Abstract
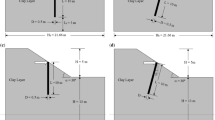
Granular piles, either ordinary or encased with geosynthetic materials are being extensively used as one of the ground improvement techniques, depending on the strength of the adjoining soil. The optimum granular pile (GP) length is still a matter of research, even though the approach is widely established in the literature. In the present study, a thorough and detailed parametric analysis has been carried out to ascertain the optimum length for ordinary and encased granular piles using a 2D axisymmetric finite element model. The soil behaviour has been modelled with the linearly elastic perfectly plastic Mohr–Coulomb failure criterion constitutive model. The parameters considered in this study are area replacement ratio, encasement stiffness, soil properties, infill material properties, and crust layer thickness. The findings revealed that the parameters with the greatest influence on the optimum length are the area replacement ratio, encasement stiffness, surrounding soil strength properties, and friction angle of the infill material. For encased granular piles, the optimum length was often found to be longer than ordinary granular piles. It was found that the optimum length for ordinary and encased GP ranges between 0.8–2.12 and 1–2.75 times of footing diameter (D), respectively. Through this study, an effort has also been made to investigate how the aforementioned parameters affect the radial bulging of the end-bearing GP. The upper section of 0.5–1.5D showed excessive bulging in each case. Additionally, the optimum encasement length was determined, and it was found that increasing the encasement length beyond 1.5D results in minimal improvement. Furthermore, a multiple regression analysis was employed to establish the correlation between the optimum length of GP and potential influencing factors.




























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors affirm that the data supporting the findings of this study can be found within the article. Furthermore, upon a reasonable request, the corresponding author is willing to provide the raw data that underlie the findings of this study.
Abbreviations
- GP:
-
Granular pile
- OGP:
-
Ordinary granular pile
- EGP:
-
Encased granular pile
- H :
-
Soil bed thickness
- L :
-
Granular pile length
- L op :
-
Optimum granular pile length
- L e :
-
Encasement length
- L e,op :
-
Optimum encasement length
- D :
-
Footing diameter
- χ :
-
Normalized depth
- χ :
-
L/D
- λ :
-
Improvement factor
- v:
-
Poisson’s ratio
- ϒsat :
-
Saturated unit weight
- k o :
-
Coefficient of earth pressure at rest
- c s :
-
Soil cohesion
- ϕ s/c :
-
Internal frictional angle soil/granular pile
- Ψ s /c :
-
Dilation angle soil/granular pile
- E s/c :
-
Soil/granular pile stiffness
- a r :
-
Area replacement ratio
- d c :
-
GP diameter
- t g :
-
Granular bed thickness
- J g :
-
Encasement stiffness
References
Barksdale RD, Bachus RC (1983) Design and construction of stone columns, vol. I (No. FHWA/RD-83/026; SCEGIT-83-104). Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center
Ayadat T (2022) Geotechnical performance of encapsulated and stabilized stone columns in a collapsible soil. Int J Geomech 22(6):04022057
Hajiazizi M, Nasiri M (2018) Experimental and numerical study of earth slope reinforcement using ordinary and rigid stone columns. Int J Min GeoEng 52(1):23–30
Pham TA, Dias D (2021) 3D numerical study of the performance of geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported embankments. Soils Found 61(5):1319–1342
Shahu JT, Madhav MR, Hayashi S (2000) Analysis of soft ground-granular pile-granular mat system. Comput Geotech 27(1):45–62
Schiosser F, Juran Y (1979) Parametres de conception pour sols artificiellement ameliores. In: Vol. 5 of Comptes Rendus clu 7eme Congres Europeen de Brighton. British Geotechnical Society, Brighton, UK, pp 227–252
Ambily AP, Gandhi SR (2007) Behavior of stone columns based on experimental and FEM analysis. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 133(4):405–415
Chen JF, Li LY, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Xu C, Rajesh S, Feng SZ (2021) Centrifuge modeling of geosynthetic-encased stone column-supported embankment over soft clay. Geotext Geomembr 49(1):210–221
Dar LA, Shah MY (2023) Numerical study on the seismic behaviour of embankments on stone column-reinforced soft soils. Transp Infrastruct Geotechnol 10(2):239–258
Hughes JMO, Withers NJ, Greenwood DA (1975) A field trial of the reinforcing effect of a stone column in soil. Geotechnique 25(1):31–44
McKenna JM, Eyre WA, Wolstenholme DR (1975) Performance of an embankment supported by stone columns in soft ground. Geotechnique 25(1):51–59
McKelvey D, Sivakumar V, Bell A, Graham J (2004) Modelling vibrated stone columns in soft clay. Proc Inst Civ Eng Geotech Eng 157(3):137–149
Wehr J (2006) The undrained cohesion of the soil as criterion for the column installation with a depth vibrator. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on vibratory pile driving and deep soil vibratory compaction. TRANSVIB, Paris, pp 157–162
Almeida MSS, Hosseinpour I, Riccio M (2013) Performance of a geosynthetic-encased column (GEC) in soft ground: numerical and analytical studies. Geosynth Int 20(4):252–262
Fattah MY, Zabar BS, Hassan HA (2016) Experimental analysis of embankment on ordinary and encased stone columns. Int J Geomech 16(4):04015102
Miranda M, Da Costa A (2016) Laboratory analysis of encased stone columns. Geotext Geomembr 44(3):269–277
Dash SK, Bora MC (2013) Influence of geosynthetic encasement on the performance of stone columns floating in soft clay. Can Geotech J 50(7):754–765
Al-Taie ET, Al-Kalali HH, Fattah MY (2019) Evaluation of settlement and bearing capacity of embankment on soft soil with reinforced geogrids. Int J Eng Res Technol (Ahmedabad) 8(6):99–103
Hasan M, Samadhiya NK (2017) Performance of geosynthetic-reinforced granular piles in soft clays: model tests and numerical analysis. Comput Geotech 87:178–187
Rezaei MM, Lajevardi SH, Saba H, Ghalandarzadeh A, Zeighami E (2019) Laboratory study on single stone columns reinforced with steel bars and discs. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 5:1–14
Thakur A, Rawat S, Gupta AK (2021) Experimental and numerical investigation of load carrying capacity of vertically and horizontally reinforced floating stone column group. Geotech Geol Eng 39:3003–3018
Dutta S, Padade AH, Mandal JN (2012) Experimental study on natural bamboo geogrid encased stone column. In: Proc. 5th ARC on Geosynth., Geosynth. Asia-2012, pp 417–426
Basu P, Samadhiya NK, De Dalal SS (2018) An experimental study on random fiber mixed granular pile. Int J Geotech Eng 12(1):1–12
Babu MRD, Dheerendra SR, Nayak S, Majeed JA (2010) Load settlement behavior of stone columns with circumferential nails. In: Indian geotechnical conference, pp 579–82
Fattah MY, Shlash KT, Al-Waily MJ (2013) Experimental evaluation of stress concentration ratio of model stone columns strengthened by additives. Int J Phys Model Geotech 13(3):79–98
Kang B, Wang J, Zhou Y, Huang S (2023) Study on bearing capacity and failure mode of multi-layer-encased geosynthetic-encased stone column under dynamic and static loading. Sustainability 15(6):5205
Mohamadi Merse M, Hosseinpour I, Payan M, Jamshidi Chenari R, Mohapatra SR (2023) Shear strength behavior of soft clay reinforced with ordinary and geotextile-encased granular columns. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 9(6):79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-023-00492-5
Shahu JT, Kumar S, Bhowmik R (2023) Ground improvement for transportation infrastructure: experimental investigations on cyclic behavior of a group of granular columns. Int J Geomech 23(3):04022309
Pradeep NM, Kumar S, Shukla SK (2023) Evaluation of strength behavior of aggregates mixed with tire chips in granular piles. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 2023:1–16
Pradeep N, Kumar S (2023) Soft soil improvement with encased granular piles composed of aggregates and tire chips mixture: experimental and numerical studies. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 2023:1–25
Ng KS, Tan SA (2015) Settlement prediction of stone column group. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 1:1–13
Sivakumar V, McKelvey D, Graham J, Hughes D (2004) Triaxial tests on model sand columns in clay. Can Geotech J 41(2):299–312
Muir Wood D, Hu W, Nash DF (2000) Group effects in stone column foundations: model tests. Geotechnique 50(6):689–698
Narasimha Rao S, Prasad YVSN, Hanumanta Rao V (1992) Use of stone columns in soft marine clays. In: Proceedings of the 45th Canadian geotechnical conference, Toronto, Ont, vol 9
Miranda M, Fernández-Ruiz J, Castro J (2021) Critical length of encased stone columns. Geotext Geomembr 49(5):1312–1323
Najjar SS, Sadek S, Maakaroun T (2010) Effect of sand columns on the undrained load response of soft clays. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 136(9):1263–1277
Remadna A, Benmebarek S, Benmebarek N (2020) Numerical analyses of the optimum length for stone column reinforced foundation. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 6:1–12
Debnath P, Dey AK (2017) Bearing capacity of geogrid reinforced sand over encased stone columns in soft clay. Geotext Geomembr 45(6):653–664
Black JA, Sivakumar V, Bell A (2011) The settlement performance of stone column foundations. Géotechnique 61(11):909–922
Tan SA, Ng KS, Sun J (2014) Column group analyses for stone column reinforced foundation. In: From soil behavior fundamentals to innovations in geotechnical engineering: honoring Roy E. Olson, pp 597–608
Malarvizhi SN (2007) Comparative study on the behavior of encased stone column and conventional stone column. Soils Found 47(5):873–885
Al-Ani W, Grizi A, Wanatowski D (2021, November) Settlement analysis of column-like elements. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering. International society for soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering.
Hamzh A, Mohamad H, Bin Yusof MF (2022) The effect of stone column geometry on soft soil bearing capacity. Int J Geotech Eng 16(2):200–210
Balaam NP, Brown PT (1977) Settlement analysis of soft clay reinforced with granular piles. In: Proc. Fifth Asian Conf. Soil Eng. Bangkok, Thailand, no. 81–92 (1978)
Castro J (2017) Modeling stone columns. Materials 10(7):782
Choobbasti AJ, Pichka H (2014) Improvement of soft clay using installation of geosynthetic-encased stone columns: numerical study. Arab J Geosci 7:597–607
Jaky J (1944) The coefficient of earth pressure at rest. J Soc Hung Archit Eng 1944:1
Dar LA, Shah MY (2021) Three dimensional numerical study on behavior of geosynthetic encased stone column placed in soft soil. Geotech Geol Eng 39(3):1901–1922
Hasan M, Samadhiya NK (2016) Experimental and numerical analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced floating granular piles in soft clays. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 2:1–13
Kadhim ST, Parsons RL, Han J (2018) Three-dimensional numerical analysis of individual geotextile-encased sand columns with surrounding loose sand. Geotext Geomembr 46(6):836–847
Lo SR, Zhang R, Mak J (2010) Geosynthetic-encased stone columns in soft clay: a numerical study. Geotext Geomembr 28(3):292–302
Murugesan S, Rajagopal K (2006) Geosynthetic-encased stone columns: numerical evaluation. Geotext Geomembr 24(6):349–358
Tandel YK, Solanki CH, Desai AK (2013) 3D FE analysis of an embankment construction on GRSC and proposal of a design method. Int Schol Res Not 2013:1
Ng KS, Tan SA (2014) Design and analyses of floating stone columns. Soils Found 54(3):478–487
Debbabi IE, Saddek RM, Rashid ASA, Muhammed AS (2020) Numerical modeling of encased stone columns supporting embankments on sabkha soil. Civ Eng J 6(8):1593–1608
Hughes JMO, Withers NJ (1974) Reinforcing of soft cohesive soils with stone columns: 18F, 9R. Ground Engng. V7, N3, MAY, 1974, P42–49. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstracts 11(11):A234
Aslani M, Nazariafshar J, Ganjian N (2019) Experimental study on shear strength of cohesive soils reinforced with stone columns. Geotech Geol Eng 37:2165–2188
Boumekik NEI, Labed M, Mellas M, Mabrouki A (2021) Optimization of the ultimate bearing capacity of reinforced soft soils through the concept of the critical length of stone columns. Civ Eng J 7(9):1472–1487
Basack S, Indraratna B, Rujikiatkamjorn C (2016) Modeling the performance of stone column–reinforced soft ground under static and cyclic loads. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 142(2):04015067
Ng KS (2018) Numerical study on bearing capacity of single stone column. Int J GeoEng 9:1–10
Mugahed Sakr M, Azzam WR, Mohamed MK (2022) Behaviour of encased stone columns in soft clay. J Eng Res 6(3):71–75
Keykhosropur L, Soroush A, Imam R (2012) 3D numerical analyses of geosynthetic encased stone columns. Geotext Geomembr 35:61–68
Walton G, Diederichs MS, Alejano LR, Arzúa J (2014) Verification of a laboratory-based dilation model for in situ conditions using continuum models. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(6):522–534
Mitchell JK (1981) Soil improvement-state of the art report. In: Proc., 11th Int. Conf. on SMFE, vol 4, pp 509–565
Gu M, Zhao M, Zhang L, Han J (2016) Effects of geogrid encasement on lateral and vertical deformations of stone columns in model tests. Geosynth Int 23(2):100–112
Yoo C, Lee D (2012) Performance of geogrid-encased stone columns in soft ground: full-scale load tests. Geosynth Int 19(6):480–490
Yoo C (2010) Performance of geosynthetic-encased stone columns in embankment construction: numerical investigation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 136(8):1148–1160
Yoo C (2015) Settlement behavior of embankment on geosynthetic-encased stone column installed soft ground–a numerical investigation. Geotext Geomembr 43(6):484–492
Muzammil SP, Varghese RM, Joseph J (2018) Numerical simulation of the response of geosynthetic encased stone columns under oil storage tank. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 4:1–12
Xu Z, Zhang L, Zhou S (2021) Influence of encasement length and geosynthetic stiffness on the performance of stone column: 3D DEM-FDM coupled numerical investigation. Comput Geotech 132:103993
Gholaminejad A, Mahboubi A, Noorzad A (2020) Encased stone columns: coupled continuum—discrete modelling and observations. Geosynth Int 27(6):581–592
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shaid Yousuf performed the numerical modelling, analysed the data, and wrote the paper. N K Samadhiya reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yousuf, S., Samadhiya, N.K. Numerical Evaluation of Pile Length, Lateral Bulging and Encasement Length: A Comparative Study on Ordinary and Encased Granular Piles. Int. J. of Geosynth. and Ground Eng. 10, 48 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-024-00556-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-024-00556-0