mater
ASTM C597 (2016) Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity Through Concrete. Am Soc Test Mater West Conshohocken, PA USA
ASTM International (2017) ASTM C595–17, Standard specification for blended hydraulic cements. ASTM Int
Awoyera P, Adesina A (2019) A critical review on application of alkali activated slag as a sustainable composite binder. Case Stud Constr Mater 11:e00268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2019.e00268
Awoyera P, Adesina A (2020) Durability properties of alkali activated slag composites: short overview. Silicon 12:987–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00199-1
Awoyera PO, Akinwumi II, Karthika V et al (2020) Lightweight self-compacting concrete incorporating industrial rejects and mineral admixtures: strength and durability assessment. Silicon 12:1779–1785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00279-2
Aydin S, Baradan B (2014) Effect of activator type and content on properties of alkali-activated slag mortars. Compos Part B Eng 57:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.10.001
Bernal SA, Rodríguez ED, De Gutiérrez RM, Provis JL (2015) Performance at high temperature of alkali-activated slag pastes produced with silica fume and rice husk ash based activators. Mater Constr. https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2015.03114
Çelikten S, Sarıdemir M, Özgür Deneme İ (2019) Mechanical and microstructural properties of alkali-activated slag and slag + fly ash mortars exposed to high temperature. Constr Build Mater 217:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.055
Chang JJ (2003) A study on the setting characteristics of sodium silicate-activated slag pastes. Cem Concr Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)01096-7
Dai X, Aydin S, Yardimci MY et al (2020) Influence of water to binder ratio on the rheology and structural Build-up of Alkali-Activated Slag/Fly ash mixtures. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120253
Dener M, Karatas M, Mohabbi M (2021) High temperature resistance of self compacting alkali activated slag/portland cement composite using lightweight aggregate. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123250
Dener M (2022) Engineering properties of self-compacting alkali-activated blast furnace slag mortars produced with lightweight pumice aggregate. Master’s Thesis. Fırat University
El-Hassan H, Shehab E, Al-Sallamin A (2021) Effect of curing regime on the performance and microstructure characteristics of alkali-activated slag-fly ash blended concrete. J Sustain Cem Mater. https://doi.org/10.1080/21650373.2021.1883145
Fang S, Lam ESS, Li B, Wu B (2020) Effect of alkali contents, moduli and curing time on engineering properties of alkali activated slag. Constr Build Mater 249:118799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118799
Gao X, Yu QL, Brouwers HJH (2015) Characterization of alkali activated slag-fly ash blends containing nano-silica. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.086
Guerrieri M, Sanjayan J, Collins F (2009) Residual compressive behavior of alkali-activated concrete exposed to elevated temperatures. Fire Mater 33:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.983
Guerrieri M, Sanjayan J, Collins F (2010) Residual strength properties of sodium silicate alkali activated slag paste exposed to elevated temperatures. Mater Struct Constr 43:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-009-9546-3
Hu X, Shi C, Shi Z, Zhang L (2019) Compressive strength, pore structure and chloride transport properties of alkali-activated slag/fly ash mortars. Cem Concr Compos. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103392
Ismail I, Bernal SA, Provis JL et al (2013) Influence of fly ash on the water and chloride permeability of alkali-activated slag mortars and concretes. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.07.106
Jena S, Panigrahi R (2019) Performance assessment of geopolymer concrete with partial replacement of ferrochrome slag as coarse aggregate. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.045
Karakoç MB, Türkmen I, Maraş MM et al (2014) Mechanical properties and setting time of ferrochrome slag based geopolymer paste and mortar. Constr Build Mater 72:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.021
Karakoç MB, Türkmen I, Maraş MM et al (2016) Sulfate resistance of ferrochrome slag based geopolymer concrete. Ceram Int 42:1254–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.09.058
Karatas M, Dener M, Benli A, Mohabbi M (2019) High temperature effect on the mechanical behavior of steel fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete containing ground pumice powder. Struct Concr. https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.201900067
Koksal F, Bayraktar OY, Bodur B et al (2022) Insulating and fire-resistant performance of slag and brick powder based one-part alkali-activated lightweight mortars. Struct Concr. https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.202200607
Krizan D, Zivanovic B (2002) Effects of dosage and modulus of water glass on early hydration of alkali-slag cements. Cem Concr Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00717-7
Kürklü G (2016) The effect of high temperature on the design of blast furnace slag and coarse fly ash-based geopolymer mortar. Compos Part B Eng 92:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.02.043
Lee WKW, Van Deventer JSJ (2003) Use of infrared spectroscopy to study geopolymerization of heterogeneous amorphous aluminosilicates. Langmuir. https://doi.org/10.1021/la026127e
Li YL, Zhao XL, Singh Raman RK, Al-Saadi S (2018) Thermal and mechanical properties of alkali-activated slag paste, mortar and concrete utilising seawater and sea sand. Constr Build Mater 159:704–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.104
Mobasheri F, Shirzadi Javid AA, Mirvalad S et al (2022) Durability and mechanical properties of pumice-based geopolymers: a sustainable material for future. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00651-6
Mohabbi Yadollahi M, Dener M (2019) Investigation of elevated temperature on compressive strength and microstructure of alkali activated slag based cements. Eur J Environ Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2018.1557562
Nasr D, Pakshir AH, Ghayour H (2018) The influence of curing conditions and alkaline activator concentration on elevated temperature behavior of alkali activated slag (AAS) mortars. Constr Build Mater 190:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.099
Özcan A, Karakoç MB (2019) Evaluation of sulfate and salt resistance of ferrochrome slag and blast furnace slag-based geopolymer concretes. Struct Concr. https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.201900061
Provis JL (2018) Alkali-activated materials. Cem Concr Res 114:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2017.02.009
Provis JL, Bernal SA (2014) Geopolymers and related alkali-activated materials. Annu Rev Mater Res 44:299–327. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-070813-113515
Provis JL, Palomo A, Shi C (2015) Advances in understanding alkali-activated materials. Cem Concr Res 78:110–125
Puertas F, Varga C, Alonso MM (2014) Rheology of alkali-activated slag pastes. Effect of the nature and concentration of the activating solution. Cem Concr Compos. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.07.012
Qaidi SMA, Tayeh BA, Ahmed HU, Emad W (2022a) A review of the sustainable utilisation of red mud and fly ash for the production of geopolymer composites. Constr Build Mater 350:128892
Qaidi SMA, Tayeh BA, Isleem HF et al (2022b) Sustainable utilization of red mud waste (bauxite residue) and slag for the production of geopolymer composites: a review. Case Stud Constr Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e00994
Rovnaník P, Bayer P, Rovnaníková P (2013) Characterization of alkali activated slag paste after exposure to high temperatures. Constr Build Mater 47:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.06.070
Saif MS, El-Hariri MOR, Sarie-Eldin AI et al (2022) Impact of Ca+ content and curing condition on durability performance of metakaolin-based geopolymer mortars. Case Stud Constr Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e00922
Saraya MESI (2014) Study physico-chemical properties of blended cements containing fixed amount of silica fume, blast furnace slag, basalt and limestone, a comparative study. Constr Build Mater 72:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.08.071
Shoaei P, Ghassemi P, Ameri F et al (2021) Comparative study on the effect of fiber type and content on the fire resistance of alkali-activated slag composites. Constr Build Mater 288:1231365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123136
ASTM Standard C191 (2019) Standard test methods for time of setting of hydraulic cement by Vicat Needle
Tayeh BA, Zeyad AM, Agwa IS, Amin M (2021) Effect of elevated temperatures on mechanical properties of lightweight geopolymer concrete. Case Stud Constr Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00673
EN TS (2019) 12390–7. Beton–Sertleşmiş Bet Deneyleri, Bölüm 7:
Türkmen İ, Karakoç MB, Kantarcı F et al (2016) Fire resistance of geopolymer concrete produced from Elazığ ferrochrome slag. Fire Mater 40:836–847. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.2348
Vikas G, Rao TDG (2021) Setting time, workability and strength properties of alkali activated fly ash and slag based geopolymer concrete activated with high silica modulus water glass. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00598-8
Yön MŞ, Karataş M (2022) Evaluation of the mechanical properties and durability of self-compacting alkali-activated mortar made from boron waste and granulated blast furnace slag. J Build Eng 61:105263
Yön MŞ, Arslan F, Karatas M, Benli A (2022) High-temperature and abrasion resistance of self-compacting mortars incorporating binary and ternary blends of silica fume and slag. Constr Build Mater 355:129244
Zhang G, Yang H, Ju C, Yang Y (2020) Novel selection of environment-friendly cementitious materials for winter construction: alkali-activated slag/Portland cement. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120592
Zhang G, Lin R, Wang Y, Wang X (2022) Case Studies in Construction Materials Influence of K + and CO 2 3 in activator on high-temperature performance of alkali-activated slag-ceramic powder binary blends. Case Stud Constr Mater 17:e01306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01306
Acknowledgements
The author states that the acknowledgment information is not applicable for this paper.
Funding
The author states that the funding information is not applicable for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dener, M. Effect of Ferrochrome Slag Substitution on High Temperature Resistance and Setting Time of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 47, 2833–2843 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01087-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01087-w