Abstract
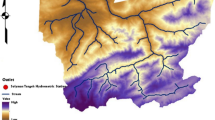
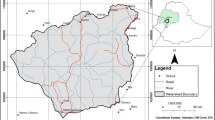
Climate change is one of the notable changes experienced around the world today and this is as a result of Global warming. The environmental impact of climate change, especially in densely populated developing countries such as Nigeria cannot be overlooked without seeking to provide useful information to help avert the consequences arising from it. Therefore, the aim of this research is to simulate the effect of climate change on the stream-flow of Ala River, Akure, Nigeria and this aim is achieved by projecting future rainfall due to climate change and simulating a hydrologic model of the river. Precipitation change experienced in the world climate system was considered and projection of precipitation for Ala, Akure was done by statistically downscaling General Circulation Model (GCM) under the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.0) climate scenario. The projected climate change alongside other hydrologic parameters was input into Hydrologic Engineering Centre-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) version 4.2 to simulate a hydrologic model so as to achieve the peak discharges at a different cross-section of the river reach. The peak discharges obtained for the Ala River basin indicate a continuous increase of the runoff generated as a result of an increase in precipitation as the years progresses resulting from a change in the climate system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinseye FM (2010) Climate variability and effects of weather elements on cocoa and cashew crops in Nigeria, (Doctoral dissertation, The Federal University of Technology, Akure).
Akinseye FM, Ogunrayi OA, Goldberg V, Bernhofer C (2016) Descriptive analysis of rainfall and temperature trends over Akure, Nigeria. J GeogrReg Plan 9(11):195–202
Al-Khafaji MS, Al-Chalabi RD (2020) Impact of Climate Change on the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Stream Flow and Sediment Yield of Darbandikhan Watershed, Iraq. Eng Technol J 38(2A):265–276
Ayeni AO, Balogun II, Soneye AS (2011) Seasonal assessment of physico-chemical concentration of polluted urban river: a case of Ala River in southwestern Nigeria. Res J Environ Sci 5(1):22–35
Benestad RE, Chen D, Hanssen-Bauer I (2008) Empirical-statistical downscaling. World Scientific Publishing Company, London
Bhuiyan HA, McNairn H, Powers J, Merzouki A (2017) Application of HEC-HMS in a cold region watershed and use of RADARSAT-2 soil moisture in initializing the model. Hydrology 4(1):9
Chu X, Steinman A (2009) Event and continuous hydrologic modeling with HEC-HMS. J Irrig Drain Eng 135(1):119–124
Das S (2019) Four decades of water and sediment discharge records in Subarnarekha and Burhabalang basins: an approach towards trend analysis and abrupt change detection. Sustain Water ResourManag 5(4):1665–1676
Din SU, Khan NM, Israr M, Nabi H, Khan M (2019) Runoff modelling using HEC-HMS for rural watershed. Int J AdvEng Res Dev 6(12):79–85
Fan L, Chen D, Fu C, Yan Z (2013) Statistical downscaling of summer temperature extremes in Northern China. Adv Atmos Sci 30(4):1085–1095
Gyawali R, Watkins DW (2013) Continuous hydrologic modeling of snow-affected watersheds in the Great Lakes basin using HEC-HMS. J HydrolEng 18(1):29–39
Ibitoye MO, Komolafe AA, Adegboyega AAS, Adebola AO, Oladeji OD (2019) Analysis of vulnerable urban properties within river Ala floodplain in Akure Southwestern Nigeria. Spat Inform Res 28:431–455
IPCC (2007). Climate change (2007) The Fourth Assessment Report (AR4). Synthesis report for policy makers.https://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/syr/ar4-syr-spm.pdf. Accessed 5 Jan 2019
Joshi N, Bista A, Pokhrel I, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2019) Rainfall-runoff simulation in Cache River Basin, Illinois, using HEC-HMS. World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019: watershed management, irrigation and drainage, and water resources planning and management. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, pp 348–360
Kabiri R, Bai VR, Chan A (2015) Assessment of hydrologic impacts of climate change on the runoff trend in Klang Watershed, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 73(1):27–37
Kadam AS (2011) Event based rainfall-runoff simulation using HEC-HMS model. Unpublished P.G. thesis submitted to Department of Soil and Water Conservation Engineering., CAET, Dr. PDKV, Akola.
Khoi DN (2016) Comparison of the HEC-HMS and SWAT hydrological models in simulating the stream flow. J Sci Technol 53(5A):189–195
Munyaneza O, Mukubwa A, Maskey S, Uhlenbrook S, Wenninger J (2014) Assessment of surface water resources availability using catchment modeling and the results of tracer studies in the mesoscaleMigina catchment, Rwanda. J Hydrol Earth Syst 18(12):5289–5301
Nyaupane N, Mote SR, Bhandari M, Kalra A, Ahmad S (2018) Rainfall-runoff simulation using climate change based precipitation prediction in HEC-HMS model for Irwin Creek, Charlotte, North Carolina. World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2018: watershed management, irrigation and drainage, and water resources planning and management. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, pp 352–363
Olalekan BG, Fadesola A (2017) Review of best practice approaches in combatting vulnerability to flood disaster risk in Ala-river flooding Akure, Ondo State. Niger J Environ Stud 3(1):5
Opere A, Omwoyo A, Mueni P, Arango M (2019) Impact of climate change on water resources in Eastern Africa. Hydrology and water resources management in arid, semi-arid, and tropical regions. IGI Global, Derry Township, pp 199–227
Osinowo AA, Okogbue EC, Ogungbenro SB, Fashanu O (2015) Analysis of global solar irradiance over climatic zones in Nigeria for solar energy applications. J Solar Energy. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/819307
Owoyemi FB (1996) A geologic-geophysical investigation of rain-induced erosional features in Akure metropolis. Unpublished M.Sc. Thesis, Federal University of Technology, Akure, pp 11–18
Pirnia A, Golshan M, Darabi H, Adamowski J, Rozbeh S (2019) Using the Mann-Kendall test and double mass curve method to explore stream flow changes in response to climate and human activities. J Water Clim Change 10(4):725–742
Pohle I, Gädeke A, Schümberg S, Hinz C, Koch H (2019) Management influences on stream-flow variability in the past and under potential climate change in a Central European mining region. Water ResourManag 33(15):5191–5206
Shashikanth K, Sukumar P (2017) India Monsoon rainfall projections for future using GCM model output under climate change. AdvComputSciTechnol 10:1501–1516
Tassew BG, Belete MA, Miegel K (2019) Application of HEC-HMS model for flow simulation in the Lake Tana basin: the case of GilgelAbay catchment, upper Blue Nile basin. Ethiop Hydrol 6(1):21
Teng F, Huang W, Ginis I (2018) Hydrological modeling of storm runoff and snowmelt in Taunton River Basin by applications of HEC-HMS and PRMS models. Nat Hazards 91(1):179–199
Yener MK, Sorman AU, Sorman AA, Gezgin T (2007) Modeling studies with HEC-HMS and runoff scenarios in yuvacik basin. Int Congress River Basin Manag 4(2007):621–634
Yilmaz AG, Imteaz MA, Ogwuda O (2012) Accuracy of HEC-HMS and LBRM models in simulating snow runoffs in Upper Euphrates Basin. J HydrolEng 17(2):342–347
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the management of the Federal University of Technology, Akure, Nigeria for their technical support.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akinwumi, A.M., Adewumi, J.R. & Obiora-Okeke, O.A. Impact of climate change on the stream-flow of Ala River, Akure, Nigeria. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 7, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00484-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00484-7