Abstract
Purpose
Using a three-dimensional finite element method (3D-FEM), we compared the stress patterns and displacement on the implants, bone tissues, and prostheses in end-to-end implant-supported and cantilever implant bridges in the maxillary incisal region.
Methods
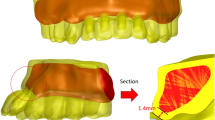
Using a 3D-FEM, a model was constructed of the implant by rotating and adding threads according to the ITI Dental Implant System aesthetic requirements. The implant, prosthesis, and maxillary bone were assembled to form three different implant-supported bridges at different implant sites. Next, a 100-N load was applied at 0°, 30°, and 60°, and the stress values, displacements, and stress distribution were compared.
Results
The stress distribution and displacement of the three models were similar in all three angles. In all three models, under axial loading, the stresses were majorly concentrated in the cortical bone around the implant neck and the apex; whereas the rest remaining stress was small and evenly distributed. Under oblique loading, the stresses were majorly concentrated in the cortical bone around the implant neck, and the stress value in the neck was greater than that in the apex. The cantilever implant bridge model produces I-type leverage action and its stress (implant 30°: 83.5 ± 6.9 Mpa or 133.8 ± 10.3 MPa vs. 65.1 ± 8.5Mpa; 60°: 115.1 ± 2.6 MPa or 141.0 ± 9.7 MPa vs. 98.1 ± 6.8 MPa. Cortical bone 30°: 48.6 ± 9.5 Mpa or 67.8 ± 5.9 MPa vs. 41.6 ± 9.8Mpa and 60°: 67.3 ± 6.3 MPa or 68.9 ± 10.2 MPa vs. 61.7 ± 6.4 MPa) and displacement (30°: 132.0 ± 13.2 μm or 169.0 ± 18.5 μm vs. 128 ± 7 μm and 60°: 168.0 ± 5.6 μm or 172.0 ± 19.2 μm vs. 167.0 ± 9.0 μm) are greater than those of the end-to-end implant-supported bridge model (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
End-to-end implant-supported bridges have more uniform stress distribution and less displacement than single-implant cantilever beam bridges. End-to-end implant-supported bridges are ideal for replacing four consecutive missing incisors in the maxillary incisor region.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kim, W. J., Cho, Y. D., Ku, Y., & Ryoo, H. M. (2022). The worldwide patent landscape of dental implant technology. Biomaterials Research, 26(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-022-00307-0
Haugen, H. J., & Chen, H. (2022). Is there a better biomaterial for dental implants than titanium?-A review and meta-study analysis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 13(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13020046
Bilder, L., Stepco, E., Uncuta, D., Machtei, E., Sgan-Cohen, H., Bilder, A., & Aizenbud, D. (2019). Traumatic Dental Injuries among adolescents in Republic of Moldova. The Journal Of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry, 43(4), 269–273. https://doi.org/10.17796/1053-4625-43.4.8.
Bhatavadekar, N. (2012). Peri-implant soft tissue management: Where are we? Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology, 16(4), 623–627. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-124X.106938
Yousif, A., Raghoebar, G. M., Putters, T. F., Vissink, A., & Schortinghuis, J. (2020). Calvarial bone grafts to augment the alveolar process in partially dentate patients: A prospective case series. International Journal of Implant Dentistry, 6(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-020-00251-5
Xu, L., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., & Chen, J. (2018). Clinical research on a flapless surgical technique application of narrow implants. Medicine (Baltimore), 97(44), e12646. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000012646.
Alemayehu, D. B., & Jeng, Y. R. (2021). Three-dimensional finite element investigation into effects of implant thread design and loading rate on stress distribution in dental implants and anisotropic bone. Materials (Basel), 14(22), 6974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226974
Wang, P., Xu, H., Gu, R., Zhu, L., Bai, D., & Xue, C. (2022). Integrating maxillary dentition and 3D facial photo using a modified CAD/CAM facebow. Bmc Oral Health, 22(1), 365. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-022-02394-w.
Heo, K. H., Lim, Y. J., Kim, M. J., & Kwon, H. B. (2018). Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the splinted implant prosthesis in a reconstructed mandible. The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics, 10(2), 138–146. https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2018.10.2.138
Zhang, D., Zheng, L., Wang, Q., Lu, L., & Ma, J. (2015). Displacements prediction from 3D finite element model of maxillary protraction with and without rapid maxillary expansion in a patient with unilateral cleft palate and alveolus. Biomedical Engineering Online, 14, 80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-015-0074-9.
Thompson, M. C., Field, C. J., & Swain, M. V. (2011). The all-ceramic, inlay supported fixed partial denture. Part 2. Fixed partial denture design: A finite element analysis. Australian Dental Journal, 56(3), 302–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1834-7819.2011.01341.x.
Velasco-Ortega, E., Del Jimenez-Martin, R., Moreno-Munoz, I., Nunez-Marquez, J., Rondon-Romero, E., Cabanillas-Balsera, J. L., Jimenez-Guerra, D., Ortiz-Garcia, A., Lopez-Lopez, I., & Monsalve-Guil, J. (2022). Long-term treatment outcomes of implant prostheses in partially and totally edentulous patients. Materials (Basel), 15(14), 4910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144910
Grutter, L., & Belser, U. C. (2009). Implant loading protocols for the partially edentulous esthetic zone. International Journal Of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, 24 Suppl, 169–179.
Krennmair, G., Seemann, R., Weinlander, M., Wegscheider, W., & Piehslinger, E. (2011). Implant-prosthodontic rehabilitation of anterior partial edentulism: A clinical review. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, 26(5), 1043–1050.
Assaf, M. (2022). Dental implant therapeutic trends among dentists in palestine: A cross-sectional questionnaire study. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.24301
Clemente, M. P., Moreira, A., Carvalho, N., Bernardes, G., Ferreira, A. P., Amarante, J. M., & Mendes, J. (2020). Orofacial trauma on the anterior zone of a trumpet’s player maxilla: Concept of the oral rehabilitation—A case report. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249423
Chen, Z., Zhang, S., Zhou, J., & Liang, H. (2022). Immediate versus delayed implantation for single-tooth restoration of maxillary anterior teeth: A comparative analysis on efficacy. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2022, 4490335. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4490335
Slutzkey, G. S., Cohen, O., Chaushu, L., Rahmanov, A., Mijiritsky, E., Beitlitum, I., & Kolerman, R. (2022). Immediate maxillary full-arch rehabilitation of periodontal patients with terminal dentition using tilted implants and bone augmentation: A 5-year retrospective cohort study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102902
He, Y. T., Ma, C. L., Qiao, G., Liu, J. Y., Wang, Y., Song, J., Liu, Y., & Wang, Z. H. (2019). Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cantilever fixed bridge supported by implants with mandibular central incisor. Chinese Journal of Stomatology, 54(7), 463–468. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2019.07.006
Huang, H. L., Lin, T. W., Tsai, H. L., Wu, Y., Wu, A. Y. J. J. J. M., & Engineering, B. (2022). Biomechanical effects of bone atrophy, implant design, and vertical or tilted of posterior implant on all-on-four concept implantation: Finite element analysis. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 42, 488–497.
Rungsiyakull, C., Rungsiyakull, P., Suttiat, K., & Duangrattanaprathip, N. (2022). Stress distribution pattern in mini dental implant-assisted RPD with different clasp designs: 3D finite element analysis. International Journal Of Dentistry, 2022, 2416888. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2416888
Manafi Khajeh Pasha, A., Mahmoudi Sheykhsarmast, R., Manafi Khajeh Pasha, S., Khashabi, E. J. J. M., & Engineering, B. (2021). Influence of treatment plans on stress and deformation distribution in mandibular implant-supported overdenture and mandibular bone under traumatic load: A 3D FEA. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 41(4), 543–557.
Kwon, Y. J., Kim, J. G., & Lee, W. (2022). A framework for effective face-mask contact modeling based on finite element analysis for custom design of a facial mask. PLoS ONE, 17(7), e0270092. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270092
Vaquette, C., Mitchell, J., & Ivanovski, S. (2021). Recent advances in vertical alveolar bone augmentation using additive manufacturing technologies. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 798393. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.798393
Wu, V., van Oers, R. F. M., Schulten, E., Helder, M. N., Bacabac, R. G., & Klein-Nulend, J. (2018). Osteocyte morphology and orientation in relation to strain in the jaw bone. International Journal of Oral Science, 10(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-017-0007-5
Agrawal, R., Narang, S., Ahmed, H., Prasad, S., Reddy, S., & Aila, S. (2021). Influence of occlusal bite forces on teeth with altered periodontal support: A three-dimensional finite element stress analysis. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences, 13(Suppl 1), S688–S691. https://doi.org/10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_785_20
Mora, P., Nunwong, C., Sriromreun, P., Kaewsriprom, P., Srisorrachatr, U., Rimdusit, S., & Jubsilp, C. (2022). High performance composites based on highly filled Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polybenzoxazine for Post Application. Polymers (Basel), 14(20), 4321. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204321.
Leandro, L. N. R., Barra Grande, M. F., Pelegrine, A. A., Nishioka, R. S., Teixeira, M. L., & Basting, R. T. (2023). Stress distribution on implant-supported zirconia crown of maxillary first molar: Effect of oblique load on natural and antagonist tooth. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2023.2195962
Zhang, C., Zeng, C., Wang, Z., Zeng, T., & Wang, Y. (2023). Optimization of stress distribution of bone-implant interface (BII). Biomaterials Advances, 147, 213342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213342
Turker, N., & Buyukkaplan, U. S. (2020). Effects of overdenture attachment systems with different working principles on stress transmission: A three-dimensional finite element study. The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics, 12(6), 351–360. https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2020.12.6.351
Mosharraf, R., Molaei, P., Fathi, A., & Isler, S. (2021). Investigating the effect of nonrigid connectors on the success of tooth-and-implant-supported fixed partial prostheses in maxillary anterior region: A finite element analysis (FEA). International Journal Of Dentistry, 2021, 5977994. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5977994
Chen, Y. C., Lin, C. L., Yu, C. H., Chang, H. C., Lin, Y. M., Lin, J. W. J. J. M., & Engineering, B. (2022). Biomechanical analysis of mandibular implant-assisted removable partial denture with distal extension. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 42(4), 534–543.
Tseng, B. T., Yen, Y. C., Cheng, C. S., Wang, C. H., Lien, K. H., Huang, C. M., & Su, K. C. J. J. M. (2022). Biomechanical effects of different miniplate thicknesses and fixation methods applied in BSSO surgery under two occlusal conditions. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 42(4), 445–458.
Funding
This study was funded by Youth Project of Jincheng People’s Hospital (No.: JSY-2021Y010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SGZ and NNZ conceptualized and designed the study. SGZ and WW collected, organized, and drafted the information. QTC and GBL analyzed the data. SGZ wrote the manuscript. NNZ performed manuscript revision. All the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Jincheng People’s Hospital Ethics Committee. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent to participate was obtained from the participants before the study.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Wang, W., Cao, Q. et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Stress Analysis of Different Implant-Supported Bridges in the Maxillary Incisal Regions. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 43, 322–331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-023-00795-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-023-00795-y