Abstract
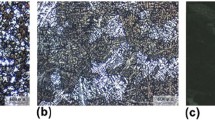
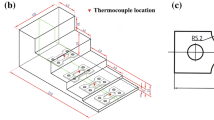
The influence of external magnetic field in the sand casting process on the microstructures and mechanical properties of A357 aluminum-silicon (Al–Si) alloys was investigated. Different magnetic field intensities such as 0, 6.3, and 10.7 mT were applied respectively by Helmholtz coils with an autotransformer. Applied an external magnetic fields during the solidification process, the microstructures of as-cast A357 alloy performed grain refinement of α-Al, reduction of secondary dendritic arm spacing, and fibrous structure of eutectic silicon. After T6 heat treatment, the morphology of eutectic silicon particles became fragmented and spheroidized. Therefore, the magnetic field enhanced the mechanical properties of A357 alloys, including hardness, ultimate tensile strength (UTS), yield strength (YS), and elongation (El). Compared the samples without magnetic field and with the field of 10.7 mT, the values of hardness, UTS, YS and El increased 17.9%, 10.6%, 8.8%, and 48%, respectively. The higher the magnetic field we apply, the better performance of sand-cast A357 we can get. Moreover, the magnetic field during A357 solidification process attributed to the preferred orientation (111) of α-Al and uniformly dimples in fractography. In conclusion, an inexpensive and facile technique has been proposed to enhance the quality index of the sand-casting A357 alloys via the influence by external magnetic fields on the microscopic properties of materials, especially for α-Al grain refinement and eutectic-silicon spheroidization.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.M.P. Ferreira, E. Bayraktar, I. Miskioglu, M.H. Robert, New magnetic aluminum matrix composites (Al-Zn-Si) reinforced with nano magnetic Fe 3 O 4 for aeronautical applications. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 4(3), 358–369 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2018.1432940
F.C.R. Hernandez, J.M.H. Ramírez, R. Mackay, Al-Si Alloys: Automotive, Aeronautical, and Aerospace Applications (Springer, Switzerland, 2017), pp.163–171
Q. Han, H. Xu, Fluidity of alloys under high pressure die casting conditions. Scr. Mater. 53(1), 7–10 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.03.025
S. Nafisi, D. Emadi, M.T. Shehata, R. Ghomashchi, Effects of electromagnetic stirring and superheat on the microstructural characteristics of Al–Si–Fe alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 432(1–2), 71–83 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.076
S. Eckert et al., Electromagnetic melt flow control during solidification of metallic alloys. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 220(1), 123–137 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01802-7
Y. Zuo, J. Cui, Z. Zhao, H. Zhang, L. Li, Q. Zhu, Mechanism of grain refinement of an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy prepared by low-frequency electromagnetic casting. J. Mater. Sci. 47(14), 5501–5508 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6441-z
R. Liu et al., Influence of pore characteristics and eutectic particles on the tensile properties of Al–Si–Mn–Mg high pressure die casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 783, 139280 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139280
R.K. Yajjala, N.M. Inampudi, B.R. Jinugu, Correlation between SDAS and mechanical properties of Al–Si alloy made in Sand and Slag moulds. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9(3), 6257–6267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.02.066
E. Ghassemali, M. Riestra, T. Bogdanoff, B.S. Kumar, S. Seifeddine, Hall-Petch equation in a hypoeutectic Al–Si cast alloy: grain size vs. secondary dendrite arm spacing. Procedia Eng. 207, 19–24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.731
E.A. Elsharkawi, M.H. Abdelaziz, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Effect of β-Al5FeSi and π-Al8Mg3FeSi6 phases on the impact toughness and fractography of Al–Si–Mg-based alloys. Int. J. Met. 12(1), 148–163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0153-8
K.V. Yang, P. Rometsch, C.H.J. Davies, A. Huang, X. Wu, Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and anisotropy in mechanical properties of A357 alloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 154(2017), 275–290 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.05.026
Y.X. Gan, R.A. Overfelt, Fatigue property of semisolid A357 aluminum alloy under different heat treatment conditions. J. Mater. Sci. 41(22), 7537–7544 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0838-5
M.F. Ibrahim, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Effect of aging conditions on precipitation hardening in al-si-mg and al-si-cu-mg alloys. Int. J. Met. 11(2), 274–286 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0057-z
Y. Birol, A novel Al–Ti–B alloy for grain refining Al–Si foundry alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 486(1–2), 219–222 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.07.064
Q. Wei et al., Effect of Sc on microstructure and properties of A357 alloy under different casting conditions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 20, 2051–2059 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.145
G. Eisaabadi, A. Nouri, Effect of Sr on the microstructure of electromagnetically stirred semi-solid hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys. Int. J. Met. 12(2), 292–297 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0161-8
S. Steinbach, L. Ratke, The effect of rotating magnetic fields on the microstructure of directionally solidified Al–Si–Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 413–414(December), 200–204 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2005.09.010
B. Zhang, J. Cui, G. Lu, Effect of low-frequency magnetic field on macrosegregation of continuous casting aluminum alloys. Mater. Lett. 57(11), 1707–1711 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(02)01055-8
A. Guo, X. Qiu, Z. Ke, J. Zhao, Effect of the injection velocity and the electromagnetic stirring on the mechanical properties of a rheo-diecast 357 Al alloy. Int. J. Met. 16(2), 663–673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00621-8
D. Weiss et al., Thermomagnetic processing of aluminum alloys during heat treatment. Int. J. Met. 15(1), 49–59 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00460-z
C.S. Wang, S.C. Lin, T.Y. Lin, J.Y. Wang, R. Muhfidin, I.S. Yu, Effects of Helmholtz coil magnetic fields on microstructure and mechanical properties for sand-cast A201 Al–Cu alloy. Mater. Res. Express (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abcc88
J. Zheng et al., Effectiveness analysis of resources consumption, environmental impact and production efficiency in traditional manufacturing using new technologies: case from sand casting. Energy Convers. Manag. 209, 112671 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112671
H. Khandelwal, B. Ravi, Effect of molding parameters on chemically bonded sand mold properties. J. Manuf. Process. 22, 127–133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.03.007
B. Zhang, J. Cui, G. Lu, Effects of low-frequency electromagnetic field on microstructures and macrosegregation of continuous casting 7075 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 355, 325–330 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00105-9.X
Liu et al., Heat-treatment induced defect formation in α-Al matrix in Sr-modified eutectic Al–Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 730, 208–218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.324
N. Hansen, Hall-petch relation and boundary strengthening. Scr. Mater. 51(8), 801–806 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.06.002
E. Çadırlı, H. Kaya, U. Büyük, E. Üstün, M. Gündüz, Effect of heat treatment on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Al–4Cu–1.5Mg Alloy. Int J Met 16(2), 1020–1033 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00667-8
E. Ma, Eight routes to improve the tensile ductility of bulk nanostructured metals and alloys. Jom 58(4), 49–53 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0215-5
Y. Zhang, E. Lordan, K. Dou, S. Wang, Z. Fan, Influence of porosity characteristics on the variability in mechanical properties of high pressure die casting (HPDC) AlSi7MgMn alloys. J. Manuf. Process. 56(January), 500–509 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.04.071
H.R. Ammar, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, The concept of quality index and its application for Al–Si cast alloys. Int. J. Met. 15(4), 1197–1212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00556-6
M. Drouzy, S. Jacob, M. Richard, Interpretation of tensile results by means of quality index and probable yield strength. AFS Int. Cast Metals J. 5, 43–50 (1980)
X. Shen et al., Effect of Ti/Sc atom ratio on heterogeneous nuclei, microstructure and mechanical properties of A357–0.033Sr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 671, 275–287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.06.022
Q. Bai, J. Wang, S. Xing, Y. Ma, X. Bao, Crystal orientation and crystal structure of paramagnetic α-Al under a pulsed electromagnetic field. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67352-4
Z. Chen, X. Hao, Y. Wang, K. Zhao, In-situ observation of tensile fracture in A357 casting alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30(2), 139–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.04.014
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan (NSTC 109-2221-E-259-004-MY3) and National Chung-Shan Institute of Science & Technology (XV09061P155PECS) for financially supporting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicting interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Purnomo, M.J., Hsu, YX., Lin, KZ. et al. The Enhancement of Microstructures and Mechanical Characteristics for Sand Casting A357 Alloys with Magnetic Fields by Helmholtz Coils. Inter Metalcast 18, 1455–1464 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01129-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01129-z