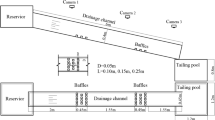
Abstract
We performed an experimental study to investigate the effects of structural strategy for improving the debris brake performance. The stony debris flow was generated by releasing water discharge from a tank that contained gravel material. The efficiency of debris brake, debris accumulation pattern and its position parameters was used to evaluate the performance of the debris brake structure. The influences of debris brake slope, opening size and nonuniformity in deck opening size parameters that have not been studied before were investigated for different debris flow conditions. The results showed that the slope of debris brake was the most important factor on debris brake performance. The suitable slope was found to be a function of the debris flow velocity, and it can increase debris brake efficiency up to 10%. The analysis of the experimental data suggests the optimum opening size ratio (i.e., the ratio of opening size to median diameter of debris) smaller than or equal to one. Experimental data indicated that the nonuniformity in opening size of the debris brake cannot improve the debris brake efficiency.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- W f :
-
Flume width
- S f :
-
Flume slope
- W db :
-
Width of debris flow brake
- L db :
-
Length of debris flow brake
- S db :
-
Slope of debris flow brake
- L o :
-
Opening size of the deck of debris flow brake
- L b :
-
Blocking size of the deck of debris flow brake
- L T :
-
Travel length of the debris flow over the debris flow brake
- V d :
-
Sediment volume stopped
- L H(max) :
-
Location of the longest height of sediments accumulated on the structure
- C :
-
Concentration
- C in :
-
The net concentration reached at the beginning of structure
- \(\gamma_{\text{s}}\) :
-
Buoyancy specific weight of sediment
- ρ :
-
Mass density
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- h :
-
Flow depth
- V :
-
Flow velocity flow
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- ρ s :
-
Mass density of debris
- D 50 :
-
Mean particle diameter
- ω :
-
Falling particle velocity
- W s :
-
Buoyancy weight of the particle
- φ s :
-
Friction angle of gravel
- \(C_{*}\) :
-
Chezy coefficient
- \(v_{*}\) :
-
Shear speed
- \(\tau_{0}\) :
-
Shear stress
References
Gonda Y (2009) Function of a debris-flow brake. J Eros Control Eng 2(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.13101/ijece.2.15
ICHARM (2008) Debris-flow dewatering brakes: a promising tool for disaster management in developing countries. In: International center for water hazard and risk management newsletter, vol 3, No. 3, p 10
Itoh T, Miyamoto K, Egashira S, Sharma KR (2007) Similarity of debris flow and important non-dimensional parameters. In: 32nd Congress of IAHR (The International Association for Hydro-Environment Engineering and Research) at Venice, Italy
Izumi I, Watanabe M, Takemura T, Mizuyama T (1982) Test of a bottom infiltration screen in Ohsawa Fan, Mt. Fuji. J Jpn Soc Eros Control Eng (Shin-sabo) 34(3):45–50. https://doi.org/10.11475/sabo1973.34.3_45
Jues C, Franzini F, Soares-Frazao S, Murillo J, Garcia-Navarro P (2015) Sediment transport in steep channels with a uniform grain size. In: E-proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress 28, The Hague, The Netherlands
Julien PY, ASCE M, Paris A (2010) Mean velocity of mudflows and debris flows. J Hydraul Eng 136(9):676–679. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000224
Kim Y, Nakagawa H, Kawaike K, Zhang H (2012) Numerical and experimental study on debris flow braker. Annu Disaster Prev Res Inst 55:471–481
Kim Y, Nakagawa H, Kawaike K, Zhang H (2013) A study on debris flow deposition by the arrangement of Sabo dam. J Jpn Soc Civ Eng 69(4):97–102. https://doi.org/10.2208/jscejhe.69.I_97
Kim Y, Nakagawa H, Kawaike K, Zhang H (2014) A study on debris flow outflow discharge at a series of Sabo dams. J JSNDS 33:43–52
Kim Y, Nakagawa H, Kawaike K, Zhang H (2017) Study on hydraulic characteristics of Sabo dam with a flap structure for debris flow. Int J Sed Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2017.05.001
Liu KF, Chen YH, Chiu YJ, Shih SS (2013) Large scale simulation of watershed mass transport—a case study of TsengWen watershed. Nat Hazard 67(2):855–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0611-4
Mizuyama T (2008) Structural countermeasures for debris flow disasters. Int J Eros Control Eng 1(2):38–43
Oppenheimer M, Saunders RR, Spradlin JE (1993) Investigating the generality of the delayed-prompt effect. Res Dev Disabil 14(6):425–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-4222(93)90036-J
Park JH, Chamroeum S, Cahng KP, Young DK (2016) A study on the effects of debris accumulation at sacrificial piles on bridge pier scour: II. Empirical formula. KSCE J Civ Eng 20(4):1552–1557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0207-5
Stancanelli LM, Stefano L, Foti E (2015) Propagation and deposition of stony debris flows at channel confluences. Water Resour Res 51(7):5101–5116. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015wr017116
Takahashi T (2014) Debris flow: mechanics, prediction and countermeasures, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Takahashi T, Nakagawa H, Harada T, Yamashiki Y (1992) Routing debris flows with particle segregation. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 118(11):1490–1507. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1992)118:11(1490)
Tian M, Hu KH, Ma C, Lei FH (2014) Effect of bed sediment entrainment on debris flow resistance. J Hydraul Eng 140(1):115–120. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000805
Tyler RN (2011) River debris: causes, impacts, and mitigation techniques. Prepared for Ocean Renewable Power Company by ACEP
Yazawa A, Mizuyama T, Morita A (1998) Experimental study on debris-flow control facilities. Civ Eng J 28(8):9–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4619-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezapourian, S., Ahmadi, M.M. & Qaderi, K. Experimental Study of Structural Strategy on Debris Brake Performance. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 45, 389–398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00461-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00461-2