Abstract
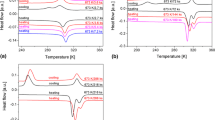
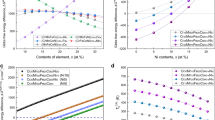
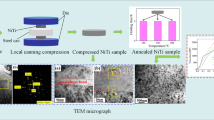
The present study describes the development of shape memory alloys based on NiAl. Initially, this system was considered a promising but unsuccessful neighbour of NiTi. Later, however, shape memory alloys like CoNiAl or CoNiGa were developed that can be considered as NiAl derivatives and already demonstrated good mechanical properties. Yet, these alloys were still inferior to NiTi in most respects. Lately, using a multi-component approach, a CoNiCuAlGaIn high entropy intermetallic compound was developed from the NiAl prototype. This new alloy featured a B2 phase and a martensitic transformation along with a remarkable strength in the as-cast state. In the long-term, this new approach might led to a breakthrough for shape memory alloys in general.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buehler WJ, Gilfrich JW, Wiley RC (1963) Effect of low-temperature phase changes on the mechanical properties of alloys near composition TiNi. J Appl Phys 34:1475–1477
Cuthill JR, McAlister AJ, Williams ML (1968) Soft X-Ray Spectroscopy of Alloys: TiNi and the Ni–Al System. J Appl Phys 39:2204–2208
Otsuka K, Ren X (1999) Martensitic transformations in nonferrous shape memory alloys. Mater Sci Eng A273–275:89–105
Sluiter M, Turchi PEA, Pinski FJ, Stocks GM (1992) Theoretical studies of phase stability in Ni-Al and NiTi alloys. J Phase Equilib 13:605–611
Luy Jianmin, Qingmiao Hu, Yang Rui (2009) A comparative study of elastic constants of NiTi and NiAl alloys from first-principle calculations. J Mater Sci Technol 25:215–217
Otsuka K, Wayman CM (1998) Shape memory materials. University Press, Cambridge
Enami K, Nenno S (1971) Memory effect in Ni-36.8 At. Pct. Al martensite. Metall Transactions 2:1487–1490
Au YK, Wayman CM (1972) Thermoelastic behavior of the martensitic transformation in β` NiAl alloys. Scripta Metall 6:1209–1214
Kainuma R, Ishida K, Nishizawa T (1992) Thermoelastic martensite and shape memory effect in B2 base Ni–Al–Fe alloy with enhanced ductility. Metall Trans A 23A:1147–1153
Enami K, Nenno S (1978) A new ordered phase in tempered 63.8 Ni–1Co–Al martensite. Trans JIM 19:571–580
Kim HY, Miyazaki S (2004) Martensitic transformation behavior in Ni–Al and Ni–Al–Re melt-spun ribbons. Scripta Mater 50:237–241
Firstov GS, Kosorukova TA, Koval YuN, Odnosum VV (2015) High entropy shape memory alloys. Mater Today 2S:S499–S504
Firstov GS, Kosorukova TA, Koval YuN, Verhovlyuk PA (2015) Directions for High-Temperature Shape Memory Alloys’ Improvement: Straight Way to High-Entropy Materials? Shape Mem Superelast 1:400–407
Lutterotti L (2015) MAUD: Materials Analysis Using Diffraction. A Rietveld extended program to perform the combined analysis. University of Trento, Italy
Chumlyakov YuI, Panchenko EYu, Ovsyannikov AV, Chusov SA, Kirillov VA, Karaman I, Maier HJ (2009) High-Temperature Superelasticity and the Shape-Memory Effect in [001] Co–Ni–Al Single Crystals. Phys Met Metall 107:194–205
Oikawa K, Wulff L, Iijima T, Gejima F, Ohmori T, Fujita A, Fukamichi K, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2001) Promising ferromagnetic Ni–Co–Al shape memory alloy system. Appl Phys Lett 79:3290–3292
Tanaka Y, Oikawa K, Sutou Y, Omori T, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2006) Martensitic transition and superelasticity of Co–Ni–Al ferromagnetic shape memory alloys with β + γ two-phase structure. Mater Sci Eng A 438–440:1054–1060
Dogan E, Karaman I, Chumlyakov YI, Luo ZP (2011) Microstructure and martensitic transformation characteristics of CoNiGa high temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater 59:1168–1183
Liu J, Xia M, Huang Y, Zheng H, Li J (2006) Effect of annealing on the microstructure and martensitic transformation of magnetic shape memory alloys CoNiGa. J Alloy Compd 417:96–99
Liu J, Zheng HX, Xia MX, Huang YL, Li JG (2005) Martensitic transformation and magnetic properties in Heusler CoNiGa magnetic shape memory alloys 52:935–938
Oikawa K, Ota T, Gejima F, Ohmori T, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2001) Phase equilibria and phase transformations in new B2-type ferromagnetic shape memory alloys of Co–Ni–Ga and Co–Ni–Al systems. Mater Trans 42:2472–2475
Oikawa K, Ota T, Imano Y, Omori T, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2006) Phase equilibria and phase transformation of Co–Ni–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloy system. J Phase Equil Diffus 27:75–82
Dogan E, Karaman I, Singh N, Chivukula A, Thawabi HS, Arroyave R (2012) The effect of electronic and magnetic valences on the martensitic transformation of CoNiGa shape memory alloys. Acta Mater 60:3545–3558
Hamilton RF, Sehitoglu H, Efstathiou C, Maier HJ, Chumlyakov Y, Zhang XY (2005) Transformation of Co–Ni–Al single crystals in tension. Scripta Mater 53:131–136
Krooß P, Niendorf T, Kadletz PM, Somsen C, Gutmann MJ, Chumlyakov YI, Schmahl WW, Eggeler G, Maier HJ (2015) Functional fatigue and tension-compression asymmetry in [001]-oriented Co49Ni21Ga30 high-temperature shape memory alloy single crystals. Shape Mem Superelast 1:6–17
Firstov GS, Van Humbeeck J, Koval YuN (2006) High Temperature Shape Memory Alloys Problems and Prospects. J Intel Mater Syst Struct 17:1041–1047
Ma J, Karaman I, Noebe RD (2010) High temperature shape memory alloys. Int Mater Rev 55:257–315
Firstov G, Koval Yu, Van Humbeeck J, Timoshevskii A, Kosorukova T, Verhovlyuk P (2015) Some physical principles of high temperature shape memory alloys design. In: Resnina N, Rubanik V (eds) Shape Memory Alloys: Properties, Technologies, Opportunities. Trans Tech Publications Inc., Zurich, pp 207–232
Firstov G, Timoshevskii A, Kosorukova T, Koval Yu, Matviychuk Yu, Verhovlyuk P (2015) Electronic and crystal structure of the high entropy TiZrHfCoNiCu intermetallics undergoing martensitic transformation. MATEC Web Conf 33:06006
Takeuchi A, Inoue A (2005) Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater Trans 46:2817–2829
Murty BS, Yeh JW, Ranganathan S (2014) High entropy alloys. Elsevier, Oxford
Zhang Y, Zuo TT, Nang Z, Cao MC, Dahmen KA, Liaw PK, Lu ZP (2014) Microstructures and properties of high entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci 61:1–93
Firstov SA (2014) Rogul’ TG, Krapivka NA, Ponomarev SS, Tkach VN, Kovylyaev VV, Gorban’ VF, Karpets MV (2014) Solid-solution hardening of a high-entropy AlTiVCrNbMo Alloy. Russ Metall 4:285–292
Zhang P, Li SX, Zhang ZF (2011) General relationship between strength and hardness. Mater Sci Eng A 529:62–73
Noebe RD, Cullers CL, Bowman RR (1992) The effect of strain rate and temperature on tensile properties of NiAl. J Mater Res 7:605–612
Bowman RR, Noebe RD (1992) Development of NiAl and NiAl-based composites for structural applications: a status report. In: Antolovich SD, Stusrud RW, MacKay RA, Anton DL, Khan T, Kissinger RD, Klarstrom DL (eds) Superalloys. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, Pittsburgh, pp 341–350
Noebe RD, Bowman RR, Nathal MV (1993) Physical and mechanical properties of the B2 compound NiAl. Int Mater Rev 38:193–232
Kimura Y, Miura S, Suzuki T, Mishima Y (1994) Microstructrure and mechanical properties of two phase alloys based on the B2-type intermetallic compound CoAl in the Co-Ni-Al system. Mater Trans, JIM 35:800–807
Wang L, Shen J, Zhang Y, Xu H, Fu H (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties of NiAl-based hypereutectic alloy obtained by liquid metal cooling and zone melted liquid metal cooling directional solidification techniques. J Mater Res 31:646–654
Acknowledgements
G.S. Firstov acknowledges support by the DAAD scholarship (91657703) in the frame of the scholarship program “Research Stays for University Academics and Scientists, 2017”. G. Gerstein and H.J. Maier acknowledge financial support by the German Research Foundation (Grant No. MA1175/79-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerstein, G., Firstov, G.S., Kosorukova, T.A. et al. Development of B2 Shape Memory Intermetallics Beyond NiAl, CoNiAl and CoNiGa. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 4, 360–368 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-0180-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-018-0180-1