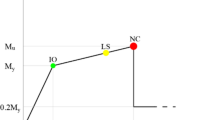
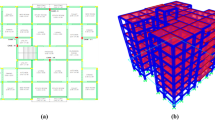
Abstract
The study presented in this paper focuses on evaluation and comparison of seismic performance of special moment frame structures designed using two different approaches. The conventional force-based procedure of the contemporary building codes and the direct displacement-based approach are the focus of study as the design methodologies applied to torsionally coupled buildings. For this purpose, two series of 4-, 8-, and 12-story steel structures are designed separately using the above different approaches. The same buildings are analyzed afterward under a suit of 11 consistent strong ground motions. At this stage, several values for torsional eccentricity are considered by displacing the mass center. Responses including the story shears and drifts, rotations of the plastic hinges, and performance levels of the beams and columns are calculated and compared. Overall, this study shows that the buildings designed based on the displacement procedure exhibit less extensive nonlinear responses more or less at all eccentricities. The reduction is more considerable at the stories where the nonlinear response is at its peak within the structure.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANSI/AISC 360–10 (2010) Specification for structural steel buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction
ASCE/SEI 7–16 (2016) Minimum design loads for buildings and other structures. Virginia: American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE)
ASCE/SEI 41–17 (2017) Seismic evaluation and retrofit of existing buildings. Virginia1: American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE)
CEN EC8 (2004) Eurocode 8 – Design Provisions for Earthquake Resistant Structures, EN-1998–1:2004: E, Comite Europeen de Normalization, Brussels
Dohadwala AT, Sheth RK, Patel IN (2014) Comparison of base shear for forced-based design method and direct displacement-based design method. International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development (IJAERD), vol 1, pp 1–9
Farahani D, Behnamfar F, Sayyadpour H, Ghandil M (2019) Seismic impact between adjacent torsionally coupled buildings. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 117:81–95
Fox M, Sullivan T, Beyer K (2014) Comparison of force-based and displacement-based design approaches for RC coupled walls in New Zealand. Bull New Zealand Soc Earthquake Eng, 47(ARTICLE), 190–205
Kowalsky MJ, Priestley MN, MacRae GA (1994) Displacement-based design: a methodology for seismic design applied to single degree of freedom reinforced concrete structures (Vol. 94, No. 16). Structural Systems Research, University of California, San Diego.
Macedo L, Castro JM (2012) Direct displacement-based seismic design of steel moment frames. In: Proceedings of 15th world conference on earthquake engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, pp 59–66
Mazzoni S, McKenna F, Scott MH, Fenves GL (2006) The open system for earthquake engineering simulation (OpenSEES) user command-language manual
Muljati I, Asisi F, Willyanto K (2015) Performance of force based design versus direct displacement based design in predicting seismic demands of regular concrete special moment resisting frames. Proc Eng 125:1050–1056
Niklanth K, Bimal AS (2016) A comparative study of force-based design and direct displacement-based design for R.C. buildings, Int J Eng Technol (IRJET), 3(5)
Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center (2000) PEER strong motion database
Priestley MJN, Calvi GM, Kowalsky MJ (2008) Displacement based seismic design of structures. IUSS Press
Sil A, Das G, Hait P (2019) Characteristics of FBD and DDBD techniques for SMRF buildings designed for seismic zone-V in India. J Build Pathol Rehabilit 4(1):1
Sullivan TJ (2013) Highlighting differences between force-based and displacement-based design solutions for reinforced concrete frame structures. Struct Eng Int 23(2):122–131
Sullivan TJ, Priestley MJN, Calvi GM (2012) A model code for the displacement-based seismic design of structures, DBD12. IUSS Press
Vidot-Vega AL, Kowalsky MJ (2013) Drift, strain limits and ductility demands for RC moment frames designed with displacement-based and force-based design methods. Eng Struct 51:128–140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shams, A.H., Behnamfar, F. Nonlinear Seismic Behavior of Torsional Buildings Designed Based on Force and Displacement Procedures. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 47, 65–78 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-022-00889-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-022-00889-8