Abstract
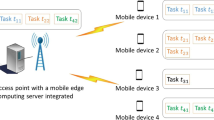
Traditional computing models and centralized cloud computing are not capable of meeting today’s application requirements, especially when deploying technologies, such as the Internet of things (IoT), 5G, and wearable devices, on a large scale. Mobile edge computing (MEC) introduces the feasibility of using edge and smart devices, such as gateways and smart phones, to perform task execution of different applications. Moreover, an efficient task scheduling approach should consider the deadlines requirements and the power consumption of the edge devices. This paper proposes a multi-objective optimization solution to assign different application tasks to different edge devices while minimizing the energy consumption of edge devices and the computation time of tasks. Task dependencies and data distribution are considered within a new and more general MEC model. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm (MOEA) framework is used to solve the optimization problem subject to deadline and power consumption constraints. Results show that the proposed multi-objective approach achieves better performance in terms of energy and computation time when compared to a single objective approach.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bughin J, Chui M, Manyika J (2013) Ten it-enabled business trends for the decade ahead. McKinsey Q. 13:1–3
Lee SK, Bae M, Kim H (2017) Future of IOT networks: a survey. Appl. Sci. 7(10):1072
Sahni Y, Cao J, Zhang S, Yang L (2017) Edge mesh: a new paradigm to enable distributed intelligence in internet of things. IEEE Access 5:16441–16458
Al-Zinati M, Alrashdan R, Al-Duwairi B, Aloqaily M (2021) A re-organizing biosurveillance framework based on fog and mobile edge computing. Multimed Tools Appl 80(11):16805–16825
Wu Q, Ding G, Xu Y, Feng S, Du Z, Wang J, Long K (2014) Cognitive internet of things: a new paradigm beyond connection. IEEE Internet Things J 1(2):129–143
Gil D, Ferrández A, Mora-Mora H, Peral J (2016) Internet of things: a review of surveys based on context aware intelligent services. Sensors 16(7):1069
Maarala AI, Su X, Riekki J (2016) Semantic reasoning for context-aware internet of things applications. IEEE Internet Things J 4(2):461–473
Mell PM, Grance T (2011) Sp 800-145. the NIST definition of cloud computing. Gaithersburg, MD, USA, Tech rep
Wang L, Tao J, Kunze M, Castellanos AC, Kramer D, Karl W (2008) Scientific cloud computing: early definition and experience. In: 2008 10th IEEE international conference on high performance computing and communications, IEEE, pp 825–830
Botta A, De Donato W, Persico V, Pescapé A (2016) Integration of cloud computing and internet of things: a survey. Future Gener Comput Syst 56:684–700
Consortium O et al. (2017) Openfog reference architecture for fog computing. In: Architecture Working Group, pp 1–162
Jalali F, Hinton K, Ayre R, Alpcan T, Tucker RS (2016) Fog computing may help to save energy in cloud computing. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 34(5):1728–1739
Bonomi F, Milito R, Zhu J, Addepalli S (2012) Fog computing and its role in the internet of things. In: Proceedings of the first edition of the MCC workshop on Mobile cloud computing, pp 13–16
Yi S, Li C, Li Q (2015) A survey of fog computing: concepts, applications and issues. In: Proceedings of the 2015 workshop on mobile big data, pp 37–42
Bonomi F, Milito R, Natarajan P, Zhu J (2014) Fog computing: a platform for internet of things and analytics. In: Big data and internet of things: a roadmap for smart environments, Springer, pp 169–186
Shi W, Cao J, Zhang Q, Li Y, Xu L (2016) Edge computing: vision and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J 3(5):637–646
Yousefpour A, Fung C, Nguyen T, Kadiyala K, Jalali F, Niakanlahiji A, Kong J, Jue JP (2019) All one needs to know about fog computing and related edge computing paradigms: a complete survey. J Syst Archit 98:289–330
Giust F, Verin G, Antevski K, Chou J, Fang Y, Featherstone W, Fontes F, Frydman D, Li A, Manzalini A et al (2018) Mec deployments in 4g and evolution towards 5g. ETSI White Pap 24(2018):1–24
Jarrah M, Jaradat M, Jararweh Y, Al-Ayyoub M, Bousselham A (2015) A hierarchical optimization model for energy data flow in smart grid power systems. Inf Syst 53:190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2014.12.003
Jarrah M, Al-Shrida F (2017) A multi-objective evolutionary solution to improve the quality of life in smart cities. In: 2017 14th international conference on smart cities: improving quality of life using ICT IoT (HONET-ICT), pp 36–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/HONET.2017.8102217
Van den Abeele F, Hoebeke J, Teklemariam GK, Moerman I, Demeester P (2015) Sensor function virtualization to support distributed intelligence in the internet of things. Wirel Pers Commun 81(4):1415–1436
Wang Z, Zhao Z, Min G, Huang X, Ni Q, Wang R (2018) User mobility aware task assignment for mobile edge computing. Future Gener Comput Syst 85:1–8
Liu CF, Bennis M, Poor HV (2017) Latency and reliability-aware task offloading and resource allocation for mobile edge computing. In: 2017 IEEE Globecom workshops (GC Wkshps), IEEE, pp 1–7
Du Y, Wang K, Yang K, Zhang G (2018) Energy-efficient resource allocation in UAV based MEC system for IOT devices. In: 2018 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), IEEE, pp 1–6
Kao YH, Krishnamachari B, Ra MR, Bai F (2017) Hermes: latency optimal task assignment for resource-constrained mobile computing. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 16(11):3056–3069
Cheng Y, Liao Y, Zhai X (2020) Energy-efficient resource allocation for UAV-empowered mobile edge computing system. In: 2020 IEEE/ACM 13th international conference on utility and cloud computing (UCC), IEEE, pp 408–413
Yaqub U, Sorour S (2018) Multi-objective resource optimization for hierarchical mobile edge computing. In: 2018 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), IEEE, pp 1–6
Song F, Xing H, Luo S, Zhan D, Dai P, Qu R (2020) A multiobjective computation offloading algorithm for mobile-edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J 7(9):8780–8799
Zhou SZ, Zhan ZH, Chen ZG, Kwong S, Zhang J (2020) A multi-objective ant colony system algorithm for airline crew rostering problem with fairness and satisfaction. IEEE Trans Intell Transport Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2994779
Fang W, Zhang Q, Sun J, Wu XJ (2020) Mining high quality patterns using multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2020.3033519
Sun J, Li H, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Zhu Y, Zang Q, Wu Z, Wei Z (2021) Multiobjective task scheduling for energy-efficient cloud implementation of hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 14:587–600. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3036896
Torquato R, Shi Q, Xu W, Freitas W (2015) A Monte Carlo simulation platform for studying low voltage residential networks. In: 2015 IEEE power energy society general meeting, p 1.https://doi.org/10.1109/PESGM.2015.7285654
Zhang X, Mao Y, Zhang J, Letaief KB (2017) Multi-objective resource allocation for mobile edge computing systems. In: 2017 IEEE 28th annual international symposium on personal, indoor, and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/PIMRC.2017.8292379
Yang M, Ma H, Wei S, Zeng Y, Chen Y, Hu Y (2020) A multi-objective task scheduling method for fog computing in cyber-physical-social services. IEEE Access 8:65085–65095. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2983742
Shi W, Dustdar S (2016) The promise of edge computing. Computer 49(5):78–81
Akyildiz IF, Wang X, Wang W (2005) Wireless mesh networks: a survey. Comput Netw 47(4):445–487
Borgia E (2014) The internet of things vision: key features, applications and open issues. Comput Commun 54:1–31
Voorneveld M (2003) Characterization of pareto dominance. Oper Res Lett 31(1):7–11
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: Nsga-ii. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Dinh TQ, Tang J, La QD, Quek TQ (2017) Offloading in mobile edge computing: task allocation and computational frequency scaling. IEEE Trans Commun 65(8):3571–3584
Tran MQ, Nguyen DT, Le VA, Nguyen DH, Pham TV (2019) Task placement on fog computing made efficient for IOT application provision. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 2019:6215454:1–6215454:17
Hadka D (2019) Moea framework user guide. version 2.7. http://moeaframework.org/. Accessed 15 Mar 2021
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: Nsga-ii. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Deb K, Jain H (2014) An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, part i: Solving problems with box constraints. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 18(4):577–601. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2013.2281535
Al Moubayed N, Petrovski A, McCall J (2014) D2MOPSO: MOPSO based on decomposition and dominance with archiving using crowding distance in objective and solution spaces. Evol Comput 22(1):47–77
Nebro A, Durillo J, Garcia-Nieto J, Coello Coello C, Luna F, Alba E (2009) SMPSO: A new PSO-based metaheuristic for multi-objective optimization. In: 2009 IEEE symposium on computational intelligence in multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM), pp 66–73. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCDM.2009.4938830
Zhang Q, Li H (2007) Moea/d: a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 11(6):712–731. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2007.892759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almasri, S., Jarrah, M. & Al-Duwairi, B. Multi-objective optimization of task assignment in distributed mobile edge computing. J Reliable Intell Environ 8, 21–33 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40860-021-00162-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40860-021-00162-1