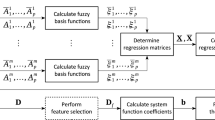
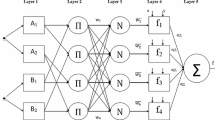
Abstract
This study aims to propose a more efficient control system for uncertain nonlinear systems. A new fuzzy hybrid neural network named as backstepping self-organizing hybrid function-link fuzzy brain emotional learning controller (BSDFFBC) is developed. The proposed hybrid structure is a type of brain-imitated neural network. The BSDFFBC is combined with a backstepping control technique, an enhancement search algorithm (ESA), and a hybrid function-link network (HFLN) to enforce its control ability. Moreover, a self-organizing mechanism is used to automatically adjust the number of neurons that can maintain the BSDFFBC to accommodate large variations in inputs and system uncertainties and can also significantly reduce the computation time. Next, a new genetic algorithm-based ESA is proposed to find the optimal parameters for the control system. Then, the online learning rules of the BSDFFBC are designed using the backstepping control technique and the gradient descent algorithm. Thus, the system structure and control parameters of the control system can be online adjusted to achieve more efficient control performance. Moreover, a robust compensation controller is added to BSDFFBC to improve the control quality of the system. Finally, the proposed BSDFFBC control system is used to control a roll-to-roll system and a magnetic ball levitation system to show its favorable control performance; and the comparisons with other controllers have shown its superiority.

































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moren, J.: Emotion and learning: a computational model of the amygdala. Cybern. Syst. 32(6), 611–636 (2001)
Ledoux, J.: The emotional brain, fear, and the amygdala. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 23(4), 727–738 (2003)
Ledoux, J.E., Phelps, E.A.: Emotional networks in the brain. In: Lewis, M., Haviland-Jones, J.M., Barrett, L.F. (eds.) Handbook of Emotions, pp. 159–179. The Guilford Press, New York (2008)
Huynh, T.-T., Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L., Vu, V.-P., Chao, F.: Self-organizing double function-link fuzzy brain emotional control system design for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 10(3), 1000–1017 (2020)
Lin, C.-M., Pham, D.-H., Huynh, T.-T.: Synchronization of chaotic system using a brain-imitated neural network controller and its applications for secure communications. IEEE Access 9, 75923–75944 (2021)
Huynh, T.-T., Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L., Nguyen, N.P., Hong, S.-K., Chao, F.: Wavelet interval type-2 fuzzy quad-function-link brain emotional control algorithm for the synchronization of 3D nonlinear chaotic systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22(8), 2546–2564 (2020)
Debnath, B., Mija, S.: Design of a multivariable stimulus for Emotional-Learning based control of a 2-DOF laboratory helicopter. ISA Trans. 118, 189–206 (2021)
Patra, J.C., Pal, R.N.: A functional link artificial neural network for adaptive channel equalization. Signal Process. 43(2), 181–195 (1995)
Saeed, M.U., Sun, Z., Elias, S.: Semi-active vibration control of building structure by self tuned brain emotional learning based intelligent controller. J. Build. Eng. 46, 103664 (2022)
Souzanchi-K, M., Akbarzadeh-T, M.-R.: Brain emotional learning impedance control of uncertain nonlinear systems with time delay: experiments on a hybrid elastic joint robot in telesurgery. Comput. Biol. Med. 138, 104786 (2021)
Affan, M., Uddin, R.: Brain emotional learning and adaptive model predictive controller for induction motor drive: a new cascaded vector control topology. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 19(9), 3122–3135 (2021)
Lin, C.-M., Nguyen, H.-B., Huynh, T.-T.: A new self-organizing double function-link brain emotional learning controller for MIMO nonlinear systems using sliding surface. IEEE Access 9, 73826–73842 (2021)
Huynh, T.-T., Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L., Cho, H.-Y., Pham, T.-T.T., Chao, F.: A new self-organizing fuzzy cerebellar model articulation controller for uncertain nonlinear systems using overlapped Gaussian membership functions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(11), 9671–9682 (2019)
Kokotovic, P.V.: The joy of feedback: nonlinear and adaptive. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 12(3), 7–17 (1992)
Lozano, R., Brogliato, B.: Adaptive control of robot manipulators with flexible joints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 37(2), 174–181 (1992)
Boyd, S., Boyd, S.P., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Holland, J.H.: Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Mitchell, M.: An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Brobbey, K.J., Haapanen, J., Gunell, M., Mäkelä, J.M., Eerola, E., Toivakka, M., Saarinen, J.J.: One-step flame synthesis of silver nanoparticles for roll-to-roll production of antibacterial paper. Appl. Surf. Sci. 420, 558–565 (2017)
Kim, S.-K., Ahn, C.K.: Self-tuning nonlinear control system design for roll-to-roll printing systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 25(6), 2667–2676 (2020)
Deng, B., Hsu, P.-C., Chen, G., Chandrashekar, B., Liao, L., Ayitimuda, Z., Wu, J., Guo, Y., Lin, L., Zhou, Y.: Roll-to-roll encapsulation of metal nanowires between graphene and plastic substrate for high-performance flexible transparent electrodes. Nano Lett. 15(6), 4206–4213 (2015)
Tran, T.T., Choi, K.-H., Chang, D.-E., Kim, D.-S.: Web tension and velocity control of two-span roll-to-roll system for printed electronics. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 5(4), 329–346 (2011)
Choi, K.-H., Thanh, T.-T., Kim, D.-S.: A precise control algorithm for single-span roll-to-roll web system using the back-stepping controller. In: 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, 2009, pp. 1709–1714
Tran, T.T., Choi, K.-H.: A backstepping-based control algorithm for multi-span roll-to-roll web system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 70(1–4), 45–61 (2014)
Lin, C.-M., Lin, M.-H., Chen, C.-W.: SoPC-based adaptive PID control system design for magnetic levitation system. IEEE Syst. J. 5(2), 278–287 (2011)
Lin, C.-M., Huynh, T.-T.: Dynamic TOPSIS fuzzy cerebellar model articulation controller for magnetic levitation system. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 36(3), 2465–2480 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Grant MOST 109-2811-E-155-504-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, HB., Lin, CM., Huynh, TT. et al. Fuzzy Hybrid Neural Network Control for Uncertainty Nonlinear Systems Based on Enhancement Search Algorithm. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 3384–3402 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01374-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01374-0