Abstract
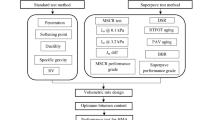
Asphalt binders are modified to address various types of distresses, especially crack-related and permanent deformation of the pavement structure. This study focuses on evaluating the effects of Gripper, a new wax additive, on the performance of natural rubber latex (NRL)-modified asphalt binders. The morphology of the modified asphalt binders was also investigated. In this study, two percentages of NRL were considered, i.e., 3% and 6% based on the weight of the asphalt binder. Penetration value, softening point, rotational viscosity, storage stability, complex modulus, phase angle, rutting potential and torsional recovery parameters were determined to analyze the base asphalt binder (60/70) and NRL-modified asphalt binders (with and without Gripper). Also, the dispersion efficiency of NRL in the asphalt binder was observed using a polarizing optical microscope. The results demonstrate that the addition of NRL improved the performance of the asphalt binder in terms of rutting and fatigue resistance. The addition of Gripper has further improved the stability and mechanical performance of modified asphalt binders. An agglomerated and globular continuous network of mixed microstructures was formed in the modified asphalt binder irrespective of aging condition. Moreover, the unaged, short-term aged and long-term aged binders prepared with the incorporation of Gripper indicate uniformly dispersed network morphology. It can therefore be concluded that the modified asphalt binders prepared with the newly introduced additive portrays better resistance toward rutting and fatigue failures.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali AW, Kim HH, Mazumder M, Lee M, Lee S (2018) Multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR) characterization of polymer modified asphalt binder containing wax additives. Int J Pavement Res Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijprt.2018.05.001
Al-Mansob RA, Ismail A, Alduri AN, Azhari CH, Karim MR, Yusoff NIM (2014) Physical and rheological properties of epoxidized natural rubber modified bitumens. Constr Build Mater 63:242–248
Al-Sabaeei A, Nur NI, Napiah M, Sutanto M (2019) A review of using natural rubber in the modification of bitumen and asphalt mixtures used for road construction. J Teknol 81(6):81–88. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v81.13487
ARRB (2010) ARRB AG:PT, T122: torsional recovery of polymer modified binders. Australia Road Research Board, Sydney
ASTM (1995) ASTM D36: standard test method for softening point of bitumen (ring-and-ball apparatus). ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
ASTM (1997) ASTM D5: standard test method for penetration of bituminous materials. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
ASTM (2006a) ASTM D2872: standard test method for effect of heat and air on moving film of asphalt (rolling thin-film oven test). Annual Books of ASTM Standards, vol 4.03. West Conshohocken, PA, USA
ASTM (2006b) ASTM D6521: standard test method for effect of heat and pressure aging of asphalt (pressure ageing vessel). Annual Books of ASTM Standards, vol 4.03. West Conshohocken, PA, USA
ASTM (2011) ASTM D7175: standard test method for determining the rheological properties of asphalt binder using a dynamic shear rheometer. Annual Books of ASTM Standards, vol 4.03. West Conshohocken, PA, USA
ASTM (2012), ASTM D4402: standard test method for viscosity determination of asphalt at elevated temperatures using a rotational viscometer. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
Azahar NBM, Hassan NBA, Jaya RP, Kadir MABA, Yunus NZBM, Mahmud MZH (2016) An overview on natural rubber application for asphalt modification. Int J Agric For Plans 2:212–218
BSI (2017) BS EN 13399: bitumen and bituminous binders. Determination of storage stability of modified bitumen, British Standards Institution
D’Angelo J, Kluttz R, Dongre RN, Stephens K, Zanzotto L (2007) Revision of the superpave high temperature binder specification: the multiple stress creep recovery test (with discussion). J Assoc Asphalt Paving Technol 76
Daniel NH, Hassan NA, Idham MK, Jaya RP, Hainin MR, Ismail CR, Azahar NM (2019) Properties of bitumen modified with latex. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/527/1/012063
Farshidi F, Jones D, Harvey JT (2013) Warm-mix asphalt study: evaluation of rubberised hot- and warm-mix asphalt with respect to emissions. In: Research report Inst Trans.Stud. University of California, Davis
Francken L (2004) Bituminous binders and mixes : state of the art and interlaboratory tests on mechanical behaviour and mix design : report of RILEM Technical Committee 152-PBM, Performance of Bituminous Materials. E & FN Spon, London
Goh SW, Hasan MRM, You Z (2013) Performances evaluation of Cecabase® RT in warm mix asphalt technology. Procedia oc Behav Sci 96:2782–2790
Golchin B, Hamzah MO, Hasan MRM (2017) Optimization in producing warm mix asphalt with polymer modified binder and surfactant-wax additive. Constr Build Mater 141:578–588
Golchin B, Hamzah MO, Omranian SR, Hasan MRM (2018) Effects of a surfactant-wax based warm additive on high temperature rheological properties of asphalt binders. Constr Build Mater 183:395–407
Hossain Z, Zaman M, O’Rear EA, Chen DH (2012) Effectiveness of water-bearing and anti- stripping additives in warm mix asphalt technology. Int J Pavement Eng 13(5):424–432
Hosseinnezhad S, Kabir SF, Oldham D, Mousavi M, Fini EH (2019) Surface functionalization of rubber particles to reduce phase separation in rubberized asphalt for sustainable construction. J Clean Prod 225:82–89
Jamshidi A (2013) Rheological properties of asphalt binders, performance and sustainability of warm-mix asphalt incorporating sasobit®. Dissertation, University Sains Malaysia
Jamshidi A, Hasan MRM, Ting M (2018) Comparative study on engineering properties and energy efficiency of asphalt mixes incorporating fly ash and cement. Constr Build Mater 168:295–304
Kakar MR, Hamzah MO, Akhtar MN, Woodward D (2016) Surface free energy and moisture susceptibility evaluation of asphalt binders modified with surfactant-based chemical additive. J Clean Prod 112:2342–2353
Kataware AV, Singh D (2017) Evaluating effectiveness of WMA additives for SBS modified binder based on viscosity, Superpave PG, rutting and fatigue performance. Constr Build Mater 146:436–444
Kataware AV, Singh D (2018) Evaluation of intermediate temperature cracking performance of warm mix additive modified asphalt binders. Constr Build Mater 184:165–176
Khatijah S, Bakar A, Abdulah ME, Kamal MM, Abd R (2018) Evaluating the rheological properties of waste natural rubber latex modified binder. In: CENVIRON Confr Proceed 01037
Poovaneshvaran S, Mohd Hasan MR, Putra Jaya R (2020) Impacts of recycled crumb rubber powder and natural rubber latex on the modified asphalt rheological behaviour, bonding, and resistance to shear. Constr Build Mater 234:117–357
Poulikakos LD, Partl MN (2010) Investigation of porous asphalt microstructure using optical and electron microscopy. J Microsc 240(2):145–154
Ramm A, Sakib N, Bhasin A, Downer MC (2016) Optical characterization of temperature- and composition-dependent microstructure in asphalt binders. J Microsc 262(3):216–225
Ranieri V, Kowalski KJ, Berloco N, Colonna P, Perrone P (2017) Influence of wax additives on the properties of porous asphalts. Constr Build Mater 145:261–271
Rodríguez-Alloza AM, Gallego J, Pérez I, Bonati A, Giuliani F (2014) High and low temperature properties of crumb rubber modified binders containing warm mix asphalt additives. Constr Build Mater 460:53–466
Sani A, Mohd Hasan MR, Shariff KA, Jamshidi A, Ibrahim AH, Poovaneshvaran S (2019) Engineering and microscopic characteristics of natural rubber latex modified binders incorporating silane additive. Int J Pavement Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2019.1573319
Sani A., Mohd Hasan MR, Shariff KA, Poovaneshvaran S, Ibrahim I (2020) Morphological identification of latex modified asphalt binder prepared with surfactants. In: Mohamed Nazri F (ed) Proceedings of AICCE'19. AICCE 2019. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 53. Springer, Cham
TAIYU KENSETSU (2018) TOUGH FIX material safety data sheet, TAIYU. https://taiyuvn.com/en/san-pham/tough-fix-hyper-for-anti-stripping/
Wen Y, Wang Y, Zhao K, Sumalee A (2017) The use of natural rubber latex as a renewable and sustainable modifier of asphalt binder. Int J Pavement Eng 8436:1–13
Wu S, Zhao Z, Xiao Y, Yi M, Chen Z, Li M (2017) Evaluation of mechanical properties and aging index of 10-year field aged asphalt materials. Constr Build Mater 155:1158–1167
Xiao F, Punith VS, Amirkhanian SN (2012) Effects of non-foaming WMA additives on asphalt binders at high performance temperatures. Fuel 94:144–155
Yu H, Leng Z, Xiao F, Gao Z (2016) Rheological and chemical characteristics of rubberised binders with non-foaming warm mix additives. Constr Build Mater 111:671–678
Yu H, Leng Z, Dong Z, Tan Z, Guo F, Yan J (2018) Workability and mechanical property characterization of asphalt rubber mixtures modified with various warm mix asphalt additives. Constr Build Mater 175:392–401
Zhao S, Huang B, Shu X, Jia X, Woods M (2012) Laboratory performance evaluation of warm-mix asphalt containing high percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement. J Transport Res Rec 2294:98–105
Ziari H, Naghavi M, Imaninasab R (2018) Performance evaluation of rubberised asphalt mixes containing WMA additives. Int J Pavement Eng 19(7):623–629
Acknowledgements
The authors of this paper would like to acknowledge the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education and Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (203/PAWAM/6071358) and Short-Term Research Grant Scheme (304/PAWAM/60313048), respectively for the financial support provided. The authors also would like to thank all material suppliers that allowed this study to be conducted. Any opinions, findings and conclusions expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education and USM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sani, A., Mohd Hasan, M.R., Shariff, K.A. et al. Physico-Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Wax Latex-Modified Asphalt Binder. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 45, 865–878 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00422-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00422-9