Abstract
Purpose
Alterations of the central nervous system are frequent complications in patients with chronic arterial hypertension (AHT). However, functional spinal cord lesions are not often detected in these patients despite diagnostic advances in neuroimaging and electrophysiology. Recently, a new non-invasive functional near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) application was developed for assessment of the peri-spinal neurovascular response (NVR) as a functional test of the spinal cord.
Methods
The continuous wave fNIRS technique was applied to detect changes in O2Hb concentration during the peri-spinal NVR triggered by non-noxious electrical stimulation of the median nerve at the wrist, and recorded at cervical and thoracic spinal levels using three different stimulation protocols in subjects with AHT treated with losartan (n = 22; 142.14 ± 133.9 months of disease) and compared to healthy control subjects (n = 37). The body mass index (BMI) and the median nerve conduction velocity (NCV) were also recorded.
Results
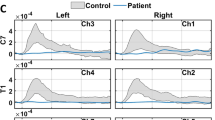
The NVR of patients with AHT showed a significantly lower amplitude (− 70.4%; cervical), longer rise time (+ 22.2%; cervical), and longer duration (+ 28.0%; thoracic) than the control group (p < 0.01). The stimulus intensity-response in the AHT group was − 53.5%, − 55.9%, and − 63% lower in amplitude than the controls (p < 0.05) for the increasing stimulus intensity steps (5; 7.5 and 10 mA, respectively) at the cervical level. Patients with BMI > 30 showed more intense changes. The median NCV was normal for both groups.
Conclusion
These data show, for the first time, the difference in peri-spinal NVR between normal subjects and losartan-treated ATH patients, indicating the potential of a non-invasive fNIRS technique to find sensory functional abnormalities of the spinal cord in these patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Leonardi-Bee, J., Bath, P. M. W., Phillips, S. J., & Sandercock, P. A. G. (2002). Blood pressure and clinical outcomes in the international stroke trial. Stroke, 33, 1315–1320. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000014509.11540.66
Kelly, D. M., & Rothwell, P. M. (2020). Blood pressure and the brain: The neurology of hypertension. Practical Neurology, 20, 100–108.
Mitchell, G. F., van Buchem, M. A., Sigurdsson, S., Gotal, J. D., Jonsdottir, M. K., Kjartansson, Ó., Garcia, M., Aspelund, T., Harris, T. B., Gudnason, V., & Launer, L. J. (2011). Arterial stiffness, pressure and flow pulsatility and brain structure and function: the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility—Reykjavik Study. Brain, 134, 3398–3407. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr253
Pantoni, L. (2010). Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. The Lancet Neurology, 9, 689–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70104-6
Bamford, J., Sandercock, P., Jones, L., & Warlow, C. (1987). The natural history of lacunar infarction: the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. Stroke, 18, 545–551. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.18.3.545
Price, T. R., Manolio, T. A., Kronmal, R. A., Kittner, S. J., Yue, N. C., Robbins, J., Anton-Culver, H., & O'Leary, D. H. (1997). Silent brain infarction on magnetic resonance imaging and neurological abnormalities in community-dwelling older adults. Stroke, 28, 1158–1164. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.28.6.1158
Valenzuela, F., Rana, M., Sitaram, R., Uribe, S., & Eblen-Zajjur, A. (2021). Non-invasive functional evaluation of the human spinal cord by assessing the peri-spinal neurovascular network with near infrared spectroscopy. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 29, 2312–2321. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3123587
Vahdat, S., Lungu, O., Cohen-Adad, J., Marchand-Pauvert, V., Benali, H., & Julien, D. (2015). Simultaneous brain-cervical cord fMRI reveals intrinsic spinal cord plasticity during motor sequence learning. PLoS Biology, 13, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002186
Pfister, D. G., Spencer, S., Adelstein, D., Adkins, D., Anzai, Y., Brizel, D. M., Bruce, J. Y., Busse, P. M., Caudell, J. J., Cmelak, A. J., Colevas, A. D., Eisele, D. W., Fenton, M., Foote, R. L., Galloway, T., Gillison, M. L., Haddad, R. I., Hicks, W. L., Hitchcock, Y. J., Jimeno, A… (2020). Head and neck cancers, version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 18, 873–898. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.0031
Willis, W., & Coggeshall, R. (2004). Sensory mechanisms of the spinal cord: Volume 1 primary afferent neurons and the spinal dorsal horn. Springer.
Kimura, J. (2013). Electrodiagnosis in diseases of nerve and muscle: Principles and practice. Oxford University Press.
Filosa, J. A., Morrison, H. W., Iddings, J. A., Du, W., & Kim, K. J. (2016). Beyond neurovascular coupling, role of astrocytes in the regulation of vascular tone. Neuroscience, 323, 96–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.064
Tarantini, S., Tran, C. H. T., Gordon, G. R., Ungvari, Z., & Csiszar, A. (2017). Impaired neurovascular coupling in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: Contribution of astrocyte dysfunction and endothelial impairment to cognitive decline. Experimental gerontology, 94, 52–58.
Bhatt, E., Nagpal, A., Greer, K. H., Grunewald, T. K., Steele, J. L., Wiemiller, J. W., Lewis, S. M., & Carey, J. R. (2007). Effect of finger tracking combined with electrical stimulation on brain reorganization and hand function in subjects with stroke. Experimental Brain Research, 182, 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1001-5
Venclove, S., Daktariunas, A., & Ruksenas, O. (2015). Functional near-infrared spectroscopy: A continuous wave type based system for human frontal lobe studies. EXCLI Journal, 14, 1145–1152. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2015-614
Chen, B. R., Kozberg, M. G., Bouchard, M. B., Shaik, M. A., & Hillman, E. M. C. (2014). A critical role for the vascular endothelium in functional neurovascular coupling in the brain. Journal of the American Heart Association, 3(3), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.114.000787
De Wit, C., & Griffith, T. M. (2010). Connexins and gap junctions in the EDHF phenomenon and conducted vasomotor responses. Pflugers Archiv European Journal of Physiology, 459(6), 897–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-010-0830-4
Kersten, P., White, P. J., & Tennant, A. (2014). Is the pain visual analogue scale linear and responsive to change? An exploration using Rasch analysis. PLoS ONE, 9(6), e99485.
Kim, J. G., & Liu, H. (2007). Variation of haemoglobin extinction coefficients can cause errors in the determination of haemoglobin concentration measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 52(20), 6295. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/52/20/014
Scholkmann, F., Kleiser, S., Metz, A. J., Zimmermann, R., Pavia, J. M., Wolf, U., & Wolf, M. (2014). A review on continuous wave functional near-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instrumentation and methodology. NeuroImage, 85, 6–27.
Figueroa, X. F., & Duling, B. R. (2009). Gap junctions in the control of vascular function. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling, 11(2), 251–266. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2117
Yücel, M. A., Aasted, C. M., Petkov, M. P., Borsook, D., Boas, D. A., & Becerra, L. (2015). Specificity of hemodynamic brain responses to painful stimuli: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Scientific Reports, 5, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09469
Ghali, M. G. Z. (2017). The brainstem network controlling blood pressure: an important role for pressor sites in the caudal medulla and cervical spinal cord. Journal of Hypertension, 35(10). Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/jhypertension/Fulltext/2017/10000/The_brainstem_network_controlling_blood_pressure_.4.aspx
Yajima, Y., Ito, S., Komatsu, K., Tsukamoto, K., Matsumoto, K., & Hirayama, A. (2008). Enhanced response from the caudal pressor area in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Research, 1227, 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.047
Paterna, S., Parrinello, G., Scaglione, R., Costa, R., Bova, A., Palumbo, V. A., Pinto, A., Amato, P., & Licata, G. (2000). Effect of Long-Term Losartan Administration on Renal Haemodynamics and Function in Hypertensive Patients. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 14(5), 529–532. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007845324117
Margiotta-Casaluci, L., Owen, S. F., Rand-Weaver, M., & Winter, M. J. (2019). Testing the translational power of the zebrafish: An inter-species analysis of responses to cardiovascular drugs. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10(JULY), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00893
Funding
This study was funded by FONDEF grant Number ID21I10092, Fondecyt Postdoc 2021 N321030 and Fundación COPEC-UC grant Number 2018R.1030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SU and AEZ participated in the design of this study. JPGA, RCC, JEO, and AEZ carried out the study, JPGA, RCC, and AEZ performed the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. SU and AEZ reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and read and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Two investigators from the present article were participants in the patent process of one of the devices used in the present method. Patent: F.I. Valenzuela, S.A. Uribe, A. Eblen-Zajjur, R. Sitaram, M. Rana. Device for recording the vascular response of the human spinal cord triggered by a suprasensible stimulus through the use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy. U.S. Patent Application 16/958,433, Feb. 25, 2021.
Ethical Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile (PUC-170914003, 2017).
Consent to Participate
Informed and written consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Appelgren, J.P.G., Caulier-Cisterna, R., Oyarzún, J.E. et al. Peri-spinal Neurovascular Response Triggered by a Painless Electrical Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Chronic Arterial Hypertension. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 43, 303–311 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-023-00789-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-023-00789-w