Abstract
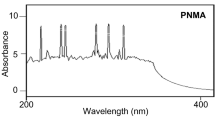
This paper reports on the synthesis and characterization of poly(2-methylaniline), PmA, a derivative of a very fascinating electronically conducting polymer polyaniline. PmA was synthesized in its salt form by one pot emulsion polymerization route using DBSA and sulfuric acid as co-dopants. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and Ultraviolet visible spectroscopic analysis confirmed formation of conducting emeraldine salt form of PmA. These PmA salts showed good redox reversibility and high purity. Thermogravimetric analysis revealed very good thermal stability up to 520 °C which is the highest reported thermal stability for PmA so far. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements clearly revealed that the PmA acts as corrosion protective coating on stainless steel with the protection efficiency of 55.59%.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdiryim T, Xiao-Gang Z, Jamal R (2005) Synthesis and characterization of poly (o-toluidine) doped with organic sulfonic acid by solid-state polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 96:1630–1634. doi:10.1002/app.21614
Ahmed S, Abd-Elrhaman M (2007) Thermokinetic studies of poly (o-toluidine) doped with perchloric acid. J Therm Anal Calorim 91:195–202. doi:10.1007/s10973-007-8364-5
Ahmed SM, Abu-Zied BM (2003) Thermal degradation studies of the reduced and oxidized poly (o-toluidine) matrix. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 70:277–289. doi:10.1016/S0165-2370(02)00137-7
Bilal S, Holze R (2006) Electrochemical copolymerization of o-toluidine and o-phenylenediamine. J Electroanal Chem 592:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2006.03.039
Bilal S, Holze R (2008) A spectroelectrochemical study of homo-/co-oligomerization and homo-/copolymers of o-phenylenediamine and o-toluidine. J Electrochem Soc 155:89–96. doi:10.1149/1.2949688
Bilal S, Holze R (2009) A correlation of electrochemical and spectroelectrochemical properties of poly (o-toluidine). Electrochim Acta 54:4851–4856. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.03.072
Bilal S, Farooq S, Holze R (2014) Improved solubility, conductivity, thermal stability and corrosion protection properties of poly (o-toluidine) synthesized via chemical polymerization. Synth Met 197:144–153. doi:10.1016/j.synthmet.2014.09.003
Ebrahim SM, Gad A, Morsy A (2010) Highly crystalline and soluble dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid doped poly (o-toluidine). Synth Met 160:2658–2663. doi:10.1016/j.synthmet.2010.10.021
Farag AAM, Ashery A, Shenashen MA (2012) Optical absorption and spectrophotometric studies on the optical constants and dielectric of poly (o-toluidine) (POT) films grown by spin coating deposition. Phys B 407:2404–2411. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2012.03.034
Ganash A (2014) Effect of current density on the corrosion protection of Poly (o-toluidine)-coated stainless steel. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:4000–4013
Gazotti WA, De Paoli MA (1996) High yield preparation of a soluble polyaniline derivative. Synth Met 80:263–269. doi:10.1016/0379-6779(96)80212-8
Gerard M, Chaubey A, Malhotra BD (2002) Application of conducting polymers to Biosens. Bioelectron 17:345–359. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(01)00312-8
Jamal R, Abdiryim T, Nurulla I (2008) Comparative studies of solid-state synthesized poly (o-methoxyaniline) and poly (o-toluidine). Polym Adv Technol 19:1461–1466. doi:10.1002/pat.1139
Kulkarni MV, Viswanath AK (2004) Comparative studies of chemically synthesized polyaniline and poly (o-toluidine) doped with p-toluene sulphonic acid. Eur Polym J 40:379–384. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2003.10.007
Kulkarni MV, Viswanath AK, Mulik UP (2005) Studies on chemically synthesized organic acid doped poly (o-toluidine). Mater Chem Phys 89:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.01.031
Kulkarni MV, Kasi Viswanath A, Khanna PK (2006) Investigation of spectroscopic and thermal properties of poly (o-toluidine) doped with polymeric acids. J Macromol Sci A: Pure Appl Chem 43:197–203. doi:10.1080/10601320500406073
Kumar D, Sharma RC (1998) Advances in conductive polymers. Eur Polym J 34:1053–1060. doi:10.1016/S0014-3057(97)00204-8
Kumari K, Ali V, Rani G, Kumar S, Lakshmi GBVS, Zulfequar M (2011) DC conductivity and spectroscopic characterization of poly (o-toluidine) doped with binary dopant ZrOCl2/AgI. Mater Sci Appl 2:1049–1057. doi:10.4236/msa.2011.28142
Li XG, Wang LX, Jin Y, Zhu ZL, Yang YL (2001) Preparation and identification of a soluble copolymer from pyrrole and o-toluidine. J Appl Polym Sci 82:510–518. doi:10.1002/app.1877
Mucuk Z, Karakışla M, Saçak M (2009) Synthesis of poly (o-toluidine) in DMF/water mixture using benzoyl peroxide. Int J Polym Anal Charact 14:403–417. doi:10.1080/10236660903031025
Probst M, Holze R (1997) A systematic spectroelectrochemical investigation of alkyl-substituted anilines and their polymers. Macromol Chem Phys 198:1499–1509. doi:10.1002/macp.1997.021980515
Ramachandran R, Kathiravan R, Rani M, Kabilan S, Jeong YT (2012) Synthesis and characterization of novel conducting 1, 5-naphthalenediamine–aniline copolymer. Synth Met 162:1636–1642. doi:10.1016/j.synthmet.2012.06.011
Shinde V, Sainkar SR, Patil PP (2005) Electrochemical synthesis and corrosion protection properties of poly (o-toluidine) coatings on low carbon steel. J Appl Polym Sci 96:685–695. doi:10.1002/app.21497
Shreepathi S, Holze R (2007) Benzoyl-peroxide-initiated inverse emulsion copolymerization of aniline and o-toluidine: effect of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid on the physicochemical properties of the copolymers. Macromol Chem Phys 208:609–621. doi:10.1002/macp.200600491
Surwade SP, Agnihotra SR, Dua V, Manohar SK (2009) Nitrogen dioxide vapor detection using poly-o-toluidine. Sens Actuators B Chem 143:454–457. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2009.09.033
Wei Y, Focke WW, Wnek GE, Ray A, MacDiarmid AG (1989) Synthesis and electrochemistry of alkyl ring-substituted polyanilines. J Phys Chem 93:495–499. doi:10.1021/j100338a095
Yilmaz H, Unal HI, Sari B (2007) Synthesis, characterization and electrorheological properties of poly (o-toluidine)/Zn conducting composites. J Appl Polym Sci 103:1058–1065. doi:10.1002/app.25310
Ziadan KM, Hussein HF, Ajeel KI (2012) Study of the electrical characteristics of poly (o-toluidine) and application in solar cell. Energy Procedia 18:157–164. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2012.05.027
Acknowledgements
Higher Education Commission, Islamabad is highly acknowledged for financial support under research grant #20-311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilal, S., Gul, H., Gul, S. et al. One Pot Synthesis of Highly Thermally Stable Poly(2-Methylaniline) for Corrosion Protection of Stainless Steel. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 42, 1915–1922 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0164-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0164-6