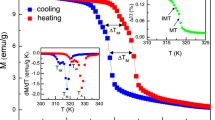
Abstract
We fabricated a Ni45Co6.4Mn37In11.6 polycrystalline sample with a specific texture by directional solidification. The alloy is characterized by wide successive structural and magnetic phase transitions that considerably extend their temperature intervals with the increase in the applied magnetic field. Under a magnetic field change μoΔH of 5 T, the working temperature window obtained from the magnetic entropy change curve for the structural and magnetic transition is as large as 66 and 52 K, respectively. As a result, the corresponding refrigeration capacity RC reached high values of 118 and 95 J kg−1, respectively, irrespective of the considerably small magnetic entropy changes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown PJ, Gandy AP, Ishida K, Kainuma R, Kanomata T, Neumann KU, Oikawa K, Ouladdiaf B, Ziebeck KRA (2006) The magnetic and structural properties of the magnetic shape memory compound Ni2Mn1.44Sn0.56. J Phys 18:2249–2259. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/18/7/012
Liu J, Scheerbaum N, Lyubina J, Gutfleisch O (2008) Reversibility of magnetostructural transition and associated magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In–Co. Appl Phys Lett 93:102512. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2981210
Liu J, Woodcock TG, Scheerbaum N, Gutfleisch O (2009) Influence of annealing on magnetic field-induced structural transformation and magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In–Co ribbons. Acta Mater 57:4911–4920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.06.054
Bourgault D, Tillier J, Courtois P, Maillard D, Chaud X (2010) Large inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni45Co5Mn37.5In12.5 single crystal above 300 K. Appl Phys Lett 96: 132501. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3372633.
Gottschall T, Skokov KP, Frincu B, Gutfleisch O (2015) Large reversible magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In–Co. Appl Phys Lett 106:021901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4905371
Cheng F, Gao L, Wang Y, Wang J, Liao X, Yang S (2019) Large refrigeration capacity in a Ni42Co8Mn37.7In12.3 magnetocaloric alloy. J Magn Magn Mater 478:234–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.01.101
Tishin AM, Spichkin YI (2019) The magnetocaloric effect and its applications. Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol
Chaturvedi A, Stefanoski S, Phan MH, Nolas GS, Srikanth H (2011) Table-like magnetocaloric effect and enhanced refrigerant capacity in Eu8Ga16Ge30-EuO composite materials. Appl Phys Lett 99:162513. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3654157
Tian HC, Zhong XC, Liu ZW, Zheng ZG, Min JX (2015) Achieving table-like magnetocaloric effect and large refrigerant capacity around room temperature in Fe78-xCexSi4Nb5B12Cu1 (x=0–10) composite materials. Mater Lett 138:64–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.09.127
Chen F, Tong YX, Li L, Sánchez Llamazares JL, Sánchez-Valdés CF, Müllner P (2017) Broad first-order magnetic entropy change curve in directionally solidified polycrystalline Ni–Co–Mn–In. J Alloys Compd 727:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.118
Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann E, Moya X, Mañosa L, Planes A (2005) Martensitic transitions and the nature of ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni–Mn–Sn alloys. Phys Rev B 72:014412. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.014412
Pötschke M, Gaitzsch U, Roth S, Rellinghaus B, Schultz L (2007) Preparation of melt textured Ni–Mn–Ga. J Magn Magn Mater 316:383–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.03.032
Zheng PQ, Kucza NJ, Wang ZL, Müllner P, Dunand DC (2015) Effect of directional solidification on texture and magnetic-field-induced strain in Ni–Mn–Ga foams with coarse grains. Acta Mater 86:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.12.005
Uwe G, Robert C, Linda W, Andrea B, Werner S, Carlgeorg O, Heinz-Günter B, Thomas L, Iñaki N, Martin P (2012) Processing routes toward textured polycrystals in ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Adv Eng Mater 14: 636–652. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201200084
Chen F, Liu WL, Shi YG, Müllner P (2015) Influence of annealing on martensitic transformation and magnetic entropy change in Ni37.7Co12.7Mn40.8Sn8.8 magnetic shape memory alloy ribbon. J Magn Magn Mater 377:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.10.077
Chen F, Tong YX, Huang YJ, Tian B, Li L, Zheng YF (2013) Suppression of γ phase in Ni38co12Mn41Sn9 alloy by melt spinning and its effect on martensitic transformation and magnetic properties. Intermetallics 36:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2013.01.004
Wu Z, Liu Z, Yang H, Liu Y, Wu G, Woodward RC (2011) Metallurgical origin of the effect of Fe doping on the martensitic and magnetic transformation behaviours of Ni50Mn40-xSn10Fex magnetic shape memory alloys. Intermetallics 19:445–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2010.10.010
Villa E, Villa E, Melzi D'Eril M, Nespoli A, Passaretti F (2018) The role of γ-phase on the thermo-mechanical properties of NiMnGaFe alloys polycrystalline samples. J Alloys Compd 763:883–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.028
Heczko O, Fähler S, Vasilchikova TM, Voloshok TN, Klimov KV, Chumlyakov YI, Vasiliev AN (2008) Thermodynamic, kinetic, and magnetic properties of a Ni54Fe19Ga27 magnetic shape-memory single crystal. Phys Rev B 77:174402. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.77.174402
Yu SY, Cao ZX, Ma L, Liu GD, Chen JL, Wu GH, Zhang B, Zhang XX (2007) Realization of magnetic field-induced reversible martensitic transformation in NiCoMnGa alloys. Appl Phys Lett 91:102507. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2783188
Kainuma R, Imano Y, Ito W, Sutou Y, Morito H, Okamoto S, Kitakami O, Oikawa K, Fujita A, Kanomata T, Ishida K (2006) Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation. Nature 439:957–960. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04493
Du J, Zheng Q, Ren WJ, Feng WJ, Liu XG, Zhang ZD (2007) Magnetocaloric effect and magnetic-field-induced shape recovery effect at room temperature in ferromagnetic Heusler alloy Ni–Mn–Sb. J Phys D 40:5523–5526. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/18/001
Krenke T, Duman E, Acet M, Wassermann E, Moya X, Mañosa L, Planes A, Suard E, Ouladdiaf B (2007) Magnetic superelasticity and inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni–Mn–In. Phys Rev B 75:104414. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.104414
Han ZD, Wang DH, Qian B, Feng JF, Jiang XF, Du YW (2010) Phase transitions, magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ni–Co–Mn–Sn ferromagnetic shape memory alloy. Jpn J Appl Phys 49:010211. https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.49.010211
Liu J, Gottschall T, Skokov KP, Moore JD, Gutfleisch O (2012) Giant magnetocaloric effect driven by structural transitions. Nat Mater 11:620–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3334
Arrott A (1957) Criterion for ferromagnetism from observations of magnetic isotherms. Phys Rev 108:1394. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.108.1394
Neumann KU, Ziebeck KRA (1995) Arrott plots for rare earth alloys with crystal field splitting. J Magn Magn Mater 140–144:967–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(94)00559-1
Wang DH, Tang SL, Huang SL, Zhang JR, Du YW (2004) The magnetic phase transition and the low-field arrott plots of (GdxDy1-x)Co2 compounds. J Magn Magn Mater 268:70–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(03)00474-8
Dong QY, Chen J, Shen J, Sun JR, Shen BG (2012) Large magnetic entropy change and refrigerant capacity in rare-earth intermetallic RCuAl (R=Ho and Er) compounds. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2676–2678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.03.052
Phan TL, Zhang P, Dan NH, Yen NH, Thanh PT, Thanh TD, Phan MH, Yu SC (2012) Coexistence of conventional and inverse magnetocaloric effects and critical behaviors in Ni50Mn50-xSnx (x=13 and 14) alloy ribbons. Appl Phys Lett 101:212403. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4767453
Castillo-Villa PO, Mañosa L, Planes A, Soto-Parra DE, Sánchez-Llamazares JL, Flores-Zúñiga H, Frontera C (2013) Elastocaloric and magnetocaloric effects in Ni–Mn–Sn(Cu) shape-memory alloy. J Appl Phys 113:053506. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4790140
Li Z, Zhang Y, Sánchez-Valdés CF, Sánchez Llamazares JL, Esling C, Zhao X, Zuo L (2014) Giant magnetocaloric effect in melt-spun Ni–Mn–Ga ribbons with magneto-multistructural transformation. Appl Phys Lett 104:044101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4863273
Acknowledgements
The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HEUCFG201836) and the State Scholarship Fund of China supported this work. PM acknowledges financial support through the National Science Foundation through Grant No DMR-1710640. J. L. Sánchez Llamazares acknowledges the support received from Laboratorio Nacional de Investigaciones en Nanociencias y Nanotecnología (LINAN, IPICyT). C. F. Sánchez-Valdés is grateful to DMCU-UACJ for supporting his research stays at IPICyT (Program PFCE and Academic Mobility Grant), and also for the financial support received from SEP-CONACYT, Mexico (Grant Number A1-S-37066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Sánchez Llamazares, J.L., Sánchez-Valdés, C.F. et al. Wide Structural and Magnetic Successive Transitions and Related Magnetocaloric Properties in a Directionally Solidified Polycrystalline Ni–Co–Mn–In Alloy. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 6, 54–60 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-020-00263-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-020-00263-5