Abstract
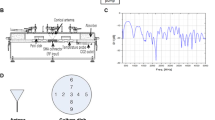
The biological effects of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation (EMF) are of high importance in biological and health studies. This study aimed to find out these effects on the structure and function of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH). The rhGH was exposed to uniform mobile phone 940-MHz EMFs for 45 min and then characterized by circular dichroism (CD), dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta potential, and intrinsic fluorescence spectroscopy techniques. The half-life of this protein in plasma has been measured by ELISA after exposure to the EMFs. The CD spectra indicated significant changes in the secondary structure of the hormone (two negative peaks at 208 and 222 nm). These changes in the secondary structure of the treated rhGH were found irreversible as there were no significant differences in the CD spectra of the samples measured at first day and 45 days afterwards. The DLS analysis showed about 27% increase in the protein size compared to that of control. The biological activity as measured by half-life of the rhGH in plasma showed a sevenfold decrease after 25 min. The injection of the radiated protein into mice had shown a significant decrease in the weight gain compared to that of control. These findings approved irreversible disruptive changes in the structure and function of the rhGH upon exposure to the EMF.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharjee S (2016) DLS and zeta potential—what they are and what they are not? J Control Release 235:337–351
Bonaccurso E, Kappl M, Butt HJ (2002) Hydrodynamic force measurements: boundary slip of water on hydrophilic surfaces and electrokinetic effects. Phys Rev Lett 88(7):076103
Brown-Borg HM, Rakoczy SG, Romanick MA, Kennedy MA (2002) Effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 on hepatocyte antioxidative enzymes. Exp Biol Med 227(2):94–104
Cunningham BC, Ultsch M, De Vos AM, Mulkerrin MG, Clauser KR, Wells JA (1991) Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by a single hormone molecule. Science 254(5033):821–825
Fahnert B, Lilie H, Neubauer P (2004) Inclusion bodies: formation and utilisation. In: Physiological stress responses in bioprocesses. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 93–142
Gerner C, Haudek V, Schandl U, Bayer E, Gundacker N, Hutter HP, Mosqoeller W (2010) Increased protein synthesis by cells exposed to a 1800-MHz radio-frequency mobile phone electromagnetic field, detected by proteome profiling. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 83(6):691–702
Gheorghe M, Mihai M, Ana-Maria M, Laurentiu-Valentin S (2009) Microwaves electromagnetic field influence on pH theoretical and experimental results. Rev Air For Acad 1:45–48
Greenfield NJ (2006) Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat Protoc 1(6):2876–2890
Grimaldi S, Lisi A, Reiti S, Manni V, Ledda M, Giuliani L (2004) Influence of 50-Hz electromagnetic field on Anurian (Xenopus laevis) metamorphosis. Sci World J 4:41–47
Haberer JE, Kiwanuka J, Nansera D, Wilson IB, Bangsberg DR (2010) Challenges in using mobile phones for collection of antiretroviral therapy adherence data in a resource-limited setting. AIDS Behav 14(6):1294–1301
Hekmat A, Saboury AA, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2013) The toxic effects of mobile phone radiofrequency (940 MHz) on the structure of calf thymus DNA. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 88:35–41
Houston BJ, Nixon B, McEwan KE, Martin JH, King BV, Aitken RJ, De Luliis GN (2019) Whole-body exposure to radiofrequency-electromagnetic energy can cause DNA damage in mouse spermatozoa via an oxidative mechanism. Sci Rep 9:17478
Ikehara M, Ohtsuka E, Tokunaga T, Taniyama Y, Iwai S, Kitano K, Fujiyama K (1984) Synthesis of a gene for human growth hormone and its expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81(19):5956–5960
Jackimska B, Wasilewska M, Adamczyk Z (2008) Characterization of globular protein solutions by dynamic light scattering, electrophoretic mobility, and viscosity measurements. Langmuir 24(13):6866–6872
Komatsu N, Saijoh K, Otsuki N, Kishi T, Micheal IP, Obiezu CV, Clayman GL (2007) Proteolytic processing of human growth hormone by multiple tissue kallikreins and regulation by the serine protease inhibitor Kazal-Type5 (SPINK5) protein. Clin Chim Acta 377(1–2):228–236
Krichevsky O, Bonnet G (2002) Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: the technique and its applications. Rep Prog Phys 65(2):251
Mann S, Cooper TG, Allen SG, Blackwell RP, Lowe AJ (2000) Exposure to radio waves near mobile phone base stations. Radiol Prot Bull 225:13–16
Pauline CN, Henikoff S (2003) SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucl Acids Res 31(13):3812–3814
Polk C, Postow E (1995) Handbook of biological effects of electromagnetic fields, 2nd edn. CRC Press, New York
Sefidbakht Y, Hosseinkhani S, Mortazavi M, Tavakkolnia I, Khellat MR, Shakiba-Herfeh M, Saviz M, Faraji-Dana R, Saboury AA, Sheibani N, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2013) Effects of 940 MHz EMF on luciferase solution: structure, function, and dielectric studies. Bioelectromagnetics 34(6):489–498
Sefidbakht Y, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Hosseinkhani S, Khodagholi F, Torkzadeh-Mahani M, Foolad F, Faraji-Dana R (2014) Effects of 940 MHz EMF on bioluminescence and oxidative response of stable luciferase producing HEK cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 13(7):1082–1092
Stetefeld J, McKenna SA, Patel TR (2016) Dynamic light scattering: a practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys Rev 8(4):409–427
Sukhorukov GB, Donath E, Lichtenfeld H, Knippel E, Knippel M, Budde A, Mohwald H (1998) Layer-by-layer self-assembly of polyelectrolytes on colloidal particles. Colloids Surf A 137:253–266
Trock DH (2000) Electromagnetic fields and magnets: Investigational treatment for musculoskeletal disorders. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 26(1):51–62
Wardell K, Jakobsson A, Nilsson GE (1993) Laser Doppler perfusion imaging by dynamic light scattering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 40(4):309–316
Wroblewski VJ, Masnyk M, Becker GW (1991) Proteolytic cleavage of human growth hormone (hGH) by rat tissues in vitro: influence on the kinetics of exogenously administered hGH. Endocrinology 129(1):465–474
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support of Malek-e-Ashtar University of Technology (Tehran). The proof editing by Hamyarapply (Tehran, Iran) is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest for authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadpour-Aghdam, M., Molaeirad, A., Faraji-Dana, R. et al. In Vitro Effects of Cellular Phone Electromagnetic Fields at 940 MHz on the Structure and Half-Life of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 44, 641–649 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00891-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00891-7