Abstract
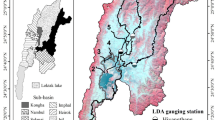
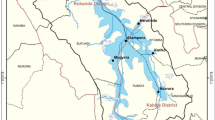
This study investigates the physico-chemical characteristics of Lakes and reservoirs in relation to the watershed condition of North Western Ethiopia. A mosaic image from Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) path/ row 169/052, 169/053, 170/052, and 170/053 for March, 2018 is used for land cover analysis. Physico-chemical parameters including Surface water temperature, pH, Turbidity, Electrical conductivity, Total dissolved solid (TDS), and Nitrate concentration have been measured using Thermometer, pH meter, Turbidity meter, Conductivity /TDS meter, and Photometer, respectively. The findings revealed that the higher areal coverage of the catchments was recorded for Gudera–Geray–Tikurwuha catchments (3371 km2) where all these three water bodies are found within the same catchment followed by Tirba Catchment (1395 km2). Other water bodies such as Zengena and Bahire Giyorgis are within independent catchment area 684 km2 and 278 km2), respectively. High levels in physico-chemical properties (turbidity, TDS and conductivity) were observed in Lake Bahire Giyorgis, Geray and Tikurwuha reservoirs whereas, these levels were considerably lower in the highland water bodies of Tirba and Zengena. These findings indicated clear differences in watershed and physico-chemical characteristics among the water bodies under consideration. These differences could be attributed to the different patterns of land use, source of pollution, vegetation cover and geochemistry of the catchments areas. Moreover, it has been noticed that the water use and abstraction by local community is not in proper management. Most of the agricultural practices such as irrigation, farming, and fishing, are implemented without considering sustainable management of the water bodies. Municipal wastes are also affecting the water bodies particularly the Tikur Wuha reservoir. Therefore, it is demanding to conduct further research on water quality, sediment load, trends in water volume and detailed study on biological components to come up with sustainable solution for the lakes and reservoirs.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahiarakwem CA, Nwankwor GI, Onyekuru SO, Idoko MA (2012) An assessment of the physical and environmental aspects of a Tropical Lake: a case study of the Oguta Lake Watershed, Niger Delta Basin, Nigeria. Am Int J Contemp Res 2(7):53–60
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington D.C.
Ayalew W (2010) Current land use practices and possible management strategies in shore area wetland ecosystem of Lake Tana: Towards improving livelihoods, productivity and biodiversity conservation. In: Mengistu S, Lemma B (eds) EFASA, Management of shallow water bodies for improved productivity and peoples' livelihoods in Ethiopia. Addis Ababa University Printing Press, Addis Ababa
Baban SMJ (1999) Use of remote sensing and geographical information systems in developing lake management strategies. Hydrobiologia 395:211–226
Barbier EB, Acreman M, Krowler D (1997) Economic valuation of wetlands: a guide for policy makers and planners. Ramsar Convention Bureau, Gland
Endalew M (2015) Preliminary survey of Geray reservoir, Amhara National Regional State, West Gojjam, JabitehnanWoreda, Ethiopia: focus on wetland management. J Coast Life Med 3(4):307–311
Endalew M, Goshu G, Zelal W (2010) Preliminary survey of Lake Gudera; management challenges (focus), Sekelaworeda, west Gojam, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Goshu G (2007) The physio-chemical characteristics of a highland crater lake and two reservoirs in north-west Amhara Region (Ethiopia). Ethiop J Sci Technol 5:17–41
GWP/INBO (2015) The handbook for management and restoration of aquatic ecosystems in river and lake basins. The Global Water Partnership (GWP) and the International Network of Basin Organizations (INBO). www.inbo-news.org.
Hakan A, Derse MA (2013) Change detection in Southern Turkey using normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI). Jo Environ EngLandscManag 21:12–18
Kebede S (2004) Environmental isotopes and geochemistry in investigating groundwater and lake hydrology: cases from the Blue Nile basin & the Ethiopian Rift (Ethiopia). PhD Dissertation.
Lakshmi P, Reddy MS, Reddy CP, Rao AN (2016) Studies of physico-chemical parameters to evaluate quality of water at different zones of Nalagonda District of Telangana, India. J Earth Sci Clim Change 7(4):1000347
Legesse D, Woldu Z, Mebrate A, Mengistou S, Ayenew T (2005) A review of the current status and an outline of a future management plan for lakes Abijata and Ziway. Draft final report. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Mailu A (2001) Preliminary assessment of the social, economic and environmental impacts of water hyacinth in the Lake Victoria basin and the status of control. In Biological and integrated control of water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes. In: ACIAR Proceedings No. 102.
Mironga J, Mathooko J, Onywere S (2012) Effect of water hyacinth infestation on the Physico-chemical characteristics of Lake Naivasha. Int J Hum Soc Sci 2(7):103–113
Mitsch W, Gosselink J (1993) Wetlands, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, p 722
Morawitz D (2006) Using NDVI to assess vegetative land cover change in central Puget Sound. Environ Monit Assess 114:85–106
Moyo P, Chapungu L, Mudzengi B (2013) Effectiveness of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) in remediating polluted water: the case of Shagashe river in Masvingo. ZimbAdvAppl Sci Res 4(4):55–62
Papastergiadou ES, Retalis A, Apostolakis A, Georgiadis T (2008) Environmental monitoring of spatio-temporal changes using remote sensing and GIS in a Mediterranean Wetland of Northern Greece. Water ResourManag 22:579–594
Tadele D, Lulekal E, Damtie D, Assefa A (2014) Floristic diversity and regeneration status of woody plants in Zengena forest, a remnant montane forest patch in northwestern Ethiopia. J For Res 25(2):329–336
WHO (2004) World health organization guidelines for drinking water quality, (3rd Ed). vol. I, Recommendations
Wondie A, Mengistu S, Vijverberg K, Dejen E (2007) Seasonal variation in primary production of a large high altitude tropical la.ke (Lake Tana, Ethiopia):effects of nutrient availability and water transparency. AquatEcol 41:195–207
Zinabu GM, Kebede E, Desta Z (2002) Long-term changes in chemical features of waters of seven Ethiopian Rift-valley lakes: chemical characteristics along a salinity-alkalinity gradient. Hydrobiologia 288:1–12
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Debre Markos University for facilitating the logistic support during field data collection for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fetene, A., Teshager, M.A. Watershed characteristics and physico-chemical analysis of lakes and reservoirs in North Western, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 6, 98 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00457-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00457-w