Abstract
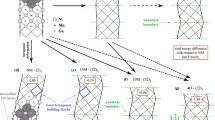
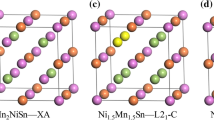
The effect of excess Mn on the stability of modulation and elastic properties was investigated using ab initio electronic structure calculations in Ni–Mn–Ga magnetic shape memory alloy. We used the structure of four layered modulated martensite known as 4O to describe modulation of the martensitic lattice. We found that elastic properties of stoichiometric 4O martensite are very similar to elastic properties of 10M martensite reported in previous calculations. The modulated structure becomes less stable than nonmodulated martensite above 3 at.% of excess Mn which corresponds very well to experimental observation at low temperature. Elastic properties of NM martensite are not significantly affected by Mn content nor local arrangements of Mn-excess atoms. We also found that Mn-excess atoms prefer occupation of distant positions for low Mn-excess composition. The occupation of closest position is preferred for alloys with higher content of Mn.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaufmann S, Niemann R, Thersleff T, Rößler UK, Heczko O, Buschbeck J, Holzapfel B, Schultz L, Fähler S (2011) Modulated martensite: why it forms and why it deforms easily. New J Phys 13:053029
Acet M, Mañosa L, Planes A (2011) Magnetic-field induced effects in martensitic Heusler-based magnetic shape memory alloys. In: Buschow KHJ (ed) Handbook of magnetic materials, vol 19. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 231–289
Heczko O, Scheerbaum N, Gutfleisch O (2009) Magnetic shape memory phenomena. In: Liu J, Fullerton E, Gutfleisch O, Sellmyer D (eds) Nanoscale magnetic materials and applications. Springer, Boston, MA, pp 399–439
Seiner H, Straka L, Heczko O (2014) A microstructural model of motion of macro-twin interfaces in Ni–Mn–Ga 10M martensite. J Mech Phys Solids 64:198–211
Ullakko K, Huang JK, Kantner C, O’Handley RC, Kokorin VV (1996) Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2MnGa single crystals. Appl Phys Lett 69:1966–1968
Schlüter K, Holz B, Raatz A (2012) Principle design of actuators driven by magnetic shape memory alloys. Adv Eng Mater 14:682–686
Karaman I, Basaran B, Karaca HE, Karsilayan AI, Chumlyakov YI (2007) Energy harvesting using martensite variant reorientation mechanism in a NiMnGa magnetic shape memory alloy. Appl Phys Lett 90:172505
Wilson SA et al (2007) New materials for micro-scale sensors and actuators: an engineering review. Mater Sci Eng R 56:1–129
Martynov VV, Kokorin VV (1992) The crystal structure of thermally- and stress-induced martensites in Ni2MnGa single crystals. J Phys III 2:739–749
Opeil CP, Mihaila B, Schulze RK, Mañosa L, Planes A, Hults WL, Fisher RA, Riseborough PS, Littlewood PB, Smith JL, Lashley JC (2008) Combined experimental and theoretical investigation of the premartensitic transition in Ni2MnGa. Phys Rev Lett 100:165703
Seiner H, Kopecký V, Landa M, Heczko O (2014) Elasticity and magnetism of Ni2MnGa premartensitic tweed. Phys Status Solidi B 251:2097–2103
Webster PJ, Ziebeck KRA, Town SL, Peak MS (1984) Magnetic order and phase transformation in Ni2MnGa. Philos Mag B 49:295–310
Lanska N, Söderberg O, Sozinov A, Ge Y, Ullakko K, Lindroos VK (2004) Composition and temperature dependence of the crystal structure of Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. J Appl Phys 95:8074–8078
Albertini F, Paoluzi A, Pareti L, Solzi M, Righi L, Villa E, Besseghini S, Passaretti F (2006) Phase transitions and magnetic entropy change in Mn-rich Ni2MnGa Alloys. J Appl Phys 100:023908
Straka L, Drahokoupil J, Pacherová O, Fabiánová K, Kopecký V, Seiner H, Hänninen H, Heczko O (2016) The relation between lattice parameters and very low twinning stress in Ni50Mn25+xGa25−x magnetic shape memory alloys. Smart Mater Struct 25:025001
Straka L, Sozinov A, Drahokoupil J, Kopecký V, Hänninen H, Heczko O (2013) Effect of intermartensite transformation on twinning stress in Ni-Mn-Ga 10M martensite. J Appl Phys 114:063504
Heczko O (2014) Magnetic shape memory effect and highly mobile twin boundaries. Mater Sci Technol 30:1559–1578
Söderberg O, Straka L, Novák V, Heczko O, Hannula S-P, Lindroos VK (2004) Tensile/compressive behaviour of non-layered tetragonal Ni52.8Mn25.7Ga21.5 alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 386:27–33
Sozinov A, Lanska N, Soroka A, Zou W (2013) 12% magnetic field-induced strain in Ni-Mn-Ga-based non-modulated martensite. Appl Phys Lett 102:021902
Soroka A, Sozinov A, Lanska N, Rameš M, Straka L, Ullakko K (2018) Composition and temperature dependence of twinning stress in non-modulated martensite of Ni-Mn-Ga-Co-Cu magnetic shape memory alloys. Scr Mater 144:52–55
Heczko O, Straka L, Novak V, Fähler S (2010) Magnetic anisotropy of nonmodulated Ni–Mn–Ga martensite revisited. J Appl Phys 107:09A914
Sozinov A, Soroka A, Lanska N, Rameš M, Straka L, Ullakko K (2017) Temperature dependence of twinning and magnetic stresses in Ni46Mn24Ga22Co4Cu4 alloy with giant 12% magnetic field-induced strain. Scr Mater 131:33–36
Dai L, Cullen J, Wuttig M (2004) Intermartensitic transformation in a NiMnGa alloy. J Appl Phys 95:6957–6959
Seguí D, Chernenko VA, Pons J, Cesari E, Khovailo V, Takagi T (2005) Low temperature-induced intermartensitic phase transformations in Ni–Mn–Ga single crystal. Acta Mater 53:111–120
Soolshenko V, Lanska N, Ullakko K (2003) Structure and twinning stress of martensites in non-stoichiometric Ni2MnGa single crystal. J Phys IV France 112:947–950
Heczko O, Kopecký V, Sozinov A, Straka L (2013) Magnetic shape memory effect at 1.7 K. Appl Phys Lett 103(7):072405
Kaufmann S, Rößler UK, Heczko O, Wuttig M, Buschbeck J, Schultz L, Fähler S (2010) Adaptive modulations of martensites. Phys Rev Lett 104:145702
Niemann R, Fähler S (2017) Geometry of adaptive martensite in Ni-Mn-based heusler alloys. J Alloys Compd 703:280–288
Zhdanov GS (1945) The numerical symbol of close packing of spheres and its application in the theory of close packings. C R Acad Sci USSR 48:39–42
Hickel T, Uijttewaal M, Al-Zubi A, Dutta B, Grabowski B, Neugebauer J (2012) Ab initio-based prediction of phase diagrams: application to magnetic shape memory alloys. Adv Eng Mater 14:547–561
Uijttewaal MA, Hickel T, Neugebauer J, Gruner ME, Entel P (2009) Understanding the phase transitions of the Ni2MnGa magnetic shape memory system from first principles. Phys Rev Lett 102:035702
Blöchl PE (1994) Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 50:17953–17979
Entel P, Gruner ME, Comtesse D, Wutting M (2013) Interaction of phase transformation and magnetic properties of Heusler alloys: a density functional theory study. JOM 65:1540–1549
Dutta B, Çakır A, Giacobbe C, Al-Zubi A, Hickel T, Acet M, Neugebauer J (2016) Ab initio prediction of martensitic and intermartensitic phase boundaries in Ni-Mn-Ga. Phys Rev Lett 116:025503
Xu N, Raulot J-M, Li Z-B, Bai J, Zhang Y-D, Zhao X, Zuo L, Esling C (2012) Oscillation of the magnetic moment in modulated martensites in Ni2MnGa studied by ab initio calculations. Appl Phys Lett 100:084106
Zelený M, Straka L, Sozinov A, Heczko O (2016) Ab initio prediction of stable nanotwin double layers and 4O structure in Ni2MnGa. Phys Rev B 94:224108
Zelený M (2018) Nanotwinning and modulation of martensitic structures in Ni2MnGa alloy: an ab initio study. Acta Phys Pol A 134:658–661
Zelený M, Straka L, Sozinov A, Heczko O (2018) Transformation paths from cubic to low-symmetry structures in Heusler Ni2MnGa compound. Sci Rep 8:7275
Gruner ME, Niemann R, Entel P, Pentcheva R, Rößler UK, Nielsch K, Fähler S (2018) Modulations in martensitic Heusler alloys originate from nanotwin ordering. Sci Rep 8:8489
Xu N, Raulot JM, Li ZB, Zhang YD, Bai J, Peng W, Meng XY, Zhao X, Zuo L, Esling C (2014) Composition dependent phase stability of Ni–Mn–Ga alloys studied by ab initio calculations. J Alloys Compd 614:126–130
Enkovaara J, Heczko O, Ayuela A, Nieminen RM (2003) Coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic order in Mn-doped Ni2MnGa. Phys Rev B 67:212405
Chen J, Li Y, Shang JX, Xu HB (2006) First principles calculations on martensitic transformation and phase instability of Ni–Mn–Ga high temperature shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett 89:231921
Buchelnikov VD, Sokolovskiy VV, Miroshkina ON, Zagrebin MA, Nokelainen J, Pulkkinen A, Barbiellini B, Lähderanta E (2019) Correlation effects on ground-state properties of ternary Heusler alloys: first-principles study. Phys Rev B 99:014426
Zunger A, Wei S-H, Ferreira LG, Bernard JE (1990) Special quasirandom structures. Phys Rev Lett 65:353–356
Soven P (1967) Coherent-potential model of substitutional disordered alloys. Phys Rev 156:809–813
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B 54:11169–11186
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficiency of ab initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci 6:15–50
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758–1775
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868; Errata: 78, 1396(E), (1997)
Methfessel M, Paxton AT (1989) High-precision sampling for Brillouin-zone integration in metals. Phys Rev B 40:3616–3621
Bučko T, Hafner J, Ángyán JG (2005) Geometry optimization of periodic systems using internal coordinates. J Chem Phys 122:124508
Yu R, Zhu J, Ye HQ (2010) Calculations of single-crystal elastic constants made simple. Comput Phys Commun 181:671–675
Zhou L, Holec D, Mayrhofer PH (2013) First-principles study of elastic properties of cubic Cr1−xAlxN alloys. J Appl Phys 113:043511
Nöger D (2019) A command line tool written in Python/Cython for finding optimized SQS structures. GitHub. https://github.com/dnoeger/sqsgenerator. Accessed 13 April 2019
Jiang CB, Muhammad Y, Deng LF, Wu W, Xu HB (2004) Composition dependence on the martensitic structures of the Mn-rich NiMnGa alloys. Acta Mater 52:2779–2785
Hu Q-M, Li C-M, Kulkova SE, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L (2010) Magnetoelastic effects in Ni2Mn1+xGa1−x alloys from first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 81:064108
Holec D, Tasnádi F, Wagner P, Friák M, Neugebauer J, Mayrhofer PH, Keckes J (2014) Macroscopic elastic properties of textured ZrN-AlN polycrystalline aggregates: from ab initio calculations to grain-scale interactions. Phys Rev B 90:184106
Vitos L (2007) Computational quantum mechanics for materials engineers. Springer, London
Zelený M, Sozinov A, Straka L, Björkman T, Nieminen RM (2014) First-principles study of Co- and Cu-doped Ni2MnGa along the tetragonal deformation path. Phys Rev B 89:184103
Mouhat F, Coudert FX (2014) Necessary and sufficient elastic stability conditions in various crystal systems. Phys Rev B 90:224104
Moakher M, Norris AN (2006) The closest elastic tensor of arbitrary symmetry to an elasticity tensor of lower symmetry. J Elastom 85:215–263
Worgull J, Petti E, Trivisonno J (1996) Behavior of the elastic properties near an intermediate phase transition in Ni2MnGa. Phys Rev B 54:15695–15699
Stipcich M, Mañosa L, Planes A, Morin M, Zarestky J, Lograsso T, Stassis C (2004) Elastic constants of Ni−Mn−Ga magnetic shape memory alloys. Phys Rev B 70:054115
Bungaro C, Rabe KM, Dal Corso A (2003) First-principles study of lattice instabilities in ferromagnetic Ni2MnGa. Phys Rev B 68:134104
Hu Q-M, Li C-M, Yang R, Kulkova SE, Johansson B, Bazhanov DI, Vitos L (2009) Site occupancy, magnetic moments, and elastic constants of off-stoichiometric Ni2MnGa from first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 79:144112
Ozdemir Kart S, Cagın T (2010) Elastic properties of Ni2MnGa from first-principles calculations. J Alloys Compd 508:177–183
Sedlák P, Seiner H, Bodnárová L, Heczko O, Landa M (2017) Elastic constants of non-modulated Ni-Mn-Ga martensite. Scr Mater 136:20–23
Zayak AT, Entel P, Enkovaara J, Ayuela A, Nieminen R (2003) First-principles investigation of phonon softenings and lattice instabilities in the shape-memory system Ni2MnGa. Phys Rev B 68:132402
Entel P et al (2006) Modelling the phase diagram of magnetic shape memory Heusler alloys. J Phys D 39:865–889
Zayak AT, Adeagbo WA, Entel P, Rabe KM (2006) e/a dependence of the lattice instability of cubic Heusler alloys from first principles. Appl Phys Lett 88:111903
Zayak AT, Entel P, Rabe KM, Adeagbo WA, Acet M (2005) Crystal structures of Ni2MnGa from density functional calculations. Phys Rev B 72:054113
Fujii S, Ishida S, Asano S (1989) Electronic structure and lattice transformation in Ni2MnGa and Co2NbSn. J Phys Soc Japan 58:3657–3665
Brown PJ, Bargawi AY, Crangle J, Neumann KU, Ziebeck KRA (1999) Direct observation of a band Jahn-Teller effect in the martensitic phase transition of Ni2MnGa. J Phys Condens Matter 11:4715–4722
Acknowledgements
We thank Alexei Sozinov for fruitful discussions. This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic within the Program OP VVV “Excellent Research Teams” under Project CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000487-MATFUN, by the Large Infrastructures for Research, Experimental Development and Innovations project “IT4Innovations National Supercomputing Center-LM2015070” and by the Czech Science Foundation under Project No. 17-00062S. D. H. and M. Z. are also grateful for the financial support through Scientific & Technological Cooperation of the Austrian Agency for International Cooperation in Education and Research (WTZ-CZ-06/8J18AT004). M. Z. also acknowledges support from the Czech-Austrian scholarship program AKTION (Contract No. ICM-2017-09370).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is an invited submission to Shape Memory and Superelasticity selected from presentations at the International Conference on Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys (ICFSMA) held June 2–7, 2019 in Prague, Czech Republic, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zelený, M., Heczko, M., Janovec, J. et al. The Effect of Local Arrangement of Excess Mn on Phase Stability in Ni–Mn–Ga Martensite: An Ab Initio Study. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 6, 35–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-019-00247-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-019-00247-0