Abstract
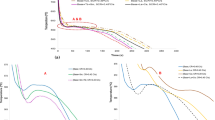
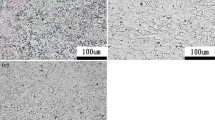
Focused on improving the elevated-temperature performance of the B319 aluminum alloy, this paper investigates, for the first time, the effects that varying Ce additions (i.e., 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, and 1.0 wt% Ce) have on the microstructure, hardness, and tensile properties of the alloy, following a conditioning process. The hardness tests were performed at room temperature before and after exposing the samples to 250 and 300 °C for 250 h. It was found that the hardness of the B319 + 0.1%Ce alloy was the highest in all three conditions, showing improvements of 9–11%. For the tensile tests, the cast alloys were tested at room temperature, 250 °C before conditioning, and at 250 and 300 °C after conditioning at their test temperatures (i.e., 250 and 300 °C) for 250 h. In all conditions, the B319 + 0.1%Ce demonstrated the greatest strength during the tensile test and consistently had YS and UTS values 6–10% greater than the unmodified B319 alloy. However, by comparing the YS and UTS values before and after conditioning, it was observed that the Ce additions had little effect on the strength retention, and in some cases (i.e., higher Ce concentrations), the strength retention was worse than for the unmodified B319 alloy.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Czerwinski, D. Sediako, S. Shaha, D. Chen, High temperature aluminum alloys for automotive powertrain. Adv. Mater. Process 174, 16–20 (2016)
C.Y. Jeong, High temperature mechanical properties of Al–Si–Mg–(Cu) alloys for automotive cylinder heads. Mater. Trans. 54(4), 588–594 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2012285
A. Lombardi, C. Ravindran, R. MacKay, Improvements in mechanical properties of 319 Al alloy engine blocks through cost-effective solution heat treatment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23(8), 2766–2771 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1065-x
J. Stroh, A. Piche, D. Sediako, A. Lombardi, G. Byczynski, The effects of solidification cooling rates on the mechanical properties of an aluminum inline-6 engine block, miner. Met. Mater. Ser., Light Met (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05864-7_65
E. Aghaie, J. Stroh, D. Sediako, M. Smith, In-Situ Fitness-For-Service Assessment of Aluminum Alloys Developed for Automotive Powertrain Lightweighting. (Springer International Publishing, 2018), pp. 397–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72284-9_53
E. Vandersluis, D. Sediako, C. Ravindran, A. Elsayed, G. Byczynski, Analysis of eutectic silicon modification during solidification of al-6si using in-situ neutron diffraction. J. Alloys Compd. 736, 172–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.118
D. Sediako, W. Kasprzak, In situ study of microstructure evolution in solidification of hypereutectic Al–Si alloys with application of thermal analysis and neutron diffraction. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 46(9), 4160–4173 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3007-0
R. Donahue, P.A. Fabiyi, Manufacturing feasibility of all-aluminum automotive engines via application of high silicon aluminum alloy, SAE Tech. Pap. Ser., no2000-01–0061, pp. 1–11 (2000). https://doi.org/10.4271/2000-01-0061
S.K. Chaudhury, D. Apelian, P. Meyer, D. Massinon, J. Morichon, Microstructure and mechanical properties of heat-treated B319 Alloy diesel cylinder heads. Metall. Mater. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 46(7), 3276–3286 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2837-0
S.K. Shaha, F. Czerwinski, W. Kasprzak, J. Friedman, D.L. Chen, Thermal stability of (AlSi) × (ZrVTi) intermetallic phases in the Al–Si–Cu–Mg cast alloy with additions of Ti, V, and Zr. Thermochim. Acta 595, 11–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2014.08.037
K.Y. Lee, S.L. Lee, C.T. Wu, W.C. Chen, J.C. Lin, Effects of T6 heat treatment on thermal stability and wear behaviour of Al-12.5Si-4.5Cu-1.0 Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. (United Kingdom) 28(6), 639–643 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284711Y.0000000057
L. Jin, K. Liu, X.G. Chen, Evolution of dispersoids and their effects on elevated-temperature strength and creep resistance in Al–Si–Cu 319 cast alloys with Mn and Mo additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. 770(138554), 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138554
J. Stroh, D. Sediako, D. Weiss, The effects of iron-bearing intermetallics on the fitness-for-service performance of a rare-earth-modified A356 alloy for next generation automotive powertrains. Metals (Basel) 11(5), 1–20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11050788
J. Stroh, D. Sediako, D. Weiss, The effect of rare earth mischmetal on the high temperature tensile properties of an A356 aluminum alloy. Light Met. 2021, 184–191 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65396-5_27
C. Xu, W. Xiao, S. Hanada, H. Yamagata, C. Ma, The effect of scandium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Si–Mg alloy: a multi-refinement modifier. Mater. Charact. 110, 160–169 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.10.030
S.K. Shaha, F. Czerwinski, W. Kasprzak, J. Friedman, D.L. Chen, Improving high-temperature tensile and low-cycle fatigue behavior of Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloys through micro-additions of Ti V, and Zr. Metall. Mater. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 46(7), 3063–3078 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2880-x
J. Royset, N. Ryum, Scandium in aluminum alloys. Int. Mater. Rev. 50(1), 19–44 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1179/174328005X14311
S. Seifeddine, S. Johansson, I. Svensson, The influence Of cooling rate and manganese content on the-Al 5 fesi phase formation and mechanical properties Of Al–Si-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 490, 385–390 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.01.056
A.R. Farkoosh, M. Pekguleryuz, The effects of manganese on the Τ-phase and creep resistance in Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Ni alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 582, 248–256 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.06.030
B.F. Kabirian, R. Mahmudi, Effects of zirconium additions on the microstructure of as-cast and aged AZ91 magnesium alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 11(3), 189–193 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200800223
S.K. Shaha, F. Czerwinski, W. Kasprzak, J. Friedman, D.L. Chen, Effect of Cr Ti, V, and Zr micro-additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of the Al–Si–Cu–Mg cast alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 47(5), 2396–2409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3365-2
D. Weiss, High Performance Aluminum Casting Alloys for Engine Applications, SAE Tech. Pap. Ser., 1(2016-32–0019), pp. 1–5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4271/2016-32-0019
J. Stroh, D. Sediako, D. Weiss, Development of cerium-reinforced specialty aluminum alloy with application of X-ray and neutron diffraction. Int. J. Met. 15(1), 29–39 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00467-6
Z. Sims et al., High performance aluminum-cerium alloys for high-temperature applications. Mater. Horiz. 4(6), 1070–1078 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7mh00391a
J. Stroh, Development of Precipitation-Strengthened Aluminum Alloys and Manufacturing Processes for Next Generation Automotive Powertrains, PhD Dissertation, University of British Columbia Okanagan, (2021). https://doi.org/10.14288/1.0396852
M.G. Mahmoud, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, F.H. Samuel, Effect of the addition of La and Ce on the solidification behavior of Al–Cu and Al–Si–Cu cast alloys. Int. J. Met. 14(1), 191–206 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00351-y
M.G. Mahmoud, Y. Zedan, A.M. Samuel, V. Songmene, F.H. Samuel, The use of rare earth metals in Al–Si–Cu casting alloys. Int. J. Met. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00640-5
M.F. Ibrahim, M.H. Abdelaziz, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, F.H. Samuel, Effect of rare earth metals on the mechanical properties and fractography of Al–Si-based alloys. Int. J. Met. 14(1), 108–124 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00336-x
D. Weiss, Improved high-temperature aluminum alloys containing cerium. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28(4), 1093–1908 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-3884-2
E. Aghaie, J. Stroh, D. Sediako, A. Rashidi, A.S. Milani, Improving the mechanical properties of the B319 aluminum alloy by addition of cerium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 793(139899), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139899
M. Mahmoud, E. Elgallad, M. Ibrahim, F. Samuel, Effect of rare earth metals on porosity formation in A356 alloy. Int. J. Met. 12(2), 251–265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0156-5
E. Rincon, H.F. Lopez, M.M. Cisneros, H. Mancha, Temperature effects on the tensile properties of cast and heat treated aluminum alloy A319. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 519(1–2), 128–140 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.05.022
D. Sediako, W. Kasprzak, F. Czerwinski, A. Nabawy, A. Farkoosh, High temperature creep evolution In Al–Si alloys developed for automotive powertrain applications: a neutron in-situ study on Hkl-plane creep response. Light Met. 2016, 131–136 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119274780.ch23
F. Xia, J. Li, Y. Guo, Z. Yang, Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of an Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Ni aluminium alloy after thermal exposure. Maertials Sci. Forum 765, 486–490 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.765.486
A. Školáková, P. Novák, L. Mejzlíková, F. Pruša, P. Salvetr, D. Vojtěch, Structure and mechanical properties of Al–Cu–Fe–X alloys with excellent thermal stability. Materials (Basel) 10(11), 1–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111269
ASTM, E3-11 Standard Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens, ASTM Copyright., vol. i, pp. 1–12 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1520/E0003-11R17
ASTM International, E384-17 Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials, pp. 1-40 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1520/E0384-17
M. Farina, P. Bell, C. Raimundo, F. Ferreira, B. Dedavid, P. Alegre, Effects of solidification rate in the microstructure of Al–Si5Cu3 aluminum cast alloy. Mater. Res. 20(2), 273–278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2017-0083
Y. Liu, M. Liu, L. Luo, J. Wang, C. Liu, Solidification behavior of AA2618 aluminum alloy and influence of cooling rate. Materials (Basel) 7(12), 7875–7890 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7127875
A. Lombardi, D. Sediako, C. Ravindran, M. Barati, Analysis of precipitation, dissolution and incipient melting of Al2Cu in B206 Al alloy using in-situ neutron diffraction. J. Alloys Compd. 784, 1017–1025 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.104
Y. Wu, J. Xiong, R. Lai, X. Zhang, Z. Guo, The microstructure evolution of an Al–Mg–Si–Mn–Cu–Ce alloy during homogenization. J. Alloys Compd. 475(1–2), 332–338 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.032
T. Gao, Y. Wu, C. Li, X. Liu, Morphologies and growth mechanisms of α-Al(FeMn)Si in Al–Si–Fe–Mn alloy. Mater. Lett. 110, 191–194 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.08.039
F. Prusa et al., High-strength ultra-fine-grained hypereutectic Al–Si–Fe–X (X = Cr, Mn) alloys prepared by short-term mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Materials (Basel) 9(12), 973 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9120973
H. Huang, Y. Cai, H. Cui, J. Huang, J. He, Influence of Mn addition on microstructure and phase formation of spray-deposited Al-25Si-xFe-yMn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 502(1–2), 118–125 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.10.005
Y. Zedan, F. Samuel, A. Samuel, H. Doty, Effects of Fe intermetallics on the machinability of heat-treated Al-(7–11)% Si alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 210(2), 245–257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.09.007
A. Ibrahim, E. Elgallad, A. Samuel, H. Doty, F. Samuel, Effects of addition of transition metals on intermetallic precipitation in Al-2%Cu–1%Si based alloys. Int. J. Met. 12(3), 1–15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0196-x
A. Samuel, E. Elgallad, M. Mahmoud, H. Doty, S. Valtierra, F. Samuel, Rare earth metal-based intermetallics formation in Al–Cu–Mg and Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloys: a metallographic study. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1–15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7607465
A. Sinha, Z. Farhat, A study of porosity effect on tribological behavior of cast Al A380M and sintered Al 6061 alloys. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 5(1), 1–16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4236/jsemat.2015.51001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghaie, E., Stroh, J. & Sediako, D. Long-Term Thermal Stability of Cerium-Modified B319 Aluminum Alloy. Inter Metalcast 17, 682–695 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00835-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00835-4