Abstract
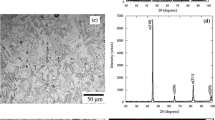
This work investigates the optimum pouring temperature during semisolid casting (rheo-casting) of Al–17%Si alloy (A390) to obtain the best combination of microstructure modification and wear resistance. Pouring semisolid slurry was done in both metallic and sand molds to observe the effect of cooling rate on the optimum pouring temperature. The molten metal/slurry was poured into the specified mold type through a cooling slope plate which was continuously water cooled. Different pouring temperatures: 670, 690, 710 and 730 °C, were applied, and their influence on the microstructure and alloy properties was analyzed. Based on the obtained results, the optimum pouring temperature for semisolid casting was decided for the two mold types. Conventional casting was conducted at the optimum temperature in both metallic and sand molds for comparison. It was observed that rheo-casting using the cooling plate is an effective process in microstructure modification of A390 alloy in terms of refining and redistributing the primary Si and fragmenting the coarse AlFeMnSi phase. The optimum temperatures to obtain small particle size of primary Si, uniform distribution and regular shape using the cooling plate technique were 690 °C and 710 °C for the metallic and sand molds, respectively. This refinement and homogenization of the microstructure enhanced the hardness and wear resistance of alloy A390.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Chen, C. Yang, C. Chao, A novel method for net-shape forming of hypereutectic Al–Si alloys by thixocasting with powder performs. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 167, 103–109 (2005)
Y.P. Wu, S.J. Wang, H. Li, X.F. Liu, A new technique to modify hypereutectic Al–24%Si alloys by a Si–P master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 477, 139–144 (2009)
T. Haga, H. Sakaguchi, H. Inui, H. Watari, S. Kumai, Aluminum alloy semisolid strip casting using an unequal diameter twin roll caster. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 14, 157–162 (2006)
Q. Jiang, C. Xu, Morphologies of primary silicon in hypereutectic Al–Si alloys with melt overheating temperature and cooling rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 437, 451–457 (2006)
Y. Haizhi, An overview of the development of Al–Si-alloy based material for engine applications. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 12, 288–297 (2003)
J. Gruzlesk, B. Closset, The treatment of liquid aluminium–silicon alloys (AFS, Des Plaines, 1990), pp. 107–126
W. Shi, B. Gao, G. Tu, S. Li, Y. Hao, F. Yu, Effect of neodymium on the primary silicon and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al–15%Si alloy. J. Rare Earths 28, 367–370 (2010)
C. Chen, Z. Liu, B. En, M.X. Wang, Y. Weng, Z. Liu, Influences of complex modification of P and RE on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al–20Si alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 17, 301–306 (2007)
Z.L. Ning, H. Wang, J.F. Sun, Deformation behavior of semisolid A356 alloy prepared by low temperature pouring. Mater. Manuf. Process. 25, 648–653 (2010)
R.A. Martinez, M.C. Flemings, Evolution of particle morphology in semisolid processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 2205–2210 (2005)
W. Khalifa, Y. Tsunekawa, S. El-Hadad, Ultrasonic rheo-die casting of A383 aluminum alloy. Solid State Phenom. 256, 282–287 (2016)
H.M. Guo, X.Q. Luo, A.S. Zhang, X.J. Yang, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 20, 1361–1366 (2010)
T. Haga, S. Suzuki, Casting of aluminum alloy ingots for thixoforming using a cooling slope. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 118, 169–172 (2001)
T. Haga, P. Kapranos, Simple rheocasting processes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 130–131, 594–598 (2002)
W. Khalifa, Y. Tsunekawa, S. El-Hadad, Microstructure characteristics and tensile property of ultrasonic treated-thixo cast A356 alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 25, 3173–3180 (2015)
N.K. Kund, P. Dutta, Numerical study of influence of oblique plate length and cooling rate on solidification and macro segregation of A356 aluminum alloy melt with experimental comparison. J. Alloys Compd. 678, 343–354 (2016)
L. Gao, F. Cao, Z. Chen, J. Xu, T. Wang, Z. Cao, T. Li, Mechanism of alloy Microstructure globularization during cooling slope process. Material Research Innovations 18, 412–417 (2014)
P. Das, S.K. Samanta, H. Chattopadhyay, P. Dutta, Microstructural evolution of A356 Al alloy during flow along a cooling slopes. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 65(6), 669–672 (2012)
M. Ramadan, N. Fathy, Solidification microstructure of rheocast hyper-eutectic Al–18Si alloy. J. Metall. Eng. 2, 149–154 (2013)
P. Samanta, P. Dutta, Microstructure evolution and rheological behavior of cooling slope processed Al–Si–Cu–Fe alloy slurry. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 2243–2256 (2016)
M.C. Flemings, R.A. Martinez, Principles of microstructural formation in semi-solid metal processing. Solid State Phenom. 116–117, 1–8 (2006)
S. Deepak Kumar, A. Mandal, M. Chakraborty, Cooling slope casting process of semisolid aluminum alloys: a review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 3, 269–283 (2014)
M.N. Mohammed, M.Z. Omar, M.S. Salleh, K.S. Alhawari, P. Kapranos, Semisolid metal processing techniques for non-dendritic feedstock production. Sci. World J. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/752175
K.S. Alhawari, M.Z. Omar, M.J. Ghazali, M.S. Salleh, M.N. Mohammed, Evaluation of the microstructure and dry sliding wear behaviour of thixoformed A319 aluminium alloy. Mater. Des. 76, 169–180 (2015)
W. Khalifa, S. El-Hadad, Y. Tsunekawa, Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of sono processed-thixo cast AC4C billets, in 71st World Foundry Congress on Advanced Sustainable Energy, 19–21 May 2014, Bilbao, Spain (2014)
S.B. Hassas-Irani, B. Zarei-Hanzaki, A. Roostaei, Microstructure evolution and semi-solid deformation behavior of an A356 aluminum alloy processed by strain induced melt activated method. Mater. Des. 46, 579–587 (2013)
N. Haghdadi, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, S. Heshmati-Manesh, H.R. Abedi, S. Hassas-Irani, The semisolid microstructural evolution of a severely deformed A356 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 49, 878–887 (2013)
H. Tahiri, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Effect of Sr–grain refiner–Si interactions on the microstructure characteristics of Al–Si hypereutectic alloys. Inter. Metalcast. 12, 307–320 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0164-5
Q. Li, B. Li, J. Liu, J. Li, D. Liu, Y. Lan, T. Xia, Modification of hypereutectic Al–20%wt Si alloy based on the addition of yttrium and Al–5Ti–1B modifiers mixing melt. Inter. Metalcast. 13, 367–383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0242-3
W. Kasprzak, M. Sahoo, J. Sokolowsk, H. Yamagata, H. Kurita, The effect of the melt temperature and the cooling rate on the microstructure of the Al–20% Si alloy used for monolithic engine blocks. Int. J. Met. Cast. (2009)
S. Nafisi, R. Ghomashchi, Semi-solid metal processing routes: an overview. J. Can. Metall. Q. 44(3), 289–303 (2005)
M. Harun, I.A. Talib, A.R. Daud, Effect of element additions on wear property of eutectic aluminium–silicon alloys. Wear 194, 54–59 (1996)
K.V. Ojha, A. Tomar, D. Singh, G.C. Kaushal, Shape, microstructure and wear of spray formed hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 487, 591–596 (2008)
A.S. Anasyida, A.R. Daud, M.J. Ghazali, Dry sliding wear behavior of Al–12Si–4Mg alloy with cerium addition. Mater. Des. 31, 365–374 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shehata, M.M., El-Hadad, S., Moussa, M.E. et al. Optimizing the Pouring Temperature for Semisolid Casting of a Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy Using the Cooling Slope Plate Method. Inter Metalcast 15, 488–499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00465-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00465-8