Abstract
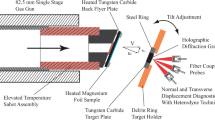
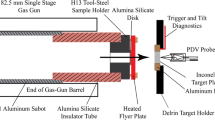
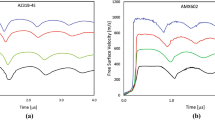
In the present paper, results of plate impact experiments designed to investigate the onset of incipient plasticity in commercial purity polycrystalline magnesium (99.9%) under weak uniaxial strain compression and elevated temperatures up to melt are presented. The dynamic stress at yield and post yield of magnesium, as inferred from the measured normal component of the particle velocity histories at the free (rear) surface of the target plate, are observed to decrease progressively with increasing test temperatures in the range from 23 to 500 °C. At (higher) test temperatures in the range 500–610 °C, the rate of decrease of dynamic stress with temperature at yield and post-yield in the sample is observed to weaken. At still higher test temperatures (617 and 630 °C), a dramatic increase in dynamic yield as well as flow stress is observed indicating a change in dominant mechanism of plastic deformation as the sample approaches the melt point of magnesium at strain rates of ~105/s. In addition to these measurements at the wavefront, the plateau region of the free surface particle velocity profiles indicates that the longitudinal (plastic) impedance of the magnesium samples decreases continuously as the sample temperatures are increased from room to 610 °C, and then reverses trend (indicating increasing material longitudinal impedance/strength) as the sample temperatures are increased to 617 and 630 °C. Electron back scattered diffraction analysis of the as-received and annealed pre-test magnesium samples reveal grain coarsening as well as grain re-orientation to a different texture during the heating process of the samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramesh K (2002) Effects of high rates of loading on the deformation behavior and failure mechanisms of hexagonal close-packed metals and alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 33(3):927–935
Zuanetti B, Wang T, Prakash V (2017) A novel approach for plate impact experiments to determine the dynamic behavior of materials under extreme conditions. J Dyn Behav Mater 3(1):64–75
Mises RV (1928) Mechanik der plastischen formänderung von kristallen. ZAMM J Appl Math Mech 8(3):161–185
Groves G, Kelly A (1963) Independent slip systems in crystals. Philos Mag 8(89):877–887
Berge F, Krüger L, Ouaziz H, Ullrich C (2015) Influence of temperature and strain rate on flow stress behavior of twin-roll cast, rolled and heat-treated AZ31 magnesium alloys. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 25(1):1–13
Wonsiewicz B, Backofen W (1967) Independent slip systems and ductility of hexagonal polycrystals. Trans Metall Soc AIME 239:1422–1433
Kumar A, Hauser F, Dorn J (1968) Viscous drag on dislocations in aluminum at high strain rates. Acta Metall 16(9):1189–1197
Regazzoni G, Kocks U, Follansbee PS (1987) Dislocation kinetics at high strain rates. Acta Metall 35(12):2865–2875
Li Q (2011) Dynamic mechanical response of magnesium single crystal under compression loading: experiments, model, and simulations. J Appl Phys 109(10):103514
Dixit N (2015) A mechanism based investigation of the dynamic behavior of pure magnesium. Dissertation, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD
Prasad KE, Li B, Dixit N, Shaffer M, Mathaudhu S, Ramesh K (2014) The dynamic flow and failure behavior of magnesium and magnesium alloys. JOM 66(2):291–304
Yoshinaga H, Horiuchi R (1964) On the nonbasal slip in magnesium crystals. Trans Jpn Inst Met 5(1):14–21
Al-Samman T, Molodov KD, Molodov DA, Gottstein G, Suwas S (2012) Softening and dynamic recrystallization in magnesium single crystals during c-axis compression. Acta Mater 60(2):537–545
Kanel G, Garkushin G, Savinykh A, Razorenov S, de Resseguier T, Proud W, Tyutin M (2014) Shock response of magnesium single crystals at normal and elevated temperatures. J Appl Phys 116(14):143504
Zaretsky E (2010) Impact response of cobalt over the 300–1400 K temperature range. J Appl Phys 108(8):083525
Prakash V, Clifton RJ (1990) Experimental and analytical investigation of dynamic fracture under conditions of plane strain. In: Ernst HA, Saxena A, McDowell DL (Eds.) Fracture mechanics: twenty-second symposium, Vol. 1, American Society for Testing, Philadelphia, pp 412–444
Liou NS, Okada M, Prakash V (2004) Formation of molten metal films during metal-on-metal slip under extreme interfacial conditions. J Mech Phys Solids 52(9):2025–2056
Yuan F, Liou N-S, Prakash V (2009) High-speed frictional slip at metal-on-metal interfaces. Int J Plast 25(4):612–634. doi:10.1016/j.ijplas.2008.12.006
Yuan F, Tsai L, Prakash V, Rajendran A, Dandekar D (2007) Spall strength of glass fiber reinforced polymer composites. Int J Solids Struct 44(24):7731–7747. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2007.05.007
Tsai L, Prakash V (2005) Structure of weak shock waves in 2-D layered material systems. Int J Solids Struct 42(2):727–750
Frutschy KJ, Clifton RJ (1998) High-temperature pressure-shear plate impact experiments using pure tungsten carbide impactors. Exp Mech 38(2):116–125
Zuanetti B, Wang T, Prakash V (2017) A compact fiber optics-based heterodyne combined normal and transverse displacement interferometer. Rev Sci Instrum 88(3):033108
Kumar P, Clifton R (1977) Optical alignment of impact faces for plate impact experiments. J Appl Phys 48(3):1366–1367
Prakash V (1998) Time-resolved friction with applications to high-speed machining: experimental observations. Tribol Trans 41(2):189–198
Clifton R, Bodner SR (1966) An analysis of longitudinal elastic-plastic pulse propagation. J Appl Mech 33(2):248–255
Okada M, Liou N-S, Prakash V, Miyoshi K (2001) Tribology of high-speed metal-on-metal sliding at near-melt and fully-melt interfacial temperatures. Wear 249(8):672–686
Prakash V, Mehta N (2012) Uniaxial compression and combined compression-and-shear response of amorphous polycarbonate at high loading rates. Polym Eng Sci 52(6):1217–1231
Yoo M (1981) Slip, twinning, and fracture in hexagonal close-packed metals. Metall Trans A 12(3):409–418
Frenkel J (1926) Über die Wärmebewegung in festen und flüssigen Körpern. Zeitschrift für Physik 35(8–9):652–669
Kanel G, Razorenov S, Baumung K, Singer J (2001) Dynamic yield and tensile strength of aluminum single crystals at temperatures up to the melting point. J Appl Phys 90(1):136–143
Hidnert P, Sweeney W (1928) Thermal expansion of magnesium and some of its alloys. Bur Stand Jour Res 1(5):771–792
Poppema T, Jaeger F (1935) The exact measurement of the specific heats of solid substances at higher temperatures. XIX. The specific heat of zinc, magnesium, and their binary alloy, MgZn. Proc Acad Sci Amst 38:510
Marsh SP (1980) LASL shock Hugoniot data. Vol. 5, University of California Press, Berkeley, CA
Shazly M, Prakash V (2008) Shock response of a gamma titanium aluminide. J Appl Phys 104(8):083513
Slutsky LJ, Garland CW (1957) Elastic constants of magnesium from 4.2 K to 300 K. Phys Rev 107(4):972–976
Greeff C, Moriarty JA (1999) Ab initio thermoelasticity of magnesium. Phys Rev B 59(5):3427
Grunschel SE (2009) Pressure-shear plate impact experiments on high-purity aluminum at temperatures approaching melt. Brown University, Providence, RI
Ghosh D, Kingstedt OT, Ravichandran G (2017) Plastic work to heat conversion during high-strain rate deformation of Mg and Mg alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 48(1):14–19
Errandonea D (2010) The melting curve of ten metals up to 12 GPa and 1600 K. J Appl Phys 108(3):033517
Choi H, Kim Y, Shin J, Bae D (2010) Deformation behavior of magnesium in the grain size spectrum from nano-to micrometer. Mater Sci Eng A 527(6):1565–1570
Somekawa H, Mukai T (2005) Effect of grain refinement on fracture toughness in extruded pure magnesium. Scr Mater 53(9):1059–1064
Ulacia I, Dudamell N, Gálvez F, Yi S, Pérez-Prado M, Hurtado I (2010) Mechanical behavior and microstructural evolution of a Mg AZ31 sheet at dynamic strain rates. Acta Mater 58(8):2988–2998
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the U.S. Department of Energy through the Stewardship Science Academic Alliance (Grant Nos. DE-NA0001989 and DE-NA0002919) in conducting the present research. The authors would also express gratitude to Swagelok Center for Surface Analysis of Materials (SCSAM) at CWRU for the EBSD data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zuanetti, B. & Prakash, V. Shock Response of Commercial Purity Polycrystalline Magnesium Under Uniaxial Strain at Elevated Temperatures. J. dynamic behavior mater. 3, 497–509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40870-017-0128-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40870-017-0128-0