Abstract
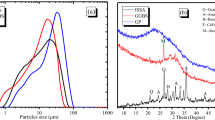
A large number of sediments deposited in the riverbed of the Yellow River, which affected the long-term stability of water level of the Yellow River. In order to relieve the influence of sediment in the Yellow River, this study aims to use the Yellow River sediment to make artificial stone by the method of alkali activation. The chemical composition and physical properties of the Yellow River sediment as well as the stone were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TG/DTG) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that the compressive strength of the specimen had a significant improvement due to alkali-activation effect. At early stage, the compressive strength of specimen was unstable. In late period, the compressive strength of the specimen increased linearly. Moreover, there was an increase in the compressive strength with the increase in Ca(OH)2 dosage at 28 and 90 days. When the dosage of Ca(OH)2 was 12.5%, the strength of specimen reached to the maximum value of 6.9 MPa at 90 days. In addition, the results indicated that the reaction products were mainly the amorphous gel and CaCO3, and they improved the properties of specimen.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidovits J (1991) Geopolymers: inorganic polymeric new materials [J]. J Therm Anal 37(12):1633–1688
De Vargas AS et al (2011) The effects of Na2O/SiO2 molar ratio, curing temperature and age on compressive strength, morphology and microstructure of alkali-activated fly ash-based geopolymers [J]. Cem Conr Comp 33(6):653–660
Dong JL, Wang LJ, Zhang LQ (2015) Study on modified feldspathic stone composite materials [J]. Yellow River 37(1):103–107
Dong JL, Zhang TT, Wang LJ (2016) Alkali-activated modified steel slag/Pisha sandstone composites [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica 33(1):132–141
Li CM, Zhang T, Wang L (2014) Mechanical properties and microstructure of alkali activated Pisha sandstone geopolymer composites [J]. Constr Build Mater 68(15):233–239
Li CM, Wang L, Zhang T et al (2016) Development of building material utilizing a low pozzolanic activity mineral [J]. Constr Build Mater 121:300–309
Lian HZ, Zhang ZL, Wang YH (2001) Rapid evaluation on activity of pozzolanic materials [J]. J Build Mater 4(3):299–304. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2001.03.019
Mu XM, Wang WZ, Gao P et al (2014) Progress and discussion on sediment load variation research of the Yellow River [J]. Yellow River 36(12):1–7
Sofi M et al (2007) Engineering properties of inorganic polymer concretes (IPCs) [J]. Cem Concr Res 37(2):251–257
Wang YG, Hu CH (2006) Study on sediment disaster and sediment utilization as resources [J]. J Sediment Res 2:65–71
Wang P, Zheng GH, Shao J et al (2012) Study on the reserved blocks made with sediment in the Yellow River via roller compacted technique [J]. Yellow River 34(5):12–13
Wang LJ, Yao WY, Leng YB (2014) Ways and principles of utilizing sediment resources the Yellow River [J]. Yellow River 7:9–12
Wang BM, Yang YQ, Zheng L, Han JN, Song WZ, Liu H (2016) Characterization of the Yellow River sediment and the corresponding utilization discussions [J]. Low Temp Arch Technol 38(8):1–3
Wright LD, Weber WJ, Yang ZS et al (1990) Processes of marine dispersal and deposition of suspended silts off the modern mouth of the Huanghe (Yellow River) [J]. Cont Shelf Res 10(1):1–40
Yu L (2002) The Huanghe (Yellow) river: a review of its development, characteristics, and future management issues [J]. Cont Shelf Res 22(3):389–403
Zhang XA, Guan RL (2010) Study on preparation of autoclaved brick by Yellow River silt and fly ash added waste papermaking liquor [J]. Allergy 65(8):1056–1057
Zhang JS, Xi-Ning LI, Chang-Hai LI et al (2005) Study on reserved bricks made by the yellow river sediment [J]. Yellow River 27(3):14–16
Zhang R, Shi N, Huang D (2013) Influence of initial curing temperature on the long-term strength of concrete [J]. Mag Concr Res 65(6):358–364
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express gratitude for the help of Mr. Huaqing Liu in the experimental design and the financial support by the Science and Technology Project of State Grid Corporation of China (GCB17201600152), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51878116) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DUT18ZD219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, X., Li, G., Zhang, Y. et al. Experimental Research on the Modification of the Yellow River Sediment. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 45, 1031–1037 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00622-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00622-x