Abstract
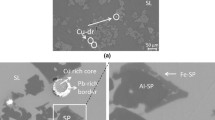
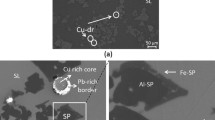
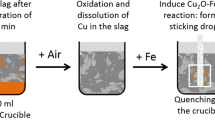
This study investigates the origin of the attachment of metal droplets to solid spinel particles in liquid slags. Previous research hinted a reactive origin: the spinel particles form by a chemical reaction together with a new droplet or alongside a droplet that was already present in the system. In this study, a smelting experiment was used to investigate this hypothesis. For such a study of the mechanism, a simple chemical system was used to avoid complex reactions. However, performing smelting experiments in simple slag systems requires an adaptation of the previously developed experimental methodology, resulting in a new ‘partial melting’ methodology. During the experiment, the atmosphere of the system was first set as oxidative, to dissolve the metallic copper in the slag and then a reductive atmosphere was used to actuate the reaction. Moreover, Ag was added to the metallic phase to act as a tracer element. The results show that the amount and size of copper droplets increase over the duration of the experiment. The fact that silver is present in the attached copper droplets in a smaller concentration than in the master alloy in this study indicates that the origin of the attachment is not purely dispersive, and either a purely reactive or a dispersion–reaction combination is possible, which confirms the hypothesis.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Degel R, Oterdoom H, Kunze J, et al (2008) Latest results of the slag cleaning reactor for copper recovery and its potential for the PGM industry. In: Proceedings of the third international platinum conference platinum transform. The Southern African Institue of Mining and Metallurgy, The Southern African Insititute of Mining and Metallurgy, Sun City, South Africa, pp 197–202
Suh I-K, Waseda Y, Yazawa A (1988) Some interesting aspects of non-ferrous metallurgical slags. High Temp Mater Process 8:65–88
Liow JL, Juusela M, Gray NB, Sutalo ID (2003) Entrainment of a two-layer liquid through a taphole. Metall Mater Trans B 34:821–832. doi:10.1007/s11663-003-0088-8
Cardona N, Coursol P, Mackey PJ, Parra R (2011) Physical chemistry of copper smelting slags and copper losses at the Paipote smelter Part 1-Thermodynamic modelling. Can Metall Q 50:318–329. doi:10.1179/000844311x13112418194761
Imris I, Sánchez M, Achurra G (2005) Copper losses to slags obtained from the El Teniente process. Miner Process Extr Metall 114:135–140. doi:10.1179/037195505X49769
Sridhar R, Toguri JM, Simeonov S (1997) Copper losses and thermodynamic considerations in copper smelting. Metall Mater Trans B 28:191–200. doi:10.1007/s11663-997-0084-5
Ip SW, Toguri JM (1992) Entrainment behavior of copper and copper matte in copper smelting operations. Metall Trans B 23:303–311. doi:10.1007/BF02656285
Minto R, Davenport WG (1972) Entrapment and flotation of matte in molten slags. Can Min Metall Bull 65:C36–42
Andrews L (2008) Base metal losses to furnace slag during processing of platinum-bearing concentrates. PhD, University of Pretoria
Malfliet A, Lotfian S, Scheunis L et al (2014) Degradation mechanisms and use of refractory linings in copper production processes: a critical review. J Eur Ceram Soc 34:849–876. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.10.005
De Wilde E, Bellemans I, Campforts M et al (2015) Wetting behaviour of Cu based alloys on spinel substrates in pyrometallurgical context. Mater Sci Technol 31:1925–1933. doi:10.1179/1743284715Y.0000000052
De Wilde E, Bellemans I, Zheng L et al (2016) Origin and sedimentation of Cu-droplets sticking to spinel solids in pyrometallurgical slags. Mater Sci Technol 32:1911–1924. doi:10.1080/02670836.2016.1151998
De Wilde E, Bellemans I, Campforts M et al (2016) Investigation of high-temperature slag/copper/spinel interactions. Metall Mater Trans B 47:3421–3434. doi:10.1007/s11663-016-0805-8
Bellemans I, De Wilde E, Claeys L et al (2017) Investigation of reactive origin for attachment of Cu-droplets to solid particles. Metall Mater Trans B 48:2459–2468
De Wilde E (2015) Methodology development and experimental determination of the origin of sticking copper droplets in pyrometallurgical slags. PhD thesis, Ghent University
De Wilde E, Bellemans I, Vervynckt S et al (2013) Towards a methodology to study the interaction between Cu droplets and spinel particles in slags. Proc EMC 2013:161–174
Wright S, Zhang L, Sun S, Jahanshahi S (2001) Viscosities of calcium ferrite slags and calcium alumino-silicate slags containing spinel particles. J Non Cryst Solids 282:15–23. doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(01)00324-6
Cnockaert V (2016) Investigation of the attachment of metallic droplets to solid particles in liquid slags. Master thesis, Ghent University
De Wilde E, Bellemans I, Campforts M et al (2016) Sessile drop evaluation of high temperature copper/spinel and slag/spinel interactions. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 26:2770–2783. doi:10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64344-3
De Wilde E, Bellemans I, Campforts M et al (2017) Study of the effect of spinel composition on metallic copper losses in slags. J Sustain Metall 3:416–427. doi:10.1007/s40831-016-0106-0
Llovet X, Valovirta E, Heikinheimo E (2000) Monte Carlo simulation of secondary fluorescence in small particles and at phase boundaries. Microchim Acta 132:205–212. doi:10.1007/s006040050013
Takeda Y, Ishiwata S, Yazawa A (1983) Distribution equilibria of minor elements between liquid copper and calcium ferrite slag. Trans Jpn Inst Met 24:518–528. doi:10.2320/matertrans1960.24.518
Rhamdhani MA, Brooks GA, Coley KS (2005) Kinetics of metal/slag reactions during spontaneous emulsification. Metall Mater Trans B 36:219–227. doi:10.1007/s11663-005-0023-2
Rhamdhani MA, Coley KS, Brooks GA (2004) Role of oxygen in interfacial phenomena during high temperature reactions. In: Irons G, Sun S (eds) Proceedings of the 43th annual conference metallurgists of CIM. Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, pp 203–217
Durinck D, Jones PT, Blanpain B, Wollants P (2008) Air-cooling of metallurgical slags containing multivalent oxides. J Am Ceram Soc 91:3342–3348. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02597.x
Acknowledgements
I. Bellemans holds a PhD fellowship of the Research Foundation - Flanders (FWO), and V. Cnockaert wishes to thank the agency for innovation by science and technology in Flanders (IWT, VLAIO, HBC.2016.0207). The authors also are grateful to the technicians and staff working at Umicore R&D Olen, for their help with the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was I. Sohn.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellemans, I., Cnockaert, V., De Wilde, E. et al. Metal Droplet Entrainment by Solid Particles in Slags: An Experimental Approach. J. Sustain. Metall. 4, 15–32 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-017-0145-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-017-0145-1