Abstract
Purpose
Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) is one of serum biomarkers that recently reported in gynecological cancers, including breast cancer. This study aimed to compare serum HE4 levels in breast cancer patients and healthy individuals.
Methods
This cross-sectional study examined serum HE4 levels in 42 patients and 36 healthy women in 2019. Samples were easily selected from women referring to a teaching hospital. Healthy women were selected from the normal population who did not have a risk factor for breast cancer. Demographic information were recorded in a checklist. Then 10 cc of venous blood was taken from each patient. After centrifugation, serum and plasma were kept at minus 80 °C. The HE4 level was measured with Immunoassay Chemi Luminescence Method and using HE4 kits made by German company Cobas.
Results
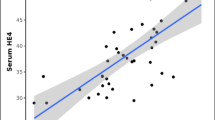
The mean age of the patients and healthy individuals was 48.76 ± 14.97 and 39.88 ± 14.05 years, respectively. The average size of tumor in patients was 4.70 ± 2.48 cm. The average serum HE4 level in patients and healthy individuals was 68.01 ± 63.39 and 50.06 ± 14.97, respectively (P = 0.46). There was a significant relationship between serum HE4 levels and age of patients (P = 0.01).
Conclusion
This study showed an increase in HE4 levels in breast cancer patients compared to healthy individuals. Preliminary results suggest that HE4 may serve as a new biomarker for breast cancer. However, more large-scale clinical studies are needed to further determine the predictive value of this biomarker as well as its molecular mechanisms in carcinogenesis and tumor progression, especially in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sites A. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2011. Bethesda: National Cancer Institute; 2014.
Gündüz UR, Gunaldi M, Isiksacan N, Gündüz S, Okuturlar Y, Kocoglu H. A new marker for breast cancer diagnosis, human epididymis protein 4: A preliminary study. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016;5(2):355–60.
Geng B, Liang M-M, Ye X-B, Zhao W-Y. Association of CA 15–3 and CEA with clinicopathological parameters in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015;3(1):232–6.
Ideo H, Hinoda Y, Sakai K, et al. Expression of mucin 1 possessing a 3′-sulfated core1 in recurrent and metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2015;137(7):1652–60.
Donepudi MS, Kondapalli K, Amos SJ, Venkanteshan P. Breast cancer statistics and markers. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10(3):506.
Bingle L, Singleton V, Bingle CD. The putative ovarian tumour marker gene HE4 (WFDC2), is expressed in normal tissues and undergoes complex alternative splicing to yield multiple protein isoforms. Oncogene. 2002;21(17):2768–73.
Kirchhoff C, Habben I, Ivell R, Krull N. A major human epididymis-specific cDNA encodes a protein with sequence homology to extracellular proteinase inhibitors. Biol Reprod. 1991;45(2):350–7.
Simmons AR, Baggerly K, Bast RC Jr. The emerging role of HE4 in the evaluation of advanced epithelial ovarian and endometrial carcinomas. Oncology (Williston Park). 2013;27(6):548.
Bignotti E, Ragnoli M, Zanotti L, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic impact of serum HE4 detection in endometrial carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer. 2011;104(9):1418–25.
Ruggeri G, Bandiera E, Zanotti L, et al. HE4 and epithelial ovarian cancer: comparison and clinical evaluation of two immunoassays and a combination algorithm. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412(15–16):1447–53.
Bandiera E, Romani C, Specchia C, et al. Serum human epididymis protein 4 and risk for ovarian malignancy algorithm as new diagnostic and prognostic tools for epithelial ovarian cancer management. Cancer Epidemiol Prev Biomark. 2011;20(12):2496–506.
Zanotti L, Bignotti E, Calza S, et al. Human epididymis protein 4 as a serum marker for diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma and prediction of clinical outcome. Clin Chem Lab Med CCLM. 2012;50(12):2189–98.
Vezzoli M, Ravaggi A, Zanotti L, et al. RERT: a novel regression tree approach to predict extrauterine disease in endometrial carcinoma patients. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–10.
Galgano MT, Hampton GM, Frierson HF. Comprehensive analysis of HE4 expression in normal and malignant human tissues. Mod Pathol. 2006;19(6):847–53.
Hellström I, Raycraft J, Hayden-Ledbetter M, Ledbetter JA, Schummer M, McIntosh M, et al. The HE4 (WFDC2) protein is a biomarker for ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63(13):3695–700.
Bingle L, Cross SS, High AS, et al. WFDC2 (HE4): a potential role in the innate immunity of the oral cavity and respiratory tract and the development of adenocarcinomas of the lung. Respir Res. 2006;7(1):61.
O’Neal RL, Nam KT, LaFleur BJ, et al. Human epididymis protein 4 is up-regulated in gastric and pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(5):734–42.
Gilks CB, Vanderhyden BC, Zhu S, van de Rijn M, Longacre TA. Distinction between serous tumors of low malignant potential and serous carcinomas based on global mRNA expression profiling. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;96(3):684–94.
Kamei M, Yamashita S-i, Tokuishi K, et al. HE4 expression can be associated with lymph node metastases and disease-free survival in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(11):4779–83.
Plebani M. HE4 in gynecological cancers: report of a European investigators and experts meeting. Clin Chem Lab Med CCLM. 2012;50(12):2127–36.
Drapkin R, Von Horsten HH, Lin Y, et al. Human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) is a secreted glycoprotein that is overexpressed by serous and endometrioid ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65(6):2162–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff and participants of this study for their important contributions.
Funding
The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences in Iran (Ethical Code: IR.KMU.AH.REC.1396.1684).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was taken from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honarvar, Z., Kalantari Khandani, B., Nazari, M. et al. Comparison of Serum Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) Levels in Breast Cancer Patients and Healthy Individuals. Indian J Gynecol Oncolog 19, 59 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40944-021-00551-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40944-021-00551-7