Abstract
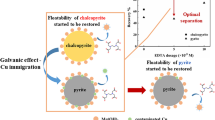
As the main sulfide mineral in cyanide tailings, how to reduce cyanide inhibition and thus improve the flotation recovery of pyrite is of great significance to the comprehensive management of hazardous solid waste. This research study delved into the potential of ceramic ball media to counteract the negative effects of cyanide on pyrite flotation. Intriguingly, it was observed that the utilization of ceramic ball media resulted in a decrease in the consumption of NaCN and dissolved oxygen within the cyanidation system, along with a reduction in the concentration of SCN−. Employing scanning electron microscopy–energy-dispersive spectrometry alongside contact angle analysis, it was demonstrated that the use of ceramic ball media mitigated the surface overoxidation caused by galvanic coupling between the iron media and pyrite. Surface chemical analysis using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF–SIMS) confirmed that the ceramic ball media optimized the chemical environment on the surface of pyrite, consequently retarding the formation of FeOOH and diminishing the adsorption of CN−, CNO−, and SCN− on the pyrite surface. Additionally, ToF–SIMS analysis further demonstrated that the ceramic ball media exhibited excellent grinding performance, excluding the non-significant contribution of impurity elements (mainly Fe). Thus, the ceramic ball media grinding showed excellent performance in the cyanidation process, improving the performance by about 10% over that of the iron ball media grinding in the flotation test.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Song Y, Chen Y et al (2020) Comparative experimental study on the harmless treatment of cyanide tailings through slurry electrolysis. Sep Purif Technol 251:117314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117314
Li H, Yin S, Li S et al (2019) Investigation on the recovery of gold from pretreated cyanide tailings using chlorination leaching process. Sep Sci Technol (Phila) 00:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1708108
Tu Y, Han P, Wei L et al (2019) Removal of cyanide adsorbed on pyrite by H2O2 oxidation under alkaline conditions. J Environ Sci (China) 78:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.10.013
Yang X, Huang X, Qiu T (2015) Recovery of zinc from cyanide tailings by flotation. Miner Eng 84:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2015.10.003
Xu S, Zanin M, Skinner W, Brito-e-Abreu S (2021) Surface chemistry of oxidised pyrite during grinding: ToF-SIMS and XPS surface analysis. Miner Eng 170:106992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106992
Ma Z, Zhang S, Xiao R (2020) Redox performance of pyrite cinder in methane chemical looping combustion. Chem Eng J 395:125097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125097
Tozsin G, Ihsan Arol A, Cayci G (2015) Use of waste pyrite as an alternative to gypsum for alkaline soil amelioration. Int J Min Reclam Environ 29:169–177
Ercan S, Kaya Z, Ortas I (2015) Effect of pyrite application on wheat-maize growth and nutrinet uptake under diverse soil conditions. J Plant Nutr 38:295–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2014.957392
Yang R, Zeng G, Zhou Z et al (2023) Naphthalene degradation dominated by homogeneous reaction in Fenton-like process catalyzed by pyrite : mechanism and application. Sep Purif Technol 310:123150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123150
Liu T, Zhang J (2020) Feasibility of band gap engineering of iron pyrite (FeS2) by codoping Os, Ru or Zn together with O. Mater Chem Phys 244:122742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122742
Prestidge CA, Ralston J, Smart RSC (1993) The competitive adsorption of cyanide and ethyl xanthate on pyrite and pyrrhotite surfaces. Int J Miner Process 38:205–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-7516(93)90076-M
De Wet JR, Pistorius PC, Sandenbergh RF (1997) The influence of cyanide on pyrite flotation from gold leach residues with sodium isobutyl xanthate. Int J Miner Process 49:149–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-7516(96)00031-2
Kostovic M, Vucinic D (2016) The influence of cyanide salts and ferrous sulphate on pyrite flotation. Physicochem Probl Miner Process 52:609–619. https://doi.org/10.5277/ppmp160208
Wang XH, Forssberg KSE (1996) The solution electrochemistry of sulfide-xanthate-cyanide systems in sulfide mineral flotation. Miner Eng 9:527–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/0892-6875(96)00041-6
Abbaspour A, Kamyabi MA (2005) Electrochemical formation of Prussian blue films with a single ferricyanide solution on gold electrode. J Electroanal Chem 584:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2005.07.008
Zhao C, Huang D, Chen J et al (2016) The interaction of cyanide with pyrite, marcasite and pyrrhotite. Miner Eng 95:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.03.015
Guo B, Peng Y, Parker G (2016) Electrochemical and spectroscopic studies of pyrite-cyanide interactions in relation to the depression of pyrite flotation. Miner Eng 92:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.03.003
Long H, Li H, Pei J et al (2020) Cleaner recovery of multiple valuable metals from cyanide tailings via chlorination roasting. Sep Sci Technol (Phila) 00:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1812650
Bas AD, Larachi F (2019) The effect of flotation collectors on the electrochemical dissolution of gold during cyanidation. Miner Eng 130:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.10.003
Li Y, Li D, Li J et al (2015) Pretreatment of cyanided tailings by catalytic ozonation with Mn2+/O3. J Environ Sci (China) 28:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.038
Zhang X, Han Y, Gao P et al (2020) Effects of particle size and ferric hydroxo complex produced by different grinding media on the flotation kinetics of pyrite. Powder Technol 360:1028–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.11.014
Rabieh A, Albijanic B, Eksteen JJ (2016) A review of the effects of grinding media and chemical conditions on the flotation of pyrite in refractory gold operations. Miner Eng 94:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.04.012
Yu J, He Y, Qu L et al (2020) Exploring the critical role of grinding modification on the flotation recovery of electrode materials from spent lithium ion batteries. J Clean Prod 274:123066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123066
Wang M, Zhao Q, Yang H et al (2020) Photocatalytic antibacterial properties of copper doped TiO2 prepared by high-energy ball milling. Ceram Int 46:16716–16724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.246
Corin KC, Song ZG, Wiese JG, O’Connor CT (2018) Effect of using different grinding media on the flotation of a base metal sulphide ore. Miner Eng 126:24–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.06.019
Zhang X, Han Y, Kawatra SK (2020) Effects of grinding media on grinding products and flotation performance of sulfide ores. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev 42:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2019.1692831
Bidari E, Aghazadeh V (2018) Pyrite from Zarshuran Carlin-type gold deposit: characterization, alkaline oxidation pretreatment, and cyanidation. Hydrometallurgy 179:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.06.019
Rabieh A, Eksteen JJ, Albijanic B (2018) Galvanic interaction of grinding media with arsenopyrite and pyrite and its effect on gold cyanide leaching. Miner Eng 116:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.10.018
Rabieh A, Eksteen JJ, Albijanic B (2017) The effect of grinding chemistry on cyanide leaching of gold in the presence of pyrrhotite. Hydrometallurgy 173:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.08.013
Bruckard WJ, Sparrow GJ, Woodcock JT (2011) A review of the effects of the grinding environment on the flotation of copper sulphides. Int J Miner Process 100:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2011.04.001
Ejtemaei M, Nguyen AV (2017) Characterisation of sphalerite and pyrite surfaces activated by copper sulphate. Miner Eng 100:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.11.005
Ruano G, Pomiro F, Ferrón J (2018) Surface chemical reactions induced on pyrite by ion bombardment. Surf Sci 667:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2017.10.009
Niu X, Chen J, Li Y et al (2019) Correlation of surface oxidation with xanthate adsorption and pyrite flotation. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.07.153
Han G, Wen S, Wang H, Feng Q (2020) Selective adsorption mechanism of salicylic acid on pyrite surfaces and its application in flotation separation of chalcopyrite from pyrite. Sep Purif Technol 240:116650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116650
Biesinger MC, Payne BP, Grosvenor AP et al (2011) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl Surf Sci 257:2717–2730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051
Lai H, Deng J, Wen S, Liu Q (2019) Elucidation of lead ions adsorption mechanism on marmatite surface by PCA-assisted ToF-SIMS, XPS and zeta potential. Miner Eng 144:106035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106035
Mu Y, Li L, Peng Y (2017) Surface properties of fractured and polished pyrite in relation to flotation. Miner Eng 101:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.11.012
Smart RSC, Skinner WM, Gerson AR (1999) XPS of sulphide mineral surfaces: metal-deficient, polysulphides, defects and elemental sulphur. Surf Interface Anal 28:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9918(199908)28:1%3c101::AID-SIA627%3e3.0.CO;2-0
Liu J, Ejtemaei M, Nguyen AV et al (2020) Surface chemistry of Pb-activated sphalerite. Miner Eng 145:106058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106058
Deng M, Karpuzov D, Liu Q, Xu Z (2013) Cryo-XPS study of xanthate adsorption on pyrite. Surf Interface Anal 45:805–810. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.5165
Khmeleva TN, Georgiev TV, Jasieniak M et al (2005) XPS and ToF-SIMS study of a chalcopyritepyrite-sphalerite mixture treated with xanthate and sodium bisulphite. Surf Interface Anal 37:699–709. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.2067
Yamashita T, Hayes P (2008) Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl Surf Sci 254:2441–2449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.063
Lai H, Deng J, Wen S (2019) Application of ToF-SIMS and PCA to study interaction mechanism of dodecylamine and smithsonite. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143698
Lai H, Liu Q, Deng J et al (2020) Surface chemistry study of Cu-Pb sulfide ore using ToF-SIMS and multivariate analysis. Appl Surf Sci 518:146270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146270
Zhao Q, Yang H, Tong L (2021) Adsorption characteristics of CN− species on the chalcopyrite surface and its response to flotation. Sep Purif Technol 276:119322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119322
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1902001), (2018YFC1902002). We are very grateful to the Shandong Zhaojin Group co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Grace Ofori-Sarpong.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Yang, H., Tong, L. et al. New Insights into Improving the Physicochemical Properties and Flotation Behavior of Pyrite Interfaces from Cyanide Tailings. J. Sustain. Metall. 9, 1155–1167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-023-00713-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-023-00713-1