Abstract
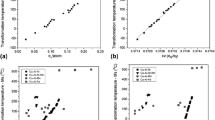
An empirical map of martensitic transformation temperatures versus average valence electrons per atom (e v/a) and valence electron concentration (c v) was developed in order to design ZrCu-based shape memory alloys (SMAs). The martensitic transformation temperatures of about 40 different alloys (Ni, Co, Hf, Ag, Ti, Al, Cr, etc.), covering nearly all possible replacements of Zr or Cu, are exhibited. The relationship between transformation temperature and cv or electron density (n) was determined. The results indicate that the transformation temperatures of ZrCu-based alloys gradually decrease until reaching an inflection point at c v = 0.218, above which the transformation temperatures go down. A linear dependence of the transformation temperatures of ZrCu-based alloys on the electron density is revealed by data-fitting. Under the guidance of these contour maps describing transformation temperatures and thermal hysteresis, a series of ZrCu-based alloys that can function under different conditions can be designed.
摘要
本文建立了一个关于马氏体相变温度和价电子数及电子浓度的经验图谱并设计了一系列ZrCu基形状记忆合金. 这些相变温度包括了所有报道过的经Ni、Co、Hf、Ag、Ti、Al、Cr等掺杂替换Zr或者Cu原子的约40种合金. 反映了转变温度和电子浓度或者电子密度之间的关系. 结果显示ZrCu基合金的转变温度逐渐下降, 当c v > 0.218时, 相变温度急剧下降. ZrCu基合金的马氏体相变温度与电子密度呈线性关系. 基于相变温度和滞后图谱的结果可以设计出在不同条件下工作的ZrCu基合金.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka K, Wayman CM. Shape Memory Materials. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998
Emre A, Osman EO, Haluk EK. Experimental investigation and modeling of the loading rate and temperature dependent superelastic response of a high performance shape-memory alloy. Smart Mater Struct, 2015, 24: 075020
Ma J, Karaman I, Noebe RD. High temperature shape memory alloy. Int Mater Rev, 2010, 55: 257–315
Firstov GS, Humbeeck JV, Koval YN. Comparison of high temperature shape memory behavior for ZrCu-based, Ti-Ni-Zr and Ti-Ni-Hf alloys. Scr Mater, 2004, 50: 243–248
Meng XL, Gao WH, Gao ZY, Cai W, Zhao LC. Substructure and interface of the superstructure martensitic in Zr50Cu50 high temperature shape memory alloy. Mater Lett, 2014, 117: 221–224
Gao WH, Meng XL, Cai W, Zhao LC. Martensite structure and phase transformation of quaternary ZrCuAlCo high temperature shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Comp, 2014, 607: 99–103
Hofmann DC. Shape memory bulk metallic glass composites. Science, 2010, 329: 1294
Pauly S, Liu G, Wang G, et al. Modeling deformation behavior of Cu-Zr-Al bulk metallic glass matrix composites. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95: 101906
Song GB, Ma N, Lee HJ, Arnold S. Design and control of a proofof-concept variable area exhaust nozzle using shape-memory alloy actuators. Smart Mater Struct, 2007, 16: 1342–1347
Glock S, Michaud VT. Thermal and damping behaviour of magnetic shape memory alloy composites. Smart Mater Struct, 2015, 24: 065025
Zarinejad M, Liu Y. Dependence of transformation temperatures of NiTi-based shape-memory alloys on the number and concentration of valence electrons. Adv Funct Mater, 2008, 18: 1–6
Zarinejad M, Liu Y, Tong YX. Transformation temperature changes due to second phase precipitation in NiTi-based shape memory alloys. Intermetallics, 2009, 17: 914–919
Zarinejad M, Liu Y. Dependence of Transformation Temperatures of Shape-memory Alloys on the Number and Concentration of Valence Electrons. New York: Nova Science Publishers Inc, 2010: 339–360
Huang YJ, Hu QD, Li JG. Des ign in Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape-memory alloy using compositional maps. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 101: 222403
Sutou Y, Imano Y, Koeda N, et al. Magnetic and martensitic transformations of NiMnX (X=In,Sn,Sb)…ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 4358
Jin X, Marioni M, Bono D, Allen SM, O’Handley RC. Empirical mapping of Ni-Mn-Ga properties with composition and valence electron concentration. J Appl Phys, 2002, 91: 8222–8224
Koval YN, Firstov GS, Kotko AV. Martensitic transformation and shape memory effect in Zr-Cu intermetallic compound. Scr Metall et Mater, 1992, 27: 1611–1616
Biffi CA, Figini A, Tuissi A. Influence of compositional ratio on microstructure and martensitic transformation of CuZr shape memory alloys. Intermetallics, 2014, 46: 4–11
Firstov GS, Koval YN, Humbeeck JV, et al. Phase transformations in Zr–29.56 at.% Cu–19.85 at.%Ni melt-spun high-temperature shape memory alloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 438-440: 816–820
Biffi CA, Figini A, Tuissi A. CuZr based shape memory alloys: effect of Cr and Co on the martensitic transformation. Mater Sci Forum, 2013, 738-739: 167–171
Javida FA, Mattern N, Pauly S, Eckert J. Martensitic transformation and thermal cycling effect in Cu-Co-Zr alloys. J Alloys Comp, 2011, 509S: S334–S337
Meng FQ, Tsuchiya K, Ii Seiichiro, Yokoyama Y. Influence of Ni on stability of martensitic transformation in Zr50Cu50-x Nix. J Alloys Comp, 2013, 577S: S136–S140
Meng FQ, Tsuchiya K, Yin FX, Ii S, Yokoyama Y. Influence of Al on stability of martensitic transformation in Zr50Cu50-x Alx. J Alloys Comp, 2012, 522: 136–140
Koval YN, Firstov GS, Kotko AV, Delaey L, Humbeeck JV. The influence of Ni and Ti on the martensitic transformation temperature and shape memory effect of the intermetallic compound ZrCu. Scr Metall et Mater, 1994, 31: 799
Firstov GS, Timoshevskii AN, Koval YN, Kalkuta S, Humbeeck JV. Phase stability during martensitic transformation in ZrCu intermetallics: crystal and electronic structure aspects. ESOMAT, 2009, 02008
Zhalko-Titarenkmo AV, Yevlashinva ML, Antonovb VN, et al. Ele ctronic and crystal structure of the ZrCu intermetallic compound close to the point of structural transformation. Phys Status Solidi B, 1994, 184: 122
Wang RL, Yan JB, Xiao HB, et al. Effect of electron density on the martensitic transition in Ni-Mn-Sn alloys. J Alloys Comp, 2011, 509: 6834–6837
Seo JW, Schryvers D. TEM investigation of the microstructure and defects of CuZr martensite. Part I: morphology and twin systems. Acta Mater, 1998, 46: 1165–1175
Firstov GS, Humbeeck JV, Koval YN. Peculiarities of the martensitic transformation in ZrCu intermetallic compound-potential high temperature SMA. J Phys IV, 2001, 11: 481–486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Weihong Gao is currently a PhD candidate in the Department of Material Physics and Chemistry at Harbin Institute of Technology, China. She received his BSc degree and MSc degree majored in material physics and chemistry at Harbin Engineering University. Her current research is mainly on martensite phase transformation; microstructure and interface of high temperature shape memory alloys.
Xianglong Meng is currently a professor at Harbin Institute of Technology. He obtained his PhD degree from Harbin Institute of Technology in 2004. His research interests focus mainly on high temperature shape memory alloys, martensitic transformation and microstructure.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, W., Meng, X., Song, G. et al. Empirical mapping of ZrCu-based alloys with valence electrons versus transformation temperatures. Sci. China Mater. 59, 151–157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-016-0124-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-016-0124-z