Abstract
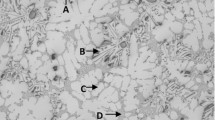
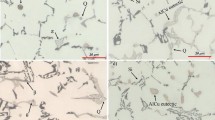
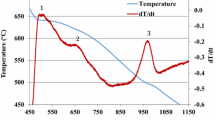
Thermal analysis of various 354 alloy melts was carried out to determine the sequence of reactions and phases formed during solidification under close-to-equilibrium cooling conditions. The main reactions observed comprised formation of the α-Al dendritic network at 598 °C followed by precipitation of the Al–Si eutectic and post-eutectic β-Al5FeSi phase at 560 °C; Mg2Si phase and transformation of the β-phase into π-Al8Mg3FeSi6 phase at 540 °C and 525 °C; and lastly, precipitation of Al2Cu and Q-Al5Mg8Cu2Si6 at 498 °C and 488 °C. As a result of the low solidification rate of the thermal analysis castings, all Zr-containing alloys are located in the L + Al3Zr region of the Al–Zr phase diagram during the melting stage. Three main reactions are detected with the addition of Ni, i.e., the formation of AlFeNi, AlCuNi and AlSiNiZr phases. Larger sizes of AlFeNi and AlCuNi phase particles were observed in higher Ni content alloys of 3.6 wt%. Mn addition helps in reducing the detrimental effects of the β-iron phase by replacing it with the less-detrimental Chinese script α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phase and sludge particles. With the use of the multi-step solution treatment—involving higher solution temperatures and longer durations, an increased amount of incipient melting is likely to occur.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Hernandez-Sandoval, G.H. Garza-Elizondo, A.M. Samuel, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, The ambient and high temperature deformation behavior of Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloy with minor Ti, Zr, Ni additions. Mater. Des. 58, 89–101 (2014)
A.M.A.Mohamed, F.H. Samuel and A.M. Samuel, Effect of Fe, Mn, Cu and Mg additions on the mechanical properties of Al-10.8 wt% Si near-eutectic alloy, in 18th Canadian Materials Science Conference (McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2006)
Z. Jia, G. Hu, B. Forbord, J.K. Solberg, Effect of homogenization and alloying elements on recrystallization resistance of Al–Zr–Mn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 444(1), 284–290 (2007)
A.J. Tolley, V. Radmilovic, U. Dahmen, On the effect of Zr on precipitate evolution in Al-Sc-Zr alloys, in Congress CONAMET/SAM 2004 Proceedings (La Serena, Chile, 2004)
F. Stadler, H. Antrekowitsch, W. Fragner, H. Kaufmann, P.J. Uggowitzer, The effect of Ni on the high-temperature strength of Al–Si cast alloys, in Materials Science Forum, Vol. 690. (Trans Tech Publications, 2011). pp. 274–277
Y.H. Cho, D.H. Joo, C.H. Kim, H.C. Lee, The effect of alloy addition on the high temperature properties of over-aged Al–Si (CuNiMg) cast alloys, in Materials Science Forum, Vol. 519. (Trans Tech Publications, 2006). pp. 461–466
V.G. Davydov, T.D. Rostova, V.V. Zakharov, Y.A. Filatov, V.I. Yelagin, Scientific principles of making an alloying addition of scandium to aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 280(1), 30–36 (2000)
K.E. Knipling, D.N. Seidman, D.C. Dunand, Ambient-and high-temperature mechanical properties of isochronally aged Al–0.06 Sc, Al–0.06 Zr and Al–0.06 Sc–0.06 Zr (at.%) alloys. Acta Mater. 59(3), 943–954 (2011)
Y. Harada, D.C. Dunand, Microstructure of Al3Sc with ternary transition-metal additions. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 329, 686–695 (2002)
M. Zeren, E. Karakulak, Influence of Ti addition on the microstructure and hardness properties of near-eutectic Al–Si alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 450(1), 255–259 (2008)
G.K. Sigworth, T.A. Kuhn, Grain refinement of aluminum casting alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 1(1), 31–40 (2007)
L. Alyaldin, Effects of Alloying Elements on Room and High Temperature Tensile Properties of Al–Si–Cu–Mg Base Alloys. Master of Engineering Thesis, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Quebec, Canada 2017
G.H. Garza-Elizondo, A.M. Samuel, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Effect of transition metals on the tensile properties of 354 alloy: role of precipitation hardening. Int. J. Metalcast. 11(3), 413–427 (2017)
L. Backerud, G. Chai, J. Tamminen, Solidification characteristics of aluminum alloys, in Foundry Alloys, vol 2 (American Foundrymen’s Society, Inc., 1990), p. 266
F.H. Samuel, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Factors controlling the type and morphology of Cu-containing phases in 319 Al alloys. AFS Trans. 104, 893–901 (1996)
A.M. Nabawy, Influence of Zirconium and Scandium on the Microstructure, Tensile Properties, and Hot-Tearing Susceptibility of Al–2 wt%Cu-Based Alloys. PhD Thesis, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Chicoutimi, Quebec, Canada, 2010
D. Srinivasan, K. Chattopadhyay, Non-equilibrium transformations involving, L12–Al3Zr in Ternary Al–X–Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A, 311–320 (2005)
E.R. Wang, X.D. Hui, G.L. Chen, Eutectic Al–Si–Cu–Fe–Mn alloys with enhanced mechanical properties at room and elevated temperature. Mater. Des. 32(8), 4333–4340 (2011)
F.H. Samuel, Incipient melting of Al5Mg8Si6Cu2 and Al2Cu intermetallics in unmodified and strontium-modified Al–Si–Cu–Mg (319) alloys during solution heat treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 33(9), 2283–2297 (1998)
H. De la Sablonnière, F.H. Samuel, Solution heat treatment of 319 aluminum alloy containing ~ 0.5 wt%Mg. Part 2—microstructure and fractography. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 9(4), 213–225 (1996)
A.S. Kabalnov, A.V. Pertsov, E.D. Shchukin, Ostwald ripening in two-component disperse phase systems: application to emulsion stability. Coll. Surf. 24, 19–32 (1987)
A. Kabalnov, Ostwald ripening and related phenomena. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 22, 1–12 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Amal Samuel for enhancing the quality of the images used in the present article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alyaldin, L., Samuel, A.M., Doty, H.W. et al. Effect of Transition Metals Addition on the Microstructure and Incipient Melting of 354-Based Alloys. Inter Metalcast 14, 47–58 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00331-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00331-2